 W
W1221 Amor is an asteroid and near-Earth object on an eccentric orbit, approximately 1 kilometer (0.6 miles) in diameter. It is the namesake of the Amor asteroids, the second-largest subgroup of near-Earth objects. It was discovered by Eugène Delporte at the Uccle Observatory in 1932, the first time that an asteroid was seen to approach Earth so closely. The assumed S-type asteroid is one of few low-numbered asteroids for which no rotation period has been determined. It was assigned the provisional designation 1932 EA1 and named for Cupid, also known as "Amor" in Latin, the Roman equivalent of the Greek god Eros.
 W
WAurora is one of the largest main-belt asteroids. With an albedo of only 0.04, it is darker than soot, and has a primitive composition consisting of carbonaceous material. It was discovered by J. C. Watson on September 6, 1867, in Ann Arbor, and named after Aurora, the Roman goddess of the dawn.
 W
WBellona is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German astronomer R. Luther on March 1, 1854, and named after Bellōna, the Roman goddess of war; the name was chosen to mark the beginning of the Crimean War. It is a stony (S-type) asteroid with a cross-section size of around 100–120 km. 28 Bellona is orbiting the Sun with a period of 4.63 years.
 W
W161989 Cacus is a stony asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and a potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 1 kilometer in diameter. It was discovered on 8 February 1978, by German astronomer Hans-Emil Schuster at ESO's La Silla Observatory in northern Chile.
 W
WCamilla is one of the largest asteroids from the outermost edge of the asteroid belt, approximately 220 kilometers. It is a member of the Sylvia family and located within the Cybele group. It was discovered on 17 November 1868, by English astronomer Norman Pogson at Madras Observatory, India, and named after Camilla, Queen of the Volsci in Roman mythology. The X-type asteroid is a rare trinary asteroid with two minor-planet moons discovered in 2001 and 2016, respectively. It is elongated in shape and has a short rotation period of 4.8 hours.
 W
WCeres is the largest astronomical object in the asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Ceres was the first asteroid discovered, on 1 January 1801 by Giuseppe Piazzi at Palermo Astronomical Observatory in Sicily. Originally considered a planet, it was reclassified as an asteroid in the 1850s after the discovery of over 20 other objects in similar orbits. In 2006, it was reclassified again as a dwarf planet because, at 940 km (580 mi) in diameter, it is the only asteroid large enough for its collective gravity to pull it into an spheroid. This makes Ceres the only dwarf planet inside Neptune's orbit.
 W
WDejopeja is a large M-type Main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on February 28, 1878, and was named after Deiopea, a Roman nymph.
 W
WEgeria is a large main-belt G-type asteroid. It was discovered by Annibale de Gasparis on November 2, 1850. Egeria was named by Urbain Le Verrier, whose computations led to the discovery of Neptune, after the mythological nymph Egeria of Aricia, Italy, the wife of Numa Pompilius, second king of Rome.
 W
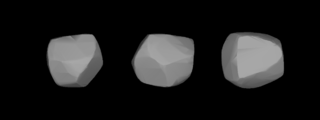
W72 Feronia is a quite large and dark main belt asteroid. It was the first asteroid discovery by C. H. F. Peters, on May 29, 1861, from Hamilton College, New York State. It was initially thought that Peters had merely seen the already known asteroid 66 Maja, but T.H. Safford showed that it was a new body. Safford named it after Feronia, a Roman fertility goddess.
 W
WFides is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German astronomer Karl Theodor Robert Luther on October 5, 1855, and named after Fides, the Roman goddess of loyalty. Fides was the last of the main-belt asteroids to be assigned an iconic symbol. 37 Fides is also a S-type asteroid in the Tholen classification system.
 W
WFlora is a large, bright main-belt asteroid. It is the innermost large asteroid: no asteroid closer to the Sun has a diameter above 25 kilometres or two-elevenths that of Flora itself, and not until the tiny 149 Medusa was discovered was a single asteroid orbiting at a closer mean distance known. It is the seventh-brightest asteroid with a mean opposition magnitude of +8.7. Flora can reach a magnitude of +7.9 at a favorable opposition near perihelion, such as occurred in November 2007. Flora may be the residual core of an intensely heated, thermally evolved, and magmatically differentiated planetesimal which was subsequently disrupted.
 W
WFortuna is one of the largest main-belt asteroids. It has a composition similar to 1 Ceres: a darkly colored surface that is heavily space-weathered with the composition of primitive organic compounds, including tholins.
 W
W3 Juno is a large asteroid in the asteroid belt. Juno was the third asteroid discovered, in 1804, by German astronomer Karl Harding. It is one of the twenty largest asteroids and one of the two largest stony (S-type) asteroids, along with 15 Eunomia. It is estimated to contain 1% of the total mass of the asteroid belt.
 W
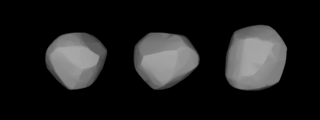
WLaetitia is a large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomer Jean Chacornac on 9 February 1856 and named after Laetitia, a minor Roman goddess of gaiety. The spectrum matches an S-type, indicating a stony (silicate) composition. It is orbiting the Sun with a period of 4.61 years and is spinning on its axis once every 5.1 hours.
 W
WLucina is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Alphonse Borrelly on June 8, 1875, and named after Lucina, the Roman goddess of childbirth. It is large, dark and has a carbonaceous composition. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.
 W
WMinerva is a large trinary main-belt asteroid. It is a C-type asteroid, meaning that it has a dark surface and possibly a primitive carbonaceous composition. It was discovered by J. C. Watson on 24 August 1867, and named after Minerva, the Roman equivalent of Athena, goddess of wisdom. An occultation of a star by Minerva was observed in France, Spain and the United States on 22 November 1982. An occultation diameter of ~170 km was measured from the observations. Since then two more occultations have been observed, which give an estimated mean diameter of ~150 km for diameter.
 W
W90482 Orcus, provisional designation 2004 DW, is a trans-Neptunian dwarf planet with a large moon, Vanth. It has a diameter of 910 km (570 mi). The surface of Orcus is relatively bright with albedo reaching 23 percent, neutral in color and rich in water ice. The ice is predominantly in crystalline form, which may be related to past cryovolcanic activity. Other compounds like methane or ammonia may also be present on its surface. It was discovered by American astronomers Michael Brown, Chad Trujillo, and David Rabinowitz on 17 February 2004.
 W
W679 Pax is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered by German astronomer August Kopff on January 28, 1909. It is named after Pax, a Roman goddess. It is orbiting the Sun with a period of 4.16 years and an eccentricity of 0.31.
 W
WPluto is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It was the first and the largest Kuiper belt object to be discovered. After Pluto was discovered in 1930, it was declared to be the ninth planet from the Sun. Beginning in the 1990s, its status as a planet was questioned following the discovery of several objects of similar size in the Kuiper belt and the scattered disc, including the dwarf planet Eris. This led the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2006 to formally define the term "planet"—excluding Pluto and reclassifying it as a dwarf planet.
 W
WPomona is a stony main-belt asteroid that is 81 kilometres (50 mi) in diameter. It was discovered by German-French astronomer Hermann Mayer Salomon Goldschmidt on October 26, 1854, and is named after Pōmōna, the Roman goddess of fruit trees.
 W
WProserpina is a main-belt asteroid discovered by German astronomer R. Luther on May 5, 1853. It is named after the Roman goddess Proserpina, the daughter of Ceres and the Queen of the Underworld. Another main-belt asteroid, 399 Persephone, discovered in 1895, is named after her Greek counterpart.
 W
WSylvia is the 8th-largest asteroid in the asteroid belt. It is the parent body of the Sylvia family and member of Cybele group located beyond the main asteroid belt. Sylvia was the first asteroid known to possess more than one moon.
 W
WThisbe, minor planet designation 88 Thisbe, is the 13th largest main-belt asteroids. It was discovered by C. H. F. Peters on June 15, 1866, and named after Thisbe, heroine of a Roman fable. An occultation of a star by Thisbe was observed on October 7, 1981. Results from the occultation indicate a larger than expected diameter of 232 km.
 W
WVesta is one of the largest objects in the asteroid belt, with a mean diameter of 525 kilometres (326 mi). It was discovered by the German astronomer Heinrich Wilhelm Matthias Olbers on 29 March 1807 and is named after Vesta, the virgin goddess of home and hearth from Roman mythology.
 W
WVictoria is a large main-belt asteroid, orbiting the Sun with a period of 3.56 years and an eccentricity of 0.221. It is a stony (S-type) asteroid, about 112–124 km across with an albedo of 0.18 and a rotation period of 8.66 hours. Victoria has been observed to occult a star three times since its discovery. Radar and speckle interferometry observations show that the shape of Victoria is elongated, and it is suspected to be a binary asteroid, with a moon of irregular shape.