 W
WThe United States military's Air Force Satellite Communications (AFSATCOM) is a network of ground and space systems to allow rapid dissemination of communications to a worldwide audience. AFSATCOM's creation was during the height of the Cold War to guarantee that Emergency Action Messages would be received by Strategic Air Command nuclear forces.
 W
WAlfa was the designation of an Italian ballistic missile program that started in 1971 under the control of the GRS. It was related to the Polaris A-3 missile.
 W
WArea 2 is a division of the Nevada Test Site in the Mojave Desert. The area is located 18 miles south-east of Area 51.
 W
WThe Ares was a proposed intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) derived from the Titan II missile. It was a single-stage rocket with a high-performance engine to increase the rocket's specific impulse. Both Aerojet and Rocketdyne carried out engine design studies for the project, but Ares was ultimately cancelled in favour of solid-fuel ICBMs, which were safer to store and could be launched with much less notice. The Ares missile series was canceled due to the inconvenience of using liquid fuel. Some reasons included extensive protection from corrosion within the silos, as well as the liquid fuel propellant, ideally used in the proposed Ares missiles, being more expensive to maintain. Thus making the transition to use the Minuteman II missiles, that ran on solid fuel, easier because solid fuel was more reliable for sand was less expensive than previous projects. Hence the cancellation of the Ares missile series.
 W
WA bomb tower is a lightly constructed tower, often 100 to 700 feet high, built to hold a nuclear weapon for an above ground nuclear test. The tower holds the bomb for the purpose of the investigation of its destructive effects and for the adjustment of measuring instruments, such as high-speed cameras. Normally, the bomb tower disintegrates completely on detonation due to the enormous heat of the explosion.
 W
WThe Cold and the Dark: The World after Nuclear War is a 1984 book by Paul R. Ehrlich, Carl Sagan, Donald Kennedy, and Walter Orr Roberts.
 W
WThe Defense Nuclear Facilities Safety Board is an independent agency of the United States government based in Washington, D.C. Established in 1988, the DNFSB oversees the nuclear weapons complex administered by the U.S. Department of Energy. The DNFSB is independent of the Department of Energy. The DNFSB's most important power is its ability to give recommendations to the Secretary of Energy.
 W
WHeavy ICBM is a term that was created in the 1970s to describe a class of Soviet and Russian ICBMs. They were characterized by a heavy throw-weight of 5 to 9 metric tons, several times that of an LGM-30 Minuteman, and a length of over 35 meters, and were thus capable of delivering a large number of warheads in a single MIRV missile.
 W
WInternational Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Safeguards are a system of inspection and verification of the peaceful uses of nuclear materials as part of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), supervised by the International Atomic Energy Agency.
 W
WJackass Flats is a shallow alluvial basin located in the southwest portion of the Nevada National Security Site in Nye County, Nevada. The area lies east of Yucca Mountain, south of the Calico Hills and Shoshone Mountain and northwest of Skull Mountain. The valley drains to the southwest via the Tonopah and Fortymile washes into the Amargosa Valley across US Route 95 at the town of Amargosa Valley, Nevada. The "flat" covers an area of approximately 120 square miles (310 km2) and ranges in elevation from about 2,800 ft (850 m) just north of US 95 to 4,000 ft (1,200 m) at the mountain bases to the north and east.
 W
WLyon – Mont Verdun Air Base is located to the northwest of Lyon. It is a center for air defense operations transferred to the site from the now-deactivated headquarters of the French Air Force at Taverny Air Base – BA921 near Paris, with an underground alternate strategic command center hardened against chemical and nuclear attack.
 W
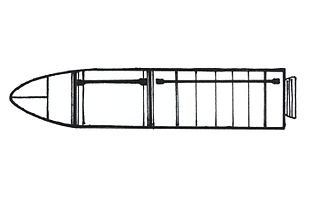
WThe M1 MSBS was the first French submarine-launched ballistic missile.
 W
WThe M4 was a French submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) deployed on the nuclear Redoutable-class submarines.
 W
WThe Maneuverable Reentry Vehicle is a type of ballistic missile whose warhead is capable of autonomously tracking ground targets. It often requires some terminal active homing guidance to make sure the missile does not miss the target, because of the frequent trajectory shifts. Refer to atmospheric reentry.
 W
WMedium Atomic Demolition Munition (MADM) was a tactical nuclear weapon developed by the United States during the Cold War. They were designed to be used as nuclear land mines and for other tactical purposes, with a relatively low explosive yield from a W45 warhead, between 1 and 15 kilotons. Each MADM weighed less than 400 lb (181 kg) total. They were deployed between 1965 and 1986.
 W
WThis is a list of projected numbers of casualties should a nuclear weapon be detonated in a certain city or other population center.
 W
WNukespeak: Nuclear Language, Visions and Mindset is a 1982 book by Stephen Hilgartner, Richard C. Bell and Rory O'Connor. This book is a concise history of nuclear weapons and nuclear power in the United States, with special emphasis on the language of the "nuclear mindset".
 W
WOperations Order No. 35 was an order issued by the 509th Composite Group on August 5, 1945 for the atomic bombing mission on Hiroshima, Japan, during World War II. The Order was signed by Operations Officer Major James I. Hopkins, Jr. who would later fly Big Stink in the August 9, 1945 atomic bombing raid on Nagasaki, Japan, under the call sign "Dimples 90".
 W
WThe Primary Alerting System (PAS), was a network of land-line connections used by the Strategic Air Command (SAC) for command and control of its nuclear forces. PAS provided immediate and simultaneous voice communications to all (SAC) unit command posts and missile launch control facilities.
 W
WThe Scottish Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament is the Scottish representative body of the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND). The Scottish CND campaigns for the abolition of British nuclear weapons to contribute to the global elimination of all nuclear weapons.
 W
WSukhoy Nos is a cape on Severny Island, the northern island of the archipelago Novaya Zemlya, projecting westward into the Barents Sea. The site lies near the southwestern corner of the island, 15 km (9.3 mi) from Mityushikha Bay, north of Matochkin Strait, which separates Severny from Yuzhny Island, the southern island of the archipelago.
 W
WUpshot-Knothole Dixie was the fourth test-firing of Operation Upshot–Knothole, an atomic weapons test series conducted in 1953 by the United States at the Nevada Test Site.
 W
WThe W74 was an experimental American nuclear artillery shell.
 W
WThe W76 is a United States thermonuclear warhead, designed for use on the UGM-96 Trident I sea-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) and subsequently moved to the UGM-133 Trident II as Trident I was phased out of service. The first variant, the W76 mod 0 (W76-0) was manufactured from 1978 to 1987, and was gradually replaced by the W76 mod 1 (W76-1) between 2008 and 2018, completely replacing the Mod 0 in the active stockpile. In 2018 it was announced that some Mod 1 warheads would be converted to a new low-yield W76 mod 2 (W76-2) version. The first Mod 2 warheads were deployed in late 2019.
 W
WThe W82 was a low-yield tactical nuclear warhead developed by the United States and designed to be used in a 155 mm artillery shell. It was conceived as a more flexible replacement for the W48, the previous generation of 155 mm nuclear artillery shell. A previous attempt to replace the W48 with the W74 munition was canceled due to cost.