 W
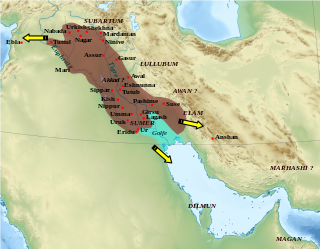
WThe Akkadian Empire was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad and its surrounding region. The empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire exercised influence across Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Anatolia, sending military expeditions as far south as Dilmun and Magan in the Arabian Peninsula.
 W
WThe 4.2-kiloyear BP aridification event was one of the most severe climatic events of the Holocene epoch. It defines the beginning of the current Meghalayan age in the Holocene epoch.
 W
WAkkad was the name of a Mesopotamian city and its surrounding area. Akkad was the capital of the Akkadian Empire, which was the dominant political force in Mesopotamia during a period of about 150 years in the last third of the 3rd millennium BC.
 W
WThe Anubanini petroglyph, also called Sar-e Pol-e Zohab II or Sarpol-i Zohab relief, is a rock relief from the Akkadian Empire period or the Isin-Larsa period and is located in Kermanshah Province, Iran. The rock relief is believed to belong to the Lullubi culture and is located 120 kilometers away from the north of Kermanshah, close to Sarpol-e Zahab. Lullubi reliefs are the earliest rock reliefs of Iran, later ones being the Elamite reliefs of Eshkaft-e Salman and Kul-e Farah.
 W
WThe Barton Cylinder is a Sumerian creation myth, written on a clay cylinder in the mid to late 3rd millennium BCE, which is now in the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. Joan Goodnick Westenholz suggests it dates to around 2400 BC.
 W
WThe Bassetki Statue is a monument from the Akkadian period in Mesopotamia. It was discovered in the 1974 during leveling of the site of the village Bassetki for military purposes. The pedestal contains an inscription in Akkadian, indicating that the statue once stood in the doorway of a palace of the Akkadian ruler Naram-Sin. The statue was cast from pure copper, weighs 150 kilograms (330 lb) and shows a seated, nude human figure on a round pedestal. Only the lower part of the figure is preserved.
 W
WSargon of Akkad, also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC. He is sometimes identified as the first person in recorded history to rule over an empire.
 W
WEnheduanna is the earliest known poet whose name has been recorded. She was the High Priestess of the goddess Inanna and the moon god Nanna (Sīn). She lived in the Sumerian city-state of Ur.
 W
WInanna is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess associated with love, beauty, sex, war, justice and political power. She was originally worshiped in Sumer under the name "Inanna", and was later worshipped by the Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians under the name Ishtar. She was known as the "Queen of Heaven" and was the patron goddess of the Eanna temple at the city of Uruk, which was her main cult center. She was associated with the planet Venus and her most prominent symbols included the lion and the eight-pointed star. Her husband was the god Dumuzid and her sukkal, or personal attendant, was the goddess Ninshubur.
 W
WIndus–Mesopotamia relations are thought to have developed during the second half of 3rd millennium BCE, until they came to a halt with the extinction of the Indus valley civilization after around 1900 BCE. Mesopotamia had already been an intermediary in the trade of lapis lazuli between South Asia and Egypt since at least about 3200 BCE, in the context of Egypt-Mesopotamia relations.
 W
WThe Sumerian King List or Chronicle of the One Monarchy is an ancient literary composition written in Sumerian that was likely created and redacted to legitimize the claims to power of various city-states and kingdoms in southern Mesopotamia during the late third and early second millennium BC. It does so by repetitively listing Sumerian cities, the kings that ruled there, and the lengths of their reigns. Especially in the early part of the list, these reigns often span thousands of years. In the oldest known version, dated to the Ur III period but probably based on Akkadian source material, the SKL reflected a more linear transition of power from Kish, the first city to receive kingship, to Akkad. In later versions from the Old Babylonian period, the list consisted of a large number of cities between which kingship was transferred, reflecting a more cyclical view of how kingship came to a city, only to be inevitably replaced by the next. In its best-known and best-preserved version, as recorded on the Weld-Blundell Prism, the SKL begins with a number of fictional antediluvian kings, who ruled before a flood swept over the land, after which kingship went to Kish. It ends with a dynasty from Isin, which is well-known from other contemporary sources.
 W
WKing of Sumer and Akkad was a royal title in Ancient Mesopotamia combining the titles of "King of Akkad", the ruling title held by the monarchs of the Akkadian Empire with the title of "King of Sumer". The title simultaneously laid a claim on the legacy and glory of the ancient empire that had been founded by Sargon of Akkad and expressed a claim to rule the entirety of lower Mesopotamia. Despite both of the titles "King of Sumer" and "King of Akkad" having been used by the Akkadian kings, the title was not introduced in its combined form until the reign of the Neo-Sumerian king Ur-Nammu, who created it in an effort to unify the southern and northern parts of lower Mesopotamia under his rule. The older Akkadian kings themselves might have been against linking Sumer and Akkad in such a way.
 W
WKing of the Four Corners of the World, alternatively translated as King of the Four Quarters of the World, King of the Heaven's Four Corners or King of the Four Corners of the Universe and often shortened to simply King of the Four Corners, was a title of great prestige claimed by powerful monarchs in ancient Mesopotamia. Though the term "four corners of the world" does refer to specific geographical places within and near Mesopotamia itself, these places were thought to represent locations near the actual edges of the world and as such, the title should be interpreted as something equivalent to "King of all the known world", a claim to universal rule over the entire world and everything within it.
 W
WKing of the Universe, also interpreted as King of Everything, King of the Totality, King of All or King of the World, was a title of great prestige claiming world domination used by powerful monarchs in ancient Mesopotamia. The title is sometimes applied to God in the Judeo-Christian and Abrahamic tradition.
 W
WThe king of Akkad was the ruler of the city of Akkad and its empire, in ancient Mesopotamia. In the 3rd millennium BC, from the reign of Sargon of Akkad to the reign of his great-grandson Shar-Kali-Sharri, the Akkadian Empire represented the dominant power in Mesopotamia and the first known great empire.
 W
WThe Lullubi or Lulubi were a group of tribes during the 3rd millennium BC, from a region known as Lulubum, now the Sharazor plain of the Zagros Mountains of modern Iraqi Kurdistan, and the Kermanshah Province of Iran. Lullubi was neighbour and sometimes ally with the Simurrum kingdom. Frayne (1990) identified their city Lulubuna or Luluban with the region's modern Iraqi town of Halabja.
 W
WManishtushu was the third king of the Akkadian Empire, reigning from c. 2270 BC until his assassination in 2255 BC. He was the son of Sargon the Great, the founder of the Akkadian Empire, and he was succeeded by his son, Naram-Sin.
 W
WNaram-Sin also transcribed Narām-Sîn or Naram-Suen, was a ruler of the Akkadian Empire, who reigned c. 2254–2218 BC, and was the third successor and grandson of King Sargon of Akkad. Under Naram-Sin the empire reached its maximum strength. He was the first Mesopotamian king known to have claimed divinity for himself, taking the title "God of Akkad", and the first to claim the title "King of the Four Quarters, King of the Universe".
 W
WRimush was the second king of the Akkadian Empire. He was the son of Sargon of Akkad and Queen Tashlultum. He was succeeded by his brother Manishtushu, and was an uncle of Naram-Sin of Akkad.
 W
WSargon of Akkad, also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC. He is sometimes identified as the first person in recorded history to rule over an empire.
 W
WIn the Akkadian language Shakkanakku, was a title designating a military governor. Mari was ruled by a dynasty of hereditary Shakkanakkus which was originally set by the Akkadian Empire and gained independence following Akkad's collapse. It is considered that the Shakkanakka gained some form of independence and came to be considered as "Kings" from the time of Apil-Kin. A critical analysis of the Shakkanakku List of Mari has been published.
 W
WShar-Kali-Sharri was a king of the Akkadian Empire.
 W
WThe Simurrum Kingdom was an important city state of the Mesopotamian area from around 2000 BCE to 1500 BCE, during the period of the Akkadian Empire down to Ur III. The Simurrum Kingdom disappears from records after the Old Babylonian period. It was neighbour and sometimes ally with the Lullubi kingdom.
 W
WUrkesh or Urkish is a tell, or settlement mound, located in the foothills of the Taurus Mountains in Al-Hasakah Governorate, northeastern Syria. It was founded during the fourth millennium BC possibly by the Hurrians on a site which appears to have been inhabited previously for a few centuries.
 W
WThe Victory Stele of Naram-Sin is a stele that dates to approximately 2254-2218 BC, in the time of the Akkadian Empire, and is now in the Louvre in Paris. The relief measures six feet in height and was carved in pink limestone. It depicts the King Naram-Sin of Akkad leading the Akkadian army to victory over the Lullubi, a mountain people from the Zagros Mountains. It shows a narrative of the King crossing the steep slopes into enemy territory; on the left are the ordered imperial forces keeping in rank while marching over the disordered defenders that lie broken and defeated. Naram-Sin in shown as by far the most important figure; he is shown towering over his enemy and troops and all eyes gaze up toward him. The weak and chaotic opposing forces are shown being thrown from atop the mountainside, impaled by spears, fleeing and begging Naram-Sin for mercy as well as being trampled underfoot by Naram-Sin himself. This is supposed to convey their uncivilized and barbaric nature making the conquest justified.