 W
WThe Angolan Civil War was a civil war in Angola, beginning in 1975 and continuing, with interludes, until 2002. The war began immediately after Angola became independent from Portugal in November 1975. The war was a power struggle between two former anti-colonial guerrilla movements, the communist People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) and the anti-communist National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA). The war was used as a surrogate battleground for the Cold War by rival states such as the Soviet Union, Cuba, South Africa and the United States.
 W
WThe 55 Day War occurred in Angola, following the 1992 elections, when the city of Huambo was disrupted by a confrontation between the People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) and National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA). The war lasted 55 days, beginning on 9 January 1993.
 W
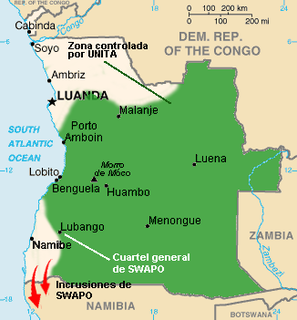
WThe Cuban intervention in Angola began on 5 November 1975, when Cuba sent combat troops in support of the communist-aligned People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) against the pro-western National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA) and National Liberation Front of Angola (FNLA). The intervention came after the outbreak of the Angolan Civil War, which occurred after the former Portuguese colony was granted independence after the Angolan War of Independence. The civil war quickly became a proxy war between the Eastern Bloc led by the Soviet Union and the Western Bloc led by the United States. South Africa and the United States backed UNITA and the FNLA, while communist nations backed the MPLA.
 W
WThe Directorate of Information and Security of Angola was the secret police of the communist People's Republic of Angola from 1975 until its absorption by the Interior Ministry in 1979.
 W
WExecutive Outcomes is a private military company (PMC) founded in South Africa by Eeben Barlow, a former lieutenant-colonel of the South African Defence Force, in 1989. It later became part of the South African-based holding company Strategic Resource Corporation. The company was reestablished in 2021.
 W
WThe Front for the Liberation of the Enclave of Cabinda is a guerrilla and political movement fighting for the independence of the Angolan province of Cabinda. Formerly under Portuguese administration, with the independence of Angola from Portugal in 1975, the territory became an exclave province of the newly independent Angola. The FLEC fights the Cabinda War in the region occupied by the former kingdoms of Kakongo, Loango and N'Goyo.
 W
WThe 1989 Jamba Hercules crash was an air accident involving a Lockheed Hercules L-100 aircraft that crashed on final approach to Jamba, Cuando Cubango, Angola on 27 November 1989. The flight had originated at Kamina Airport, Zaire, and was attempting a low-level approach at night. The aircraft was owned by CIA front company Tepper Aviation; it was delivering arms to UNITA. The crash killed "Bud" Peddy, the head of Tepper Aviation, who was acting as the plane's pilot. On board were several Americans, two West Germans, and a Briton. All were killed in the crash.
 W
WThe United Nations Observer Mission in Angola was established by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1118 of 30 June 1997. Due to the collapse of the peace process in Angola, UN Secretary General recommended to the UN Security Council that MONUA's mandate not be renewed. The mission officially terminated in on 24 February 1999, per the terms of Resolution 1213.
 W
WThe National Front for the Liberation of Angola is a political party and former militant organisation that fought for Angolan independence from Portugal in the war of independence, under the leadership of Holden Roberto.
 W
WThe People's Armed Forces of Liberation of Angola or FAPLA was originally the armed wing of the People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) but later (1975–1991) became Angola's official armed forces when the MPLA took control of the government.
 W
WThe United Nations Angola Verification Mission II, established May 1991 and lasting until February 1995, was the second United Nations peacekeeping mission, of a total of four, deployed to Angola during the course of the Angolan Civil War, the longest war in modern African history. Specifically, the mission was established to oversee and maintain the multilateral ceasefire of 1990 and the subsequent Bicesse Accords in 1991, which instituted an electoral process for the first time including the two rival factions of the civil war, the People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA), the de facto government of Angola, with control of Luanda and most of the country since independence in 1975, and the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA).
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 626, adopted unanimously on 20 December 1988, after noting an agreement between Angola and Cuba regarding the withdrawal of Cuban troops from Angola and considering a report by the Secretary-General, the Council endorsed the report and established the United Nations Angola Verification Mission I for a period of thirty-one months.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 696, adopted unanimously on 30 May 1991, after noting the recent desire to sign the Bicesse Accords between the MPLA and UNITA in Angola, the recent withdrawal of all Cuban troops and considering a report by the Secretary-General, the Council approved Javier Pérez de Cuéllar's recommendations and established the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II, noting that the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission I (1989–1991) was coming to an end.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 785, adopted unanimously on 30 October 1992, after recalling resolutions 696 (1991) and 747 (1992), and expressing its concern at the deteriorating political situation and the resumption of hostilities by UNITA in Angola, the Council approved a recommendation by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to extend the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 30 November 1992.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 793, adopted unanimously on 30 November 1992, after recalling resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992) and 785 (1992), and expressing its concern at the deteriorating political situation and the resumption of hostilities in Angola, the Council approved a recommendation by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to extend the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II for a further two months until 31 January 1993.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 804, adopted unanimously on 29 January 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992) and 793 (1992), and expressing its concern at lack of implementation of the "Acordos de Paz para Angola" in Angola, the council approved a recommendation by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to extend the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II for a further three months until 30 April 1993.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 811, adopted unanimously on 12 March 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992) and 804 (1993), the Council expressed its concern at recent fighting and condemned the violations of the "Acordos de Paz" peace agreement in Angola by UNITA, including its rejection of election results and negotiations in addition to its resumption of hostilities.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 823, adopted unanimously on 30 April 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993) and 811 (1993), the Council expressed support for the ongoing peace talks in Abidjan between the Government of Angola and UNITA under United Nations auspices and decided to extend the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 31 May 1993.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 834, adopted unanimously on 1 June 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993) and 823 (1993), the council indicated its concern at the deteriorating political, military and humanitarian situation in Angola and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II for a period of 45 days ending 15 July 1993.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 851, adopted unanimously on 15 July 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993), 823 (1993) and 834 (1993), the Council noted the continuing deterioration of the situation in Angola and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 15 September 1993, discussing further the peace process in the country.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 864, adopted unanimously on 15 September 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993), 823 (1993), 834 (1993) and 851 (1993), the Council noted the continuing situation in Angola and went on to condemn and place international sanctions on UNITA.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 890, adopted unanimously on 15 December 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993), 823 (1993), 834 (1993), 851 (1993) and 864 (1993) on the situation in Angola, the council noted the slight improvements in the country and extended the stationing of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 16 March 1994.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 922, adopted unanimously on 31 May 1994, after reaffirming Resolution 696 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions on Angola, the council discussed the peace process during the civil war and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 30 June 1994.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 945, adopted unanimously on 29 September 1994, after reaffirming Resolution 696 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions on Angola, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 31 October 1994 and discussed the implementation of peace agreements.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 966, adopted unanimously on 8 December 1994, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 868 (1993) and all resolutions on Angola, the Council discussed the monitoring of a ceasefire in the country and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 8 February 1995.