 W
WAquarius is a launch vehicle concept designed for low-cost by Space Systems/Loral to carry small, inexpensive payloads into LEO.
 W
WAres I was the crew launch vehicle that was being developed by NASA as part of the Constellation program. The name "Ares" refers to the Greek deity Ares, who is identified with the Roman god Mars. Ares I was originally known as the "Crew Launch Vehicle" (CLV).
 W
WThe Ares V was the planned cargo launch component of the cancelled NASA Constellation program, which was to have replaced the Space Shuttle after its retirement in 2011. Ares V was also planned to carry supplies for a human presence on Mars. Ares V and the smaller Ares I were named after Ares, the Greek god of war.
 W
WThe Baikal booster was a proposed reusable flyback booster for the Angara rocket family based on the Angara Universal Rocket Module in 2001. It was designed by the Molniya Research and Industrial Corporation for the Khrunichev Space centre, reusing the flyback and control system for the reusable Buran orbiter.
 W
WSERV, short for Single-stage Earth-orbital Reusable Vehicle, was a proposed space launch system designed by Chrysler's Space Division for the Space Shuttle project. SERV was so radically different from the two-stage spaceplanes that almost every other competitor entered into the Shuttle development process that it was never seriously considered for the shuttle program.
 W
WThe Europa rocket was an early expendable launch system of the European Launcher Development Organisation (ELDO), which was the precursor to the European Space Agency (ESA). It was developed with the aim to delivering space access technology, and more specifically to facilitate the deployment of European-wide telecommunication and meteorological satellites into orbit.
 W
WThe NEXUS reusable rocket was a concept design created in the 1960s by a group at General Dynamics led by Krafft Arnold Ehricke. It was intended as the next leap beyond the Saturn V, carrying up to eight times more payload. Several versions were designed, including 12,000 and 24,000 short ton vehicles with payloads of one thousand and two thousand short tons respectively. The larger version had a diameter of 202 feet. It was never built. It was a Single Stage to Orbit vehicle that would be fully recoverable upon landing in the ocean. It would use parachutes to slow descent, with retrorockets for a final soft touchdown.
 W
WThe Kistler K-1 was a two-stage, fully reusable launch vehicle design created by Kistler Aerospace. It was to accommodate a wide range of missions, including payload delivery to low Earth orbit (LEO), payload delivery to high-energy orbits with a K-1 Active Dispenser, technology demonstration flights, microgravity missions, and commercial cargo resupply, recovery, and reboost services for the International Space Station (ISS).
 W
WThe Kankoh-maru is a proposed vertical takeoff and landing (VTVL), single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO), reusable launch system. According to a document from July 1997, it would have been manufactured by Kawasaki Heavy Industries and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, with its formal name being the Kawasaki S-1.
 W
WLiberty was a 2011 launch vehicle concept proposed by Alliant Techsystems (ATK) and Astrium for phase 2 of the NASA Commercial Crew Development (CCDev) program intended to stimulate development of privately operated crew vehicles to low Earth orbit.
 W
WLiquid Fly-back Booster (LFBB) was a German Aerospace Center's (DLR's) project concept to develop a liquid rocket booster capable of reusing for Ariane 5 in order to significantly reduce the high cost of space transportation and increase environmental friendliness. LFBB would replace the existing solid rocket boosters, providing main thrust during the liftoff. Once separated, two winged boosters would perform an atmospheric entry, fly back autonomously to the French Guiana, and land horizontally on the airport like an aeroplane.
 W
WThe Magnum was a large super-heavy-lift rocket designed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center during the mid-1990s. The Magnum, which never made it past the preliminary design phase, would have been a booster some 96 meters tall, on the scale of the Saturn V and was originally designed to carry a human expedition to Mars. It was to have used two strap-on side boosters, similar to the Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs), but using liquid fuel instead. Some designs had the strap-on boosters using wings and jet engines, which would enable them to fly back to the launch area after they were jettisoned in flight. The Magnum was designed to carry around 80 tons of payload into low Earth orbit (LEO).
 W
WThe DC-X, short for Delta Clipper or Delta Clipper Experimental, was an uncrewed prototype of a reusable single-stage-to-orbit launch vehicle built by McDonnell Douglas in conjunction with the United States Department of Defense's Strategic Defense Initiative Organization (SDIO) from 1991 to 1993. Starting 1994 until 1995, testing continued through funding of the US civil space agency NASA. In 1996, the DC-X technology was completely transferred to NASA, which upgraded the design for improved performance to create the DC-XA.
 W
WMercury-Jupiter was a proposed suborbital launch configuration consisting of a Jupiter missile carrying a Mercury capsule. Two flights were planned in support of Project Mercury. On July 1, 1959, less than a year after the October, 1958 program start date, the flights were canceled due to budget constraints. The MJ-1 flight would have been a heat shield test. The MJ-2 flight was planned as a maximum dynamic pressure qualification test of the production Mercury spacecraft with a chimpanzee on board.
 W
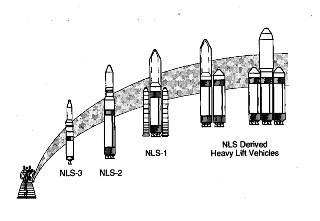
WThe National Launch System was a study authorized in 1991 by President George H. W. Bush to outline alternatives to the Space Shuttle for access to Earth orbit. Shortly thereafter, NASA asked Lockheed Missiles and Space, McDonnell Douglas, and TRW to perform a ten-month study.
 W
WThe DC-3 was one of several early design proposals for the NASA Space Shuttle designed by Maxime Faget at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in Houston. It was nominally developed by North American Aviation (NAA), although it was a purely NASA-internal design. Unlike the design that eventually emerged, the DC-3 was a fully reusable launch vehicle two-stage-to-orbit spaceplane design with a small payload capacity of about 12,000 lbs and limited maneuverability. Its inherent strengths were good low-speed handling during landing, and a low-risk development that was relatively immune to changes in weight and balance.
 W
WNova was a series of NASA rocket designs that were proposed both before and after the Saturn V rocket used in the Apollo program. Nova was NASA's first large launcher proposed in 1958 for missions similar to Saturn V was subsequently used for. The Nova and Saturn V designs closely mirrored each other in basic concept, power, size, and function. Differences were minor but practical, and the Saturn was ultimately selected for the Apollo Project, largely because it would reuse existing facilities to a greater extent and could make it to the pad somewhat earlier.
 W
WOmegA was a medium to heavy-lift launch vehicle concept that spent several years in development by Northrop Grumman during 2016–2020, with that development substantially funded by the U.S. government. OmegA was intended for launching U.S. national security satellites, as part of the U.S. Department of the Air Force National Security Space Launch (NSSL) replacement program.
 W
WThe Rockwell X-30 was an advanced technology demonstrator project for the National Aero-Space Plane (NASP), part of a United States project to create a single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) spacecraft and passenger spaceliner. Started in 1986, it was cancelled in the early 1990s before a prototype was completed, although much development work in advanced materials and aerospace design was completed. While a goal of a future NASP was a passenger liner capable of two-hour flights from Washington to Tokyo, the X-30 was planned for a crew of two and oriented towards testing.
 W
WRotary Rocket Company was a rocketry company that developed the Roton concept in the late 1990s as a fully reusable single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) crewed spacecraft. The design was initially conceived by Bevin McKinney, who shared it with Gary Hudson. In 1996, Rotary Rocket Company was formed to commercialize the concept. The Roton was intended to reduce costs of launching payloads into low earth orbit by a factor of ten.
 W
WThe Saturn C-3 was the third rocket in the Saturn C series studied from 1959 to 1962. The design was for a three-stage launch vehicle that could launch 45,000 kilograms (99,000 lb) to low Earth orbit and send 18,000 kilograms (40,000 lb) to the Moon via trans-lunar injection.
 W
WThe Saturn INT-20 was a proposed intermediate-payload follow-on from the Apollo Saturn V launch vehicle. A conical-form interstage would be fitted on top of the S-IC stage to support the S-IVB stage, so it could be considered either a retrofitted Saturn IB with a more powerful first stage, or a stubby, cut-down Saturn V without the S-II second stage.
 W
WThe Saturn-Shuttle was a preliminary concept of launching the Space Shuttle orbiter using a modified version of the first stage of the Saturn V rocket. It was studied and considered in 1971-1972.
 W
WThe Shuttle-C was a study by NASA to turn the Space Shuttle launch stack into a dedicated uncrewed cargo launcher. The Space Shuttle external tank and Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs) would be combined with a cargo module that take the place of the Shuttle orbiter and include the main engines. Various Shuttle-C concepts were investigated between 1984 and 1995.
 W
WSkybolt is a single stage space rocket designed and assembled by Starchaser Industries. It functions effectively as a scale model of Starchaser Industries' proposed Space Tourism Vehicle, "Thunderstar". Designed and built over 7 months and unveiled in 2006, Skybolt has yet to perform a full-scale test launch. Since 2007, Skybolt has been fitted to a custom mobile platform and tours the country with Starchaser's Educational Outreach Team.
 W
WThe Space Launch Initiative (SLI) was a NASA and U.S. Department of Defense joint research and technology project to determine the requirements to meet all the nation's hypersonics, space launch and space technology needs. It was also known as the 2nd Generation Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) program. The program began with the award of reusable launch vehicle study contracts in 2000.