 W
WThe Albanian–Venetian War of 1447–48 was waged between Venetian and Ottoman forces against the Albanians under George Kastrioti Skanderbeg. The war was the result of a dispute between the Republic and the Dukagjini family over the possession of the Dagnum fortress. Skanderbeg, then ally of the Dukagjini family, moved against several Venetian held towns along the Albanian coastline, in order to pressure the Venetians into restoring Dagnum. In response, the Republic sent a local force to relieve the besieged fortress of Dagnum, and urged the Ottoman Empire to send an expeditionary force into Albania. At that time the Ottomans were already besieging the fortress of Svetigrad, stretching Skanderbeg's efforts thin.
 W
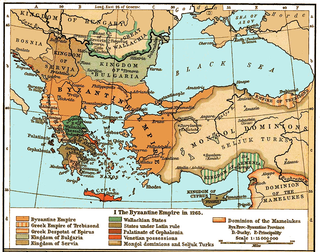
WThe Byzantine–Venetian War of 1296–1302 was an offshoot of the second Venetian–Genoese War of 1294–1299.
 W
WThe Croatian–Venetian wars were a series of periodical, punctuated medieval conflicts and naval campaigns waged for control of the northeastern coast of the Adriatic Sea between the City-state of Venice and the Principality of Croatia, at times allied with neighbouring territories – the Principality of the Narentines and Zahumlje in the south and Istrian peninsula in the north. First struggles occurred at the very beginning of the existence of two conflict parties, they intensified in the 9th century, lessened during the 10th century, but intensified again since the beginning of the 11th century.
 W
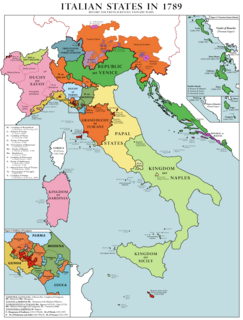
WThe Fall of the Republic of Venice was a series of events that culminated on 12 May 1797 that led to the dissolution and dismemberment of the Republic of Venice at the hands of Napoleon Bonaparte and Habsburg Austria.
 W
WWars between the Normans and the Byzantine Empire were fought from c. 1040 until 1185, when the last Norman invasion of the Byzantine Empire was defeated. At the end of the conflict, neither the Normans nor the Byzantines could boast much power as by the mid-13th century, exhaustive fighting with other powers had weakened both, leading to the Byzantines losing Asia Minor to the Ottoman Empire in the 14th century, and the Normans losing Sicily to the Hohenstaufen.
 W
WThe First Scutari War was an armed conflict in 1405–1412 between Zeta and the Venetian Republic over Scutari and other former possessions of Zeta captured by Venice.
 W
WThe French Revolutionary Wars were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Great Britain, Austria, the Holy Roman Empire, Prussia, Russia, and several other monarchies. They are divided in two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–97) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian Peninsula, the Low Countries and the Rhineland in Europe and was retroceded Louisiana in North America. French success in these conflicts ensured the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe.
 W
WThe Great Turkish War or the Wars of the Holy League was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Poland-Lithuania, Venice, Russia, and Habsburg Hungary. Intensive fighting began in 1683 and ended with the signing of the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. The war was a defeat for the Ottoman Empire, which for the first time lost large amounts of territory. It lost lands in Hungary and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, as well as part of the western Balkans. The war was also significant in that it marked the first time Russia was involved in a western European alliance.
 W
WThe First Italian War, sometimes referred to as the Italian War of 1494 or Charles VIII's Italian War, was the opening phase of the Italian Wars. The war pitted Charles VIII of France, who had initial Milanese aid, against the Holy Roman Empire, Spain and an alliance of Italian powers led by Pope Alexander VI, known as the League of Venice.
 W
WThe Italian Wars of 1499-1504 are divided into two connected, but distinct phases: the Second Italian War (1499–1501), sometimes known as Louis XII's Italian War, and the Third Italian War (1502-1504) or War over Naples. These conflicts were fought primarily by Louis XII of France on one side against a number of Italian states and King Ferdinand II of Aragon over control of the Duchy of Milan and the Kingdom of Naples. In the aftermath of the First Italian War, Louis had been determined to press his claim on the thrones of Milan and Naples; in 1499, Louis XII finally invaded Lombardy and seized Milan, starting off this phase of the Italian Wars. For the next five years, France and Spain would vie for control of Milan and Naples, with France eventually controlling the former and Spain taking the latter.
 W
WThe Italian War of 1521–1526, sometimes known as the Four Years' War, was a part of the Italian Wars. The war pitted Francis I of France and the Republic of Venice against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, Henry VIII of England, and the Papal States. The conflict arose from animosity over the election of Charles as Emperor in 1519–20 and from Pope Leo X's need to ally with Charles against Martin Luther.
 W
WThe War of the League of Cambrai, sometimes known as the War of the Holy League and several other names, was a major conflict in the Italian Wars of 1494–1559. The main participants of the war, who fought for its entire duration, were France, the Papal States, and the Republic of Venice, joined at various times by nearly every significant power in Western Europe, including Spain, the Holy Roman Empire, England, the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, the Duchy of Ferrara, and Swiss mercenaries.
 W
WThe War of the League of Cognac (1526–30) was fought between the Habsburg dominions of Charles V—primarily the Holy Roman Empire and Spain—and the League of Cognac, an alliance including the Kingdom of France, Pope Clement VII, the Republic of Venice, the Kingdom of England, the Duchy of Milan, and the Republic of Florence.
 W
WThe Wars in Lombardy were a series of conflicts between the Republic of Venice and the Duchy of Milan and their respective allies, fought in four campaigns in a struggle for hegemony in Northern Italy that ravaged the economy of Lombardy and weakened the power of Venice. They lasted from 1423 until the signing of the Treaty of Lodi in 1454. During their course, the political structure of Italy was transformed: out of a competitive congeries of communes and city-states emerged the five major Italian territorial powers that would make up the map of Italy for the remainder of the 15th century and the beginning of the Italian Wars at the turn of the 16th century. They were Venice, Milan, Florence, the Papal States and Naples. Important cultural centers of Tuscany and Northern Italy—Siena, Pisa, Urbino, Mantua, Ferrara—became politically marginalized.
 W
WThe Norwegian Crusade, led by Norwegian King Sigurd I, was a crusade or a pilgrimage that lasted from 1107 to 1111, in the aftermath of the First Crusade. The Norwegian Crusade marks the first time a European king personally went to the Holy Land.
 W
WThe Second Scutari War was an armed conflict in 1419–1426 between Zeta (1419–1421) and then the Serbian Despotate (1421–1423) on the one side and the Venetian Republic on the other, over Scutari and other former possessions of Zeta captured by Venice.
 W
WThe Smyrniote crusades (1343–1351) were two Crusades sent by Pope Clement VI against the Emirate of Aydin under Umur Beg which had as their principal target the coastal city of Smyrna in Asia Minor.
 W
WThe Venetian Crusade of 1122–1124 was an expedition to the Holy Land launched by the Republic of Venice that succeeded in capturing Tyre. It was an important victory at the start of a period when the Kingdom of Jerusalem would expand to its greatest extent under Baldwin II of Jerusalem. The Venetians gained valuable trading concessions in Tyre. Through raids on Byzantine territory both on the way to the Holy Land and on the return journey, the Venetians forced the Byzantines to confirm, as well as extend, their trading privileges with the empire.
 W
WThe Venetian–Genoese Wars were a series of struggles between the Republic of Genoa and the Republic of Venice, at times allied with other powers, for dominance in the Mediterranean Sea between 1256 and 1381. There were four bouts of open warfare, in which the fighting between the two republics took place largely at sea. Even during periods of peace, incidents of piracy and other minor outbreaks of violence between the two trading communities were commonplace.
 W
WThe War of the Euboeote Succession was fought in 1256–1258 between the Prince of Achaea, William II of Villehardouin, and a broad coalition of other rulers from throughout Frankish Greece who felt threatened by William's aspirations. The war was sparked by William's attempt to gain control of a third of the island of Euboea, which was resisted by the local Lombard barons with the aid of the Republic of Venice. The Lord of Athens and Thebes, Guy I de la Roche, also entered the war against William, along with other barons of Central Greece. Their defeat at the Battle of Karydi in May/June 1258 effectively brought the war to an end in an Achaean victory, although a definite peace treaty was not concluded until 1262.