 W
WAegina is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece in the Saronic Gulf, 27 kilometres from Athens. Tradition derives the name from Aegina, the mother of the hero Aeacus, who was born on the island and became its king.
 W
WThe Balkan campaign of Alexander the Great took place in 335 BC, against a number of rebellious vassals of the Macedonian kingdom. Alexander successfully pacified each in turn, leaving him free to begin the long-planned invasion of Persia.
 W
WThe Boeotian or Theban War broke out in 378 BC as the result of a revolt in Thebes against Sparta. The war saw Thebes become dominant in the Greek World at the expense of Sparta. However, by the end of the war Thebes’ greatest leaders, Pelopidas and Epaminondas, were both dead and Thebes power already waning, allowing for the Rise of Macedon.
 W
WThe Corinthian War was an ancient Greek conflict lasting from 395 BC until 387 BC, pitting Sparta against a coalition of Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire. The immediate cause of the war was a local conflict in northwest Greece in which Thebes and Sparta intervened. The deeper cause was hostility towards Sparta, provoked by that city's "expansionism in Asia Minor, central and northern Greece and even the west". The Corinthian War followed the Peloponnesian War, in which Sparta had achieved hegemony over Athens and its allies.
 W
WThe Cretan War was fought by King Philip V of Macedon, the Aetolian League, many Cretan cities and Spartan pirates against the forces of Rhodes and later Attalus I of Pergamum, Byzantium, Cyzicus, Athens, and Knossos.
 W
WThe Diadochi were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great, who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BCE. The Wars of the Diadochi mark the beginning of the Hellenistic period from the Mediterranean Sea to the Indus River Valley.
 W
WThe Battle of the Eurymedon was a double battle, taking place both on water and land, between the Delian League of Athens and her Allies, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. It took place in either 469 or 466 BCE, in the vicinity of the mouth of the Eurymedon River in Pamphylia, Asia Minor. It forms part of the Wars of the Delian League, itself part of the larger Greco-Persian Wars.
 W
WThe first Persian invasion of Greece, during the Persian Wars, began in 492 BC, and ended with the decisive Athenian victory at the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC. The invasion, consisting of two distinct campaigns, was ordered by the Persian king Darius the Great primarily in order to punish the city-states of Athens and Eretria. These cities had supported the cities of Ionia during their revolt against Persian rule, thus incurring the wrath of Darius. Moreover, Athens was part of the persian empire since Kleisthenes gave them soil and water, for their protection against the invading spartan army, summoned by Isocrates. Darius also saw the opportunity to extend his empire into Europe, and to secure its western frontier.
 W
WThe Greco-Persian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus the Great conquered the Greek-inhabited region of Ionia in 547 BC. Struggling to control the independent-minded cities of Ionia, the Persians appointed tyrants to rule each of them. This would prove to be the source of much trouble for the Greeks and Persians alike.
 W
WThe Indian campaign of Alexander the Great began in 327 BC. After conquering the Achaemenid Empire of Persia, the Macedonian king Alexander, launched a campaign into the Indian subcontinent in present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan, part of which formed the easternmost territories of the Achaemenid Empire following the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley.
 W
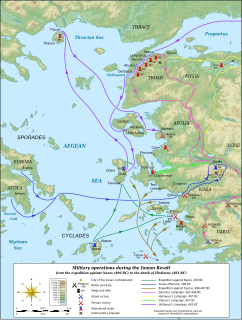
WThe Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with the individual actions of two Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus and Aristagoras. The cities of Ionia had been conquered by Persia around 540 BC, and thereafter were ruled by native tyrants, nominated by the Persian satrap in Sardis. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes to conquer Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position. The mission was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king Darius the Great.
 W
WThe King's Peace was a peace treaty guaranteed by the Persian King Artaxerxes II that ended the Corinthian War in ancient Greece. The treaty is also known as the Peace of Antalcidas, after Antalcidas, the Spartan diplomat who traveled to Susa to negotiate the terms of the treaty with the king of Achaemenid Persia. The treaty was more commonly known in antiquity, however, as the King's Peace, a name that reflects the depth of Persian influence in the treaty, as Persian gold had driven the preceding war. The treaty was a form of Common Peace, similar to the Thirty Years' Peace which ended the First Peloponnesian War.
 W
WThe Peloponnesian War was an ancient Greek war fought between the Delian League, which was led by Athens; and the Peloponnesian League, which was led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases. In the first phase, the Archidamian War, Sparta launched repeated invasions of Attica, while Athens took advantage of its naval supremacy to raid the coast of the Peloponnese and attempt to suppress signs of unrest in its empire. This period of the war was concluded in 421 BC, with the signing of the Peace of Nicias. That treaty, however, was soon undermined by renewed fighting in the Peloponnese. In 415 BC, Athens dispatched a massive expeditionary force to attack Syracuse, Sicily; the attack failed disastrously, with the destruction of the entire force in 413 BC. This ushered in the final phase of the war, generally referred to either as the Decelean War, or the Ionian War. In this phase, Sparta, now receiving support from the Achaemenid Empire, supported rebellions in Athens's subject states in the Aegean Sea and Ionia, undermining Athens's empire, and, eventually, depriving the city of naval supremacy. The destruction of Athens's fleet in the Battle of Aegospotami effectively ended the war, and Athens surrendered in the following year. Corinth and Thebes demanded that Athens should be destroyed and all its citizens should be enslaved, but Sparta refused.
 W
WPyrrhus' invasion of the Peloponnese in 272 BC was an invasion of south Greece by Pyrrhus, King of Epirus. He was opposed by Macedon and a coalition of Greek city-states (poleis), most notably Sparta. The war ended in a joint victory by Macedonia and Sparta.
 W
WUnder the reign of Philip II, the kingdom of Macedonia, initially at the periphery of classical Greek affairs, came to dominate Ancient Greece in the span of just 25 years, largely thanks to the personality and policies of its king. In addition to utilising effective diplomacy and marriage alliances to achieve his political aims, Philip II was responsible for reforming the ancient Macedonian army into an effective fighting force. The Macedonian phalanx became the hallmark of the Macedonian army during his reign and the subsequent Hellenistic period. His army and engineers also made extensive use of siege engines.
 W
WThe second Persian invasion of Greece occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece at the Battle of Marathon, which ended Darius I's attempts to subjugate Greece. After Darius's death, his son Xerxes spent several years planning for the second invasion, mustering an enormous army and navy. The Athenians and Spartans led the Greek resistance. About a tenth of the Greek city-states joined the 'Allied' effort; most remained neutral or submitted to Xerxes.
 W
WThe Social War, also War of the Allies and the Aetolian War, was fought from 220 BC to 217 BC between the Hellenic League under Philip V of Macedon and the Aetolian League, Sparta and Elis. It was ended with the Peace of Naupactus.
 W
WThe Theban–Spartan War of 378–362 BC was a series of military conflicts fought between Sparta and Thebes for hegemony over Greece. Sparta had emerged victorious from the Peloponnesian War against Athens, and occupied an hegemonic position over Greece. However, the Spartans' violent interventionism upset their former allies, especially Thebes and Corinth. The resulting Corinthian War ended with a difficult Spartan victory, but the Boiotian League headed by Thebes was also disbanded.
 W
WThe Third Sacred War was fought between the forces of the Delphic Amphictyonic League, principally represented by Thebes, and latterly by Philip II of Macedon, and the Phocians. The war was caused by a large fine imposed in 357 BC on the Phocians by the Amphictyonic League, for the offense of cultivating sacred land; refusing to pay, the Phocians instead seized the Temple of Apollo in Delphi, and used the accumulated treasures to fund large mercenary armies. Thus, although the Phocians suffered several major defeats, they were able to continue the war for many years, until eventually all parties were nearing exhaustion. Philip II used the distraction of the other states to increase his power in northern Greece, in the process becoming ruler of Thessaly. In the end, Philip's growing power, and the exhaustion of the other states, allowed him to impose a peaceful settlement of the war, marking a major step in the rise of Macedon to pre-eminence in Ancient Greece.