 W
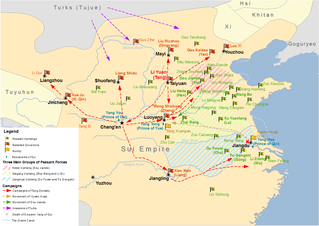
WThe transition from Sui to Tang (613-628) was the period between the end of the Sui dynasty and the start of the Tang dynasty. The Sui dynasty's territories were carved into a handful of short-lived states by its officials, generals, and agrarian rebel leaders. A process of elimination and annexation followed that ultimately culminated in the consolidation of the Tang dynasty by the former Sui general Li Yuan. Near the end of the Sui, Li Yuan installed the puppet child emperor Yang You. Li later executed Yang and proclaimed himself emperor of the new Tang dynasty.
 W
WThe Battle of Hulao or Battle of Sishui, on 28 May 621 was the main and final battle of the Luoyang–Hulao campaign between the rival Tang, Zheng, and Xia regimes during the transition from Sui to Tang. It was a decisive victory for the Tang prince Li Shimin, through which he was able to subdue two rival warlords, Dou Jiande who headed the Xia regime in Hebei, and Wang Shichong, the self-declared emperor of the Zheng dynasty. The battle was fought at the strategically important Hulao Pass, east of Luoyang.
 W
WThe Battle of Huoyi was fought in China on 8 September 617, between the forces of the rebel Duke of Tang, Li Yuan, and the army of the ruling Sui dynasty. Li Yuan, with an army of around 25,000, was advancing south along the Fen River towards the imperial capital, Daxingcheng. His advance was stalled for two weeks due to heavy rainfall and he was met at the town of Huoyi by an elite Sui army of 20,000 men. Li Yuan's cavalry, under the command of his two eldest sons, lured the Sui out of the protection of the city walls, but in the first clash between the two main armies, Li Yuan's forces were initially driven back. At that point, possibly due to a stratagem on Li Yuan's behalf, the arrival of the rest of the rebel army, or to the flanking manoeuvres of Li Yuan's cavalry, which had gotten behind the Sui army, the Sui troops collapsed and routed, fleeing back towards Huoyi. Li Yuan's cavalry, however, cut off their retreat. The battle was followed by the capture of weakly-defended Huoyi, and the advance on Daxingcheng, which fell to the rebels in November. In the next year, Li Yuan deposed the Sui and proclaimed himself emperor, beginning the Tang dynasty.
 W
WThe Battle of Qianshuiyuan, northwest of present-day Changwu, Shaanxi, was fought in 618 between the Tang and the Qin. The battle ended in victory for the Tang, whose armed forces were led by the future emperor Li Shimin.
 W
WThe Battle of Yanshi was fought on 5–6 October 618 between the armies of Wang Shichong and Li Mi, rival contenders for the succession of the Sui dynasty. Wang, who was still ostensibly a Sui loyalist and had been blockaded in Luoyang for months by Li Mi, gambled on a decisive battle and led his troops out to attack the besieging army. Li assembled his forces on a naturally defensible position north of Yanshi town, but Wang managed to surprise Li's forces and approach their camp before they could react. Aided by a secondary cavalry attack from the rear, Wang secured a decisive victory over Li's forces. Although Li managed to escape with part of his army, his authority was shattered, and his followers joined Wang. While Li Mi sought refuge in the rival Tang court, Wang consolidated his control over Henan and eventually deposed the Sui puppet ruler Yang Tong and declared himself as emperor of the new Zheng dynasty. Wang's power lasted until his surrender to the Tang prince Li Shimin in 621.
 W
WDu Ruhui (585–630), courtesy name Keming, posthumously known as Duke Cheng of Lai, was a Chinese official who served as a chancellor under Emperor Taizong in the early Tang dynasty. He and his colleague, Fang Xuanling, were often described as role models for chancellors in imperial China.
 W
WFang Qiao, courtesy name Xuanling, better known as Fang Xuanling, posthumously known as Duke Wenzhao of Liang, was a Chinese statesman and writer who served as a chancellor under Emperor Taizong in the early Tang dynasty. He was the lead editor of the historical record Book of Jin and one of the most celebrated Tang dynasty chancellors. He and his colleague, Du Ruhui, were often described as role models for chancellors in imperial China.
 W
WEmperor Gaozu of Tang, born Li Yuan, courtesy name Shude, was the founder of the Tang dynasty of China, and the first emperor of this dynasty from 618 to 626. Under the Sui dynasty, Li Yuan was the governor in the area of modern-day Shanxi, and was based in Taiyuan.
 W
WLi Jing, courtesy name Yaoshi, posthumously known as Duke Jingwu of Wei, was a Chinese general who lived in the early Tang dynasty and was most active during the reign of Emperor Taizong. In 630, Li Jing defeated the Göktürks, led by Jiali Khan, with just 3,000 cavalry soldiers in a surprise attack, allowing the Tang Empire to subjugate the Göktürks and reduce them to the status of a vassal under the Tang Empire. Li Jing and Li Shiji are considered the two most prominent early Tang generals.
 W
WLi Mi, courtesy name Xuansui (玄邃), pseudonym Liu Zhiyuan (劉智遠), was the leader of a rebel movement against the rule of the Chinese Sui dynasty. He initially was the strategist of the Sui general Yang Xuangan, who rebelled against Emperor Yang of Sui in 613 but failed, and Li subsequently led a rebellion against Emperor Yang in his own right in 617. He gained so much following that there was widespread expectation that he soon would be able to prevail over Sui forces and establish a new dynasty—so much so that even other key rebel leaders, including Dou Jiande, Meng Haigong (孟海公), Xu Yuanlang, and Zhu Can, were urging him to take imperial title. Even Li Yuan was writing him in supplicating terms that implicitly supported his imperial claim. Li Mi tried to gain control of the Sui eastern capital Luoyang, but his forced became stalemated by the Sui forces there, and he never came around to claiming the imperial title, instead accepting the title of Duke of Wei. In October 618, the Sui general Wang Shichong crushed his forces at Yanshi. Li Mi fled to Tang territory and submitted to Emperor Gaozu, but subsequently rebelled against Tang and tried to revive his own army. The Tang general Sheng Yanshi (盛彥師) captured and executed him.
 W
WLi Shiji, courtesy name Maogong, posthumously known as Duke Zhenwu of Ying, was a Chinese general who lived in the early Tang dynasty. His original family name was Xú, but he was later given the family name of the Tang imperial clan, Li, by Emperor Gaozu, the Tang dynasty's founding emperor. Later, during the reign of Emperor Gaozong, Li Shiji was known as Li Ji to avoid naming taboo because the personal name of Emperor Gaozong's predecessor, Emperor Taizong, had the same Chinese character "Shi". Li Shiji is also referred to as Xu Maogong and Xu Ji in the historical novels Shuo Tang and Sui Tang Yanyi.
 W
WLi Xiaogong (591–640), posthumously known as Prince Yuan of Hejian, often referred to by his earlier title as the Prince of Zhao Commandery, was an imperial prince and general of the Tang dynasty. He was a son of a cousin of Emperor Gaozu, the founder of the Tang dynasty, and served as a general under Emperor Gaozu. He defeated Emperor Gaozu's major competitors Xiao Xi and Fu Gongshi. He was one of the few generals of the early Tang dynasty who had already distinguished themselves in their careers before rising to prominence during the reign of Emperor Gaozu's successor, Emperor Taizong.
 W
WQin Qiong, courtesy name Shubao, better known as Qin Shubao, was a Chinese general who lived in the early Tang dynasty of China. Along with Yuchi Gong, he continues to be worshipped in China as a door god. He is also known by his posthumous name Duke Zhuang of Hu.
 W
WShi Danai (史大奈), also known by his former name Ashina Danai (阿史那大奈), was a Turkic prince and the first foreigner to be a general in the Tang army. He was probably the eldest son of Chuluo Qaghan.
 W
WThe Battle of Yanshi was fought on 5–6 October 618 between the armies of Wang Shichong and Li Mi, rival contenders for the succession of the Sui dynasty. Wang, who was still ostensibly a Sui loyalist and had been blockaded in Luoyang for months by Li Mi, gambled on a decisive battle and led his troops out to attack the besieging army. Li assembled his forces on a naturally defensible position north of Yanshi town, but Wang managed to surprise Li's forces and approach their camp before they could react. Aided by a secondary cavalry attack from the rear, Wang secured a decisive victory over Li's forces. Although Li managed to escape with part of his army, his authority was shattered, and his followers joined Wang. While Li Mi sought refuge in the rival Tang court, Wang consolidated his control over Henan and eventually deposed the Sui puppet ruler Yang Tong and declared himself as emperor of the new Zheng dynasty. Wang's power lasted until his surrender to the Tang prince Li Shimin in 621.
 W
WThe Battle of Hulao or Battle of Sishui, on 28 May 621 was the main and final battle of the Luoyang–Hulao campaign between the rival Tang, Zheng, and Xia regimes during the transition from Sui to Tang. It was a decisive victory for the Tang prince Li Shimin, through which he was able to subdue two rival warlords, Dou Jiande who headed the Xia regime in Hebei, and Wang Shichong, the self-declared emperor of the Zheng dynasty. The battle was fought at the strategically important Hulao Pass, east of Luoyang.
 W
WEmperor Taizong of Tang, previously Prince of Qin, personal name Li Shimin, was the second emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, ruling from 626 to 649. He is traditionally regarded as a co-founder of the dynasty for his role in encouraging Li Yuan, his father, to rebel against the Sui dynasty at Jinyang in 617. Taizong subsequently played a pivotal role in defeating several of the dynasty's most dangerous opponents and solidifying its rule over China.
 W
WWei Zheng (580–643), courtesy name Xuancheng, posthumously known as Duke Wenzhen of Zheng, was a Chinese politician and historian. He served as a chancellor of the Tang dynasty for about 13 years during the reign of Emperor Taizong. He was also the lead editor of the official history of the Sui dynasty, the Book of Sui, which was composed in 636.
 W
WXiao Yu (574–647), courtesy name Shiwen, posthumously known as Duke Zhenbian of Song, was an imperial prince of the Western Liang dynasty who later became an official under the Sui and Tang dynasties. He served as a chancellor during the reigns of the emperors Gaozu and Taizong in the early Tang dynasty.
 W
WYan Liben, formally Baron Wenzhen of Boling (博陵文貞男), was a Chinese painter, administrator and politician of the early Tang Dynasty. His most famous work, possibly the only genuine survival, is the Thirteen Emperors Scroll. He also painted the Portraits at Lingyan Pavilion, under Emperor Taizong of Tang, commissioned in 643 to commemorate 24 of the greatest contributors to Emperor Taizong's reign, as well as 18 portraits commemorating the 18 great scholars who served Emperor Taizong when he was the Prince of Qin. Yan's paintings included painted portraits of various Chinese emperors from the Han Dynasty up until the Sui Dynasty (581–618) period. His works were highly regarded by the Tang writers Zhu Jingxuan and Zhang Yanyuan, who noted his paintings were "works among the glories of all times".
 W
WYuchi Gong (尉遲恭) or Yuchi Rong (尉遲融) (585–658), courtesy name Jingde (敬德), also known by his posthumous name Duke Zhongwu of E, was a prominent general who lived in the early Tang dynasty. Yuchi Jingde and another general Qin Shubao are worshipped as door gods in Chinese folk religion.
 W
WZhang Gongjin, courtesy name Hongshen, titled Duke of Tan, was an official and general during the Tang Dynasty of China. He played an important role in the Xuanwu Gate Incident in 626 which helped Emperor Taizong obtained the crown. He was a key general of Tang Dynasty during the campaign against Illig Qaghan of Tujue. Because of his contributions, he was listed as one of 24 founding officials of Tang Dynasty honored on the Lingyan Pavilion.
 W
WZhangsun Wuji, courtesy name Fuji, formally the Duke of Zhao, was a Chinese politician who served as a chancellor in the early Tang dynasty. He was Empress Zhangsun's brother, which made him a brother-in-law of Emperor Taizong and a maternal uncle of Emperor Gaozong. He was an important advisor to Li Shimin when the latter was still the Prince of Qin during the reign of his father, Emperor Gaozu. He helped Li Shimin overcome his brothers Li Jiancheng and Li Yuanji in a succession struggle at the Xuanwu Gate Incident, eventually enabling Li Shimin to become the heir apparent and later the emperor. He was also instrumental in Emperor Taizong's selection of Li Zhi as the Crown Prince, and was exceedingly powerful after Li Zhi took the throne as Emperor Gaozong. However, he gradually fell out of his nephew's favour by failing to support Emperor Gaozong's decision to depose his first wife, Empress Wang, and replacing her with Empress Wu, especially after the beginning of the new year 657 with the power of Empress Wu fell more. In 659, Zhangsun Wuji was falsely accused of treason by Empress Wu's political ally, Xu Jingzong, and eventually ordered to be sent into exile by Emperor Gaozong. Xu Jingzong subsequently sent the official Yuan Gongyu (袁公瑜) to force Zhangsun Wuji to commit suicide on his way to exile.