 W
WThe German Wehrmacht used an extensive variety of combat vehicles during the Second World War. This article is a summary of those vehicles.
 W
WThe Bergetiger was the name the Allied forces gave to a German World War II armored tracked vehicle based on the Tiger. The vehicle was found abandoned on a roadside in Italy with terminal engine problems. The main gun had been removed, and a boom & winch assembly had been fitted to the turret. No other Tiger tanks modified in this manner were ever recovered.
 W
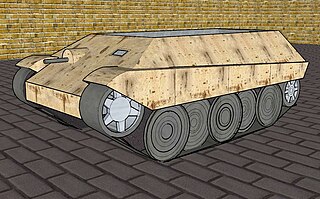
WThe Gepanzerter Mannschaftstransportwagen Kätzchen was a German armoured personnel carrier of late World War II. Auto-Union delivered two prototypes during 1944–45. The hull's shape was similar to the hull of the Panzerkampfwagen Tiger II, but much smaller. The vehicle had front wheel drive with five or six overlapping steel road wheels, possibly resembling the never-built E-25 "replacement tank"'s suspension system in appearance. Power was provided by a Maybach HL50 P engine.
 W
WThe Kfz. 13 was the first armoured reconnaissance vehicle introduced by the Reichswehr after the First World War and, by 1935, 147 units of this lightly armoured vehicle had been delivered to the fleet. The Kfz. 13 was based on a civilian car, the Adler Standard 6. Although the Kfz. 13 was equipped with all-wheel drive, the vehicle had poor cross-country capability. The unarmed version, the Kfz. 14 communications vehicle, was equipped with a radio set instead of the machine gun.
 W
WThe Leichter Panzerspähwagen was a series of light four-wheel drive armoured cars produced by Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1944.
 W
WMaultier or Sd.Kfz. 3 is the name given to series of half-track trucks used by Germany during World War II. They were based on Opel, Mercedes-Benz, Alfa-Romeo or Ford trucks.
 W
WThe Mercedes-Benz L 4500 is a heavy duty truck by Mercedes-Benz. It was built by Daimler-Benz from 1939 – 1944 in the Mercedes-Benz plant Gaggenau, and from 1944 – 1945 by Saurer. The vehicle is a long-bonnet truck and was offered as a rear-wheel-drive truck and as an all-wheel-drive truck. The German Wehrmacht used the L 4500 with armoured cabins as Flaks during World War II. Due to the lack of production material, the cabin was replaced with the simplified standardised Wehrmacht cabin and the mudwings with simplified wings in 1943. Also, the L 4500 chassis was used for the Sonderkraftfahrzeug 4.
 W
WThe term Schwerer Panzerspähwagen, covers the six- and eight-wheeled armoured cars Germany used during the Second World War.
 W
WThis article lists production figures for German armored fighting vehicles during the World War II era. Vehicles include tanks, self-propelled artillery, assault guns and tank destroyers.
 W
WThe Pantserwagen M39 or DAF Pantrado 3 was a Dutch 6×4 armoured car produced in the late thirties for the Royal Dutch Army.
 W
WThe Schwerer Wehrmachtschlepper was a German World War II half-track vehicle used in various roles between 1943 and 1945. The unarmored models were used as supply vehicles and as tractors to haul artillery. Armored versions mounted anti-aircraft guns or a 10 barrel rocket launcher (Nebelwerfer). Fewer than a thousand were built before the end of the war, but production continued after the war of an improved model in the Tatra plant in Czechoslovakia.
 W
WThe Sd.Kfz. 4 Gleisketten-Lastkraftwagen, was a 4.5-tonne military truck of Maultier ("mule") half-track family developed during World War II by Germany. Its manufacturer designation was Mercedes-Benz L4500R.
 W
WThe Sd.Kfz. 6 was a half-track military vehicle used by the German Wehrmacht during the Second World War. It was designed to be used as the main towing vehicle for the 10.5 cm leFH 18 howitzer.
 W
WThe Sd.Kfz. 7 was a half-track military vehicle used by the German Wehrmacht Heer, Luftwaffe and Waffen-SS during the Second World War. Sd.Kfz. is an abbreviation of the German word Sonderkraftfahrzeug, "special purpose vehicle". A longer designation is Sd.Kfz. 7 mittlerer Zugkraftwagen 8t, "medium towing motor vehicle 8t".
 W
WThe Sd.Kfz. 11 was a German half-track that saw widespread use in World War II. Its main role was as a prime mover for medium towed guns ranging from the 3.7 cm FlaK 43 anti-aircraft gun up to the 10.5 cm leFH 18 field howitzer. It could carry eight troops in addition to towing a gun or trailer.
 W
WThe Sd.Kfz. 234, was a family of armoured cars designed and built in Germany during World War II. The vehicles were lightly armoured, armed with a 20, 50 or 75 mm main gun, and powered by a Tatra V12 diesel engine. The Sd.Kfz. 234 broadly resembles the appearance of Sd.Kfz. 231 .
 W
WSd.Kfz. 247 schwerer geländegängiger gepanzerter Personenkraftwagen. was an armored car used by the German armed forces during World War II.
 W
WThe Sd.Kfz. 250 was a light armoured half-track, very similar in appearance to the larger Hanomag-designed Sd.Kfz. 251, and built by the DEMAG firm, for use by Nazi Germany in World War II. Most variants were open-topped and had a single access door in the rear.
 W
WThe Sd.Kfz. 251 half-track was a World War II German armored personnel carrier designed by the Hanomag company, based on its earlier, unarmored Sd.Kfz. 11 vehicle. The Sd.Kfz. 251 was designed to transport the Panzergrenadier into battle. Sd.Kfz. 251s were the most widely produced German half-tracks of the war, with at least 15,252 vehicles and variants produced by seven manufacturers. Some sources state that the Sd.Kfz. 251 was commonly referred to simply as "Hanomags" by both German and Allied soldiers after the manufacturer of the vehicle; this has been questioned, and may have been only a postwar label. German officers referred to them as SPW in their daily orders and memoirs.
 W
WThe leichter gepanzerter Munitionstransportwagen was a light armoured ammunition carrier used by Nazi Germany during World War II as early as the Battle of France in June 1940.
 W
WSd.Kfz. 253 leichter Gepanzerter Beobachtungskraftwagen was a German half-track observation vehicle that was used by artillery forward observers to accompany tank and mechanized infantry units. The vehicle belonged to the Sd.Kfz. 250 family. The appearance was similar to the Sd.Kfz. 250, but the Sd.Kfz. 253 variant was fully enclosed. Demag/Wegman manufactured 285 vehicles between 1940–1941.
 W
WSturmtiger was a World War II German assault gun built on the Tiger I chassis and armed with a 380mm rocket-propelled mortar. The official German designation was Sturmmörserwagen 606/4 mit 38 cm RW 61. Its primary task was to provide heavy fire support for infantry units fighting in urban areas. The few vehicles produced fought in the Warsaw Uprising, the Battle of the Bulge and the Battle of the Reichswald. The fighting vehicle is also known by various informal names, among which the Sturmtiger became the most popular.
 W
WZimmerit was a paste-like coating used on mid- and late-war German armored fighting vehicles during World War II. It was used to produce a hard layer covering the metal armor of the vehicle, providing enough separation that magnetically attached anti-tank mines would fail to stick to the vehicle, although Germany was the only country to use magnetic anti-tank mines in numbers. Zimmerit was often left off late-war vehicles due to the unfounded concern that it could catch fire when hit. It was developed by the German company Chemische Werke Zimmer & Co (Berlin).