 W
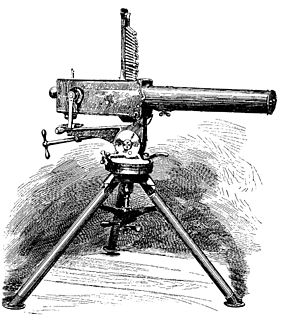
WThe Billinghurst Requa Battery gun was an early rapid-fire gun used during the American Civil War. It was invented by a Dr. Josephus Requa (1833–1910), a dentist by profession, who had at the age of 16 spent three years as an apprentice to William Billinghurst (1807–1880), a New York riflemaker.
 W
WThe Gardner gun was an early type of mechanical machine gun. It had one, two or five barrels, was fed from a vertical magazine or hopper and was operated by a crank. When the crank was turned, a feed arm positioned a cartridge in the breech, the bolt closed and the weapon fired. Turning the crank further opened the breechblock and extracted the spent case.
 W
WThe Gast gun was a German twin barrelled machine gun that was developed by Karl Gast of Vorwerk und Companie of Barmen and used during the First World War. Its unique operating system produced a very high rate of fire of 1,600 rounds per minute. The same principle was later used as the basis for the widely used Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23L series of Russian aircraft autocannon.
 W
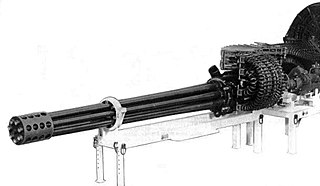
WThe Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon.
 W
WThe General Electric GAU-8/A Avenger is a 30 mm hydraulically driven seven-barrel Gatling-style autocannon that is typically mounted in the United States Air Force's Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II. Designed specifically for the anti-tank role, the Avenger delivers very powerful rounds at a high rate of fire. The GAU-8/A is also used in the Goalkeeper CIWS ship weapon system, which provides defense against short-range threats such as highly maneuverable missiles, aircraft, and fast maneuvering surface vessels. The GAU-8/A is currently produced by General Dynamics.
 W
WThe GAU-19/A is an electrically-driven, three-barrel rotary heavy machine gun that fires the .50 BMG (12.7×99mm) cartridge.
 W
WThe Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-6-23 is a six-barreled 23 mm rotary cannon used by some modern Soviet/Russian military aircraft.
 W
WThe Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-6-30 is a Russian 30 mm rotary cannon aircraft-mounted and naval autocannon used by Soviet and later CIS military aircraft. The GSh-6-30 fires a 30×165mm, 390 g projectile.
 W
WThe Glagolev-Shipunov-Gryazev GShG-7.62 is a four-barreled rotary machine gun designed in the Soviet Union, similar to firearms such as the M134 Minigun. It is a gas operated, self-powered weapon, which is in contrast with most other rotary guns. It was developed in 1968–1970 for the Mi-24 helicopter together with YakB 12.7mm machine gun, and is currently used in GUV-8700 gun pods, and flexible mounts on Kamov Ka-29.
 W
WThe M61 Vulcan is a hydraulically, electrically or pneumatically driven, six-barrel, air-cooled, electrically fired Gatling-style rotary cannon which fires 20 mm rounds at an extremely high rate. The M61 and its derivatives have been the principal cannon armament of United States military fixed-wing aircraft for sixty years.
 W
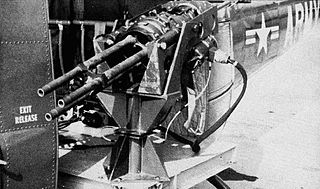
WThe M134 Minigun is an American 7.62×51mm NATO six-barrel rotary machine gun with a high rate of fire. It features a Gatling-style rotating barrel assembly with an external power source, normally an electric motor. The "Mini" in the name is in comparison to larger-caliber designs that use a rotary barrel design, such as General Electric's earlier 20 mm M61 Vulcan, and "gun" for the use of rifle ammunition as opposed to autocannon shells.
 W
WThe M197 electric cannon is a 20 mm three-barreled electric Gatling-type rotary cannon used by the United States military.
 W
WA mitrailleuse is a type of volley gun with barrels of rifle calibre that can fire either all rounds at once or in rapid succession. The earliest true mitrailleuse was invented in 1851 by Belgian Army captain Fafschamps, ten years before the advent of the Gatling gun. It was followed by the Belgian Montigny mitrailleuse in 1863. Then the French 25 barrel "Canon à Balles", better known as the Reffye mitrailleuse, was adopted in great secrecy in 1866. It became the first rapid-firing weapon deployed as standard equipment by any army in a major conflict when it was used during the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71.
 W
WThe Montigny mitrailleuse was an early type of crank-operated machine-gun developed by the Belgian gun works of Joseph Montigny between 1859 and 1870. It was an improved version of the "Mitrailleuse", invented by Belgian Captain Fafschamps in 1851 which was a fixed 50-barrelled volley gun.
 W
WThe Nordenfelt gun was a multiple-barrel organ gun that had a row of up to twelve barrels. It was fired by pulling a lever back and forth and ammunition was gravity fed through chutes for each barrel. It was produced in a number of different calibres from rifle up to 25 mm (1 inch). Larger calibres were also used, but for these calibres the design simply permitted rapid manual loading rather than true automatic fire. This article covers the anti-personnel rifle-calibre gun.
 W
WThe Phalanx CIWS is a close-in weapon system for defense against incoming threats such as small boats, surface torpedoes, anti-ship missiles and helicopters. It was designed and manufactured by the General Dynamics Corporation, Pomona Division, later a part of Raytheon. Consisting of a radar-guided 20 mm (0.8 in) Vulcan cannon mounted on a swiveling base, the Phalanx has been used by the United States Navy and the naval forces of 15 other countries. The US Navy deploys it on every class of surface combat ship, except the Zumwalt-class destroyer and San Antonio-class amphibious transport dock. Other users include the British Royal Navy, the Royal Australian Navy, the Royal Canadian Navy and the US Coast Guard .
 W
WThe Ripley Machine Gun was a volley gun, an early precursor of the machine gun, which was patented in 1861 by Ezra Ripley. Although it is likely that it was never actually produced, it demonstrated a number of basic concepts that were employed in the design of the Gatling Gun that was patented the following year.
 W
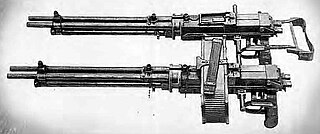
WA rotary cannon, rotary autocannon, rotary gun or Gatling cannon, is any large-caliber multiple-barreled automatic firearm that uses in a Gatling-type rotating barrel assembly to deliver a sustained saturational direct fire at much greater rates of fire than single-barreled autocannons of the same caliber. The loading, firing and ejection functions are performed simultaneously in different barrels as the whole assembly rotates, and the rotation also permits the barrels some time to cool. The rotating barrels on nearly all modern Gatling-type guns are powered by an external force such as an electric motor, although internally powered gas-operated versions have also been developed.
 W
WThe Type 100 is a double barrel machine gun of Japanese origin. The weapon is gas operated and fed from an overhead magazine. An example can be seen at the Satria Mandala Museum in Jakarta.
 W
WThe Pistola Mitragliatrice Villar Perosa M1915, official named FIAT Mod. 1915, was an Italian portable automatic firearm developed during World War I by the Officine di Villar Perosa.
 W
WThe XM214 Microgun is an American prototype 5.56 mm rotary-barreled machine gun. It was designed and built by General Electric. The XM214 was a scaled-down smaller and lighter version of the M134 Minigun, firing M193 5.56×45mm ammunition.
 W
WThe Yakushev-Borzov YakB-12.7 mm is a remotely controlled 12.7×108mm caliber four-barrel rotary cannon developed by the Soviet Union in 1973 for the Mil Mi-24 attack gunship and low-capacity troop transporter, with 1470 rounds, which can also be mounted in GUV-8700 machine-gun pods with 750 rounds. It has a high rate of fire and is also one of the few self-powered guns of the Gatling type.