 W
WThe Abbey of Sainte-Trinité, better known as the Abbaye aux Dames, is a former nunnery in Caen, Normandy, now home to the Regional Council of Normandy. The complex includes the Church of Sainte-Trinité.
 W
WBattle Abbey is a partially ruined Benedictine abbey in Battle, East Sussex, England. The abbey was built on the site of the Battle of Hastings and dedicated to St Martin of Tours. It is a Scheduled Monument.
 W
WThe Château de Caen is a castle in the Norman city of Caen in the Calvados département (Normandy). It has been officially classed as a Monument historique since 1997.
 W
WWilliam the Conqueror had men of diverse standing and origins under his command at the Battle of Hastings in 1066. With these and other men he went on in the five succeeding years to conduct the Harrying of the North and complete the Norman conquest of England.
 W
WDomesday Book – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William the Conqueror. Domesday has long been associated with the Latin phrase Domus Dei, meaning "House of God". The manuscript is also known by the Latin name Liber de Wintonia, meaning "Book of Winchester". The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle states that in 1085 the king sent his agents to survey every shire in England, to list his holdings and calculate the dues owed to him.
 W
WEudo Dapifer ;, was a Norman aristocrat who served as a steward under William the Conqueror, William II Rufus, and Henry I.
 W
WHamon Dentatus was a Norman baron who was killed while rebelling with other Norman barons against William II, Duke of Normandy at the Battle of Val-ès-Dunes. The epithet "Dentatus" or "Dens" was probably given to Hamon because he was born with teeth. Little is known about Hamon's life.
 W
WThe Harrying of the North refers to a series of campaigns waged by William the Conqueror in the winter of 1069–70 to subjugate northern England, where the presence of the last Wessex claimant, Edgar Atheling, had encouraged Anglo-Danish rebellions. William paid the Danes to go home, but the remaining rebels refused to meet him in battle, and he decided to starve them out by laying waste to the northern shires using scorched earth tactics, especially in the city of York, before relieving the English aristocracy of their positions, and installing Norman aristocrats throughout the region.
 W
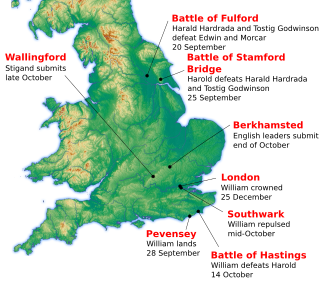
WThe Battle of Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman conquest of England. It took place approximately 7 mi (11 km) northwest of Hastings, close to the present-day town of Battle, East Sussex, and was a decisive Norman victory.
 W
WSenlac Hill is the generally accepted location in which Harold Godwinson deployed his army for the Battle of Hastings on 14 October 1066. It is located near what is now the town of Battle, East Sussex. The name Senlac was popularised by the Victorian historian E.A. Freeman, based solely on a description of the battle by the Anglo-Norman chronicler Orderic Vitalis. Freeman went on to suggest that the Normans nicknamed the area Blood lake as a pun on the English Sand lake.
 W
WHerleva was an 11th-century Norman woman known for having been mother of William the Conqueror, born to an extramarital relationship with Robert I, Duke of Normandy, and also of William's prominent half-brothers Odo of Bayeux and Robert, Count of Mortain, born to Herleva's marriage to Herluin de Conteville.
 W
WThe Hogsmill River in Surrey and Greater London, England is a small chalk stream tributary of the River Thames. It rises in Ewell and flows into the Thames at Kingston upon Thames on the lowest non-tidal reach, that above Teddington lock.
 W
WLanfranc was a celebrated Italian jurist who renounced his career to become a Benedictine monk at Bec in Normandy. He served successively as prior of Bec Abbey and abbot of St Stephen in Normandy and then as Archbishop of Canterbury in England, following its Conquest by William the Conqueror. He is also variously known as Lanfranc of Pavia, Lanfranc of Bec, and Lanfranc of Canterbury.
 W
WSeveral bridges named London Bridge have spanned the River Thames between the City of London and Southwark, in central London. The current crossing, which opened to traffic in 1973, is a box girder bridge built from concrete and steel. It replaced a 19th-century stone-arched bridge, which in turn superseded a 600-year-old stone-built medieval structure. This was preceded by a succession of timber bridges, the first of which was built by the Roman founders of London.
 W
WMatilda of Flanders was Queen of England and Duchess of Normandy by marriage to William the Conqueror, and regent of Normandy during his absences from the duchy. She was the mother of ten children who survived to adulthood, including two kings, William II and Henry I.
 W
WThe Battle of Mortemer was a defeat for Henry I of France when he led an army against his vassal, William the Bastard, Duke of Normandy in 1054. William was eventually to become known as William the Conqueror after his successful invasion and conquest of England.
 W
WThe New Forest is one of the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland and forest in Southern England, covering southwest Hampshire and southeast Wiltshire. It was proclaimed a royal forest by William the Conqueror, featuring in the Domesday Book.
 W
WThe Norman Conquest was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Bretons, Flemish, and men from other French provinces, all led by the Duke of Normandy later styled William the Conqueror.
 W
WThe Tower of London, officially Her Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is separated from the eastern edge of the square mile of the City of London by the open space known as Tower Hill. It was founded towards the end of 1066 as part of the Norman Conquest. The White Tower, which gives the entire castle its name, was built by William the Conqueror in 1078 and was a resented symbol of oppression, inflicted upon London by the new ruling elite. The castle was also used as a prison from 1100 until 1952, although that was not its primary purpose. A grand palace early in its history, it served as a royal residence. As a whole, the Tower is a complex of several buildings set within two concentric rings of defensive walls and a moat. There were several phases of expansion, mainly under kings Richard I, Henry III, and Edward I in the 12th and 13th centuries. The general layout established by the late 13th century remains despite later activity on the site.
 W
WThe Battle of Val-ès-Dunes was fought in 1047 by the combined forces of the Norman duke William I and the French king Henry I against the forces of several rebel Norman barons, led by William's cousin Guy of Brionne.
 W
WThe Battle of Varaville was a battle fought in 1057 by William, Duke of Normandy, against King Henry I of France and Count Geoffrey Martel of Anjou.
 W
WWarwick Castle is a medieval castle developed from a wooden fort, originally built by William the Conqueror during 1068. Warwick is the county town of Warwickshire, England, situated on a meander of the River Avon. The original wooden motte-and-bailey castle was rebuilt in stone during the 12th century. During the Hundred Years War, the facade opposite the town was refortified, resulting in one of the most recognisable examples of 14th-century military architecture. It was used as a stronghold until the early 17th century, when it was granted to Sir Fulke Greville by James I in 1604. Greville converted it to a country house, and it was owned by the Greville family until 1978, when it was bought by the Tussauds Group.
 W
WThe White Tower is a central tower, the old keep, at the Tower of London. It was built by William the Conqueror during the early 1080s, and subsequently extended. The White Tower was the castle's strongest point militarily, and provided accommodation for the king and his representatives, as well as a chapel. Henry III ordered the tower whitewashed in 1240.
 W
WWindsor Castle is a royal residence at Windsor in the English county of Berkshire. It is strongly associated with the English and succeeding British royal family, and embodies almost 1,000 years of architectural history.