 W
WAbolition of Forced Labour Convention, 1957, the full title of which is Convention concerning the Abolition of Forced Labour, 1957, is one of the eight ILO fundamental conventions of the International Labour Organization, which cancels certain forms of forced labour still allowed under the Forced Labour Convention of 1930, such as punishment for strikes and as a punishment for holding certain political views.
 W
WCITES is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals. It was drafted as a result of a resolution adopted in 1963 at a meeting of members of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The convention was opened for signature in 1973 and CITES entered into force on 1 July 1975.
 W
WThe International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966, and in force from 23 March 1976 in accordance with Article 49 of the covenant. Article 49 allowed that the covenant would enter into force three months after the date of the deposit of the thirty-fifth instrument of ratification or accession. The covenant commits its parties to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial. As of September 2019, the Covenant has 173 parties and six more signatories without ratification. Notable holdouts are People's Republic of China and Cuba. North Korea tried to withdraw.
 W
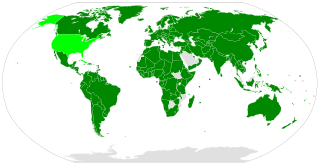
WThe Common Fund for Commodities (CFC) is an intergovernmental financial institution established within the framework of the United Nations. It is a vestige of the proposed New International Economic Order. The CFC finances commodity development projects in developing states.
 W
WThe International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 16 December 1966 through GA. Resolution 2200A (XXI), and came in force from 3 January 1976. It commits its parties to work toward the granting of economic, social, and cultural rights (ESCR) to the Non-Self-Governing and Trust Territories and individuals, including labour rights and the right to health, the right to education, and the right to an adequate standard of living. As of July 2020, the Covenant has 171 parties. A further four countries, including the United States, have signed but not ratified the Covenant.
 W
WThe Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States (OACPS) is a group of countries in Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific that was created by the Georgetown Agreement in 1975. Formerly known as African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States (ACP), the organisation's main objectives are sustainable development and poverty reduction within its member states, as well as their greater integration into the world's economy. All of the member states, except Cuba, are signatories to the Cotonou Agreement with the European Union.
 W
WThe Hague Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict is the first international treaty that focuses exclusively on the protection of cultural property in armed conflict. It was signed at The Hague, Netherlands, on 14 May 1954 and entered into force on 7 August 1956. As of September 2018, it has been ratified by 133 states.
 W
WThe International Fund for Agricultural Development is an international financial institution and a specialised agency of the United Nations that works to address poverty and hunger in rural areas of developing countries. It is the only multilateral development organization that focuses solely on rural economies and food security.
 W
WThe International Maritime Organization is a specialised agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating shipping. The IMO was established following agreement at a UN conference held in Geneva in 1948 and the IMO came into existence ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959. Headquartered in London, United Kingdom, the IMO currently has 174 member states and three associate members.
 W
WThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization (ITSO) is an intergovernmental organization charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.
 W
WThe United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. As of June 2016, 167 countries and the European Union are parties.
 W
WThe Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is an international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy, and to further the goal of achieving nuclear disarmament and general and complete disarmament. Between 1965 and 1968, the treaty was negotiated by the Eighteen Nation Committee on Disarmament, a United Nations-sponsored organization based in Geneva, Switzerland.
 W
WThe International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC) is a 1951 multilateral treaty overseen by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization that aims to secure coordinated, effective action to prevent and to control the introduction and spread of pests of plants and plant products. The Convention extends beyond the protection of cultivated plants to the protection of natural flora and plant products. It also takes into consideration both direct and indirect damage by pests, so it includes weeds.
 W
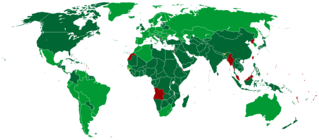
WA World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of great natural beauty. As of July 2021, a total of 1,154 World Heritage Sites exist across 167 countries. With 58 selected areas, Italy is the country with the most sites on the list.
 W
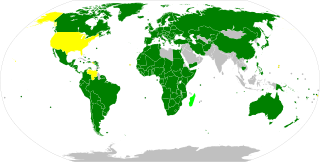
WThe International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (ICERD) is a United Nations convention. A third-generation human rights instrument, the Convention commits its members to the elimination of racial discrimination and the promotion of understanding among all races. The Convention also requires its parties to outlaw hate speech and criminalize membership in racist organizations.
 W
WThe Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees, also known as the 1951 Refugee Convention or the Geneva Convention of 28 July 1951, is a United Nations multilateral treaty that defines who a refugee is, and sets out the rights of individuals who are granted asylum and the responsibilities of nations that grant asylum. The Convention also sets out which people do not qualify as refugees, such as war criminals. The Convention also provides for some visa-free travel for holders of refugee travel documents issued under the convention.
 W
WThe Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees is a key treaty in international refugee law. It entered into force on 4 October 1967, and 146 countries are parties.
 W
WThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that assists countries in economic and industrial development. It is headquartered at the UN Office in Vienna, Austria, with a permanent presence in over 60 countries. As of April 2019, UNIDO comprises 170 member states, which together set the organization's policies, programs, and principles through the biannual General Conference.
 W
WThe Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations of 1961 is an international treaty that defines a framework for diplomatic relations between independent countries. It specifies the privileges of a diplomatic mission that enable diplomats to perform their function without fear of coercion or harassment by the host country. This forms the legal basis for diplomatic immunity. Its articles are considered a cornerstone of modern international relations. As of June 2020, it has been ratified by 193 states.
 W
WThe World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is the United Nations specialized agency entrusted with the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism, having its headquarters in Madrid, Spain. It is the leading international organization in the field of tourism, which promotes tourism as a driver of economic growth, inclusive development and environmental sustainability and offers the sector leadership and support in advancing knowledge and tourism policies worldwide. It serves as a global forum for tourism policy issues and a practical source of tourism research and knowledge. It encourages the implementation of the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism to maximize the contribution of tourism to socio-economic development, while minimizing its possible negative impacts, and is committed to promoting tourism as an instrument in achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), geared towards eliminating poverty and fostering sustainable development and peace worldwide.