 W
WThe Affero General Public License is a free software license. The first version of the Affero General Public License (AGPLv1), was published by Affero, Inc. in March 2002, and based on the GNU General Public License, version 2 (GPLv2). The second version (AGPLv2) was published in November 2007, as a transitional license to allow an upgrade path from AGPLv1 to the GNU Affero General Public License.
 W
WAlliance for Creativity and Entertainment (ACE) is a coalition launched on June 13, 2017 of over 30 major global entertainment companies and film studios aimed at protecting profits from copyrighted material.
 W
WComputer trespass is a computer crime in the United States involving unlawful access to computers. It is defined under the Computer Fraud and Abuse act.
 W
WCONTU, or the Commission on New Technological Uses of Copyrighted Works, was created to study issues associated with copyrighted works in computers and computer-related works. It was established in 1974 by the 93rd United States Congress for a period of three years as part of an effort to revise U.S. copyright law. The commission presented its final report on 31 July 1978. It recommended that computer programs be explicitly protected by copyright law. Its recommendations were largely implemented in the Computer Software Copyright Act of 1980 that became effective on December 12. It added a definition of the term "computer program" to 17 U.S.C. § 101 and amending § 117 to allow the owner of the program to make an additional copy or adaptation for use on a computer. It has been argued that the Commission erred in recommending the extension of copyright to machine-readable computer programs, because of the utility rule.
 W
WCreative Commons, since 2011, has created many "ports", or adaptions, of its licenses to make them compatible with the copyright legislation of various countries worldwide.
 W
WA Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work.
 W
W W
WeIDAS is an EU regulation on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Single Market. It was established in EU Regulation 910/2014 of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and repeals 1999/93/EC from 13 December 1999.
 W
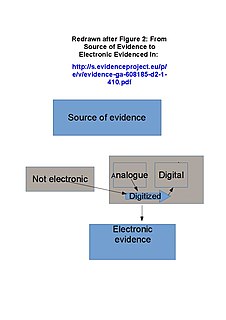
WElectronic evidence consists of these two sub-forms:analog, and digital evidence
 W
WThe Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act is a United States federal law passed by the U.S. Congress to facilitate the use of electronic records and electronic signatures in interstate and foreign commerce by ensuring the validity and legal effect of contracts entered into electronically. In 2010, both Houses of Congress passed a resolution at the request of industry leaders, recognizing June 30 as "National ESIGN Day."
 W
WEolas is a United States technology firm formed as a spin-off from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), in order to commercialize UCSF's patents for work done there by Eolas' co-founders. The company was founded in 1994 by Dr. Michael Doyle and three of his staff members from the UCSF Center for Knowledge Management. While the company has been labeled as a patent troll by accused infringers of those patents, this narrative has been characterized by recent commentators as political propaganda by big-tech, since Eolas was created at the request of UCSF, and was founded by the inventors on the university's patents.
 W
WExport of cryptographic technology and devices from the United States was severely restricted by U.S. law until 1992. The law gradually became eased until around 2000, but some restrictions still remain today.
 W
WGikII is a series of European conferences on the intersections between law, technology and popular culture. It is hosted at a different institution every year. The first conference was in 2006 and was held in Edinburgh, and was organised by Lilian Edwards and Andres Guadamuz.
 W
WThe GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is a free-software license published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). The license allows developers and companies to use and integrate a software component released under the LGPL into their own software without being required by the terms of a strong copyleft license to release the source code of their own components. However, any developer who modifies an LGPL-covered component is required to make their modified version available under the same LGPL license. For proprietary software, code under the LGPL is usually used in the form of a shared library, so that there is a clear separation between the proprietary and LGPL components. The LGPL is primarily used for software libraries, although it is also used by some stand-alone applications.
 W
WThe gpl-violations.org is a not-for-profit project founded and led by Harald Welte in 2004. It worked to make sure software licensed under the GNU General Public License was not used in ways prohibited by the license.
 W
WIn the context of patent law, using the Internet as a source of prior art when assessing whether an invention is novel and inventive, may be problematic if it is difficult to ascertain precisely when information on websites became available to the public.
 W
WLauri Love is a British activist previously wanted by the United States for his alleged activities with the hacker collective Anonymous.
 W
WThe Motion Picture Association (MPA) is an American trade association representing the five major film studios of the United States, as well as the video streaming service Netflix. Founded in 1922 as the Motion Picture Producers and Distributors of America (MPPDA) and known as the Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA) from 1945 until September 2019, its original goal was to ensure the viability of the American film industry. In addition, the MPA established guidelines for film content which resulted in the creation of the Motion Picture Production Code in 1930. This code, also known as the Hays Code, was replaced by a voluntary film rating system in 1968, which is managed by the Classification and Rating Administration (CARA).
 W
WNewzbin was a British Usenet indexing website, intended to facilitate access to content on Usenet. The site caused controversy over its stance on copyrighted material. Access to the Newzbin.com website was blocked by BT and Sky in late 2011, following legal action in the UK by Hollywood film studios.
 W
WThe Magna Carta for Philippine Internet Freedom is an internet law bill filed in the Congress of the Philippines. The bill contains provisions promoting civil and political rights and Constitutional guarantees for Philippine internet users, such as freedom of expression, as well as provisions on information and communications technology (ICT) policy, ICT4D, internet governance, e-governance, cybersecurity, cyberwarfare, cyberterrorism, and cybercrime.
 W
WA qualified website authentication certificate is a qualified digital certificate under the trust services defined in the eIDAS Regulation.
 W
WThere are a number of disputes concerning the Church of Scientology's attempts to suppress material critical of Scientology on the Internet, utilizing various methods – primarily lawsuits and legal threats, as well as front organizations. In late 1994, the Church of Scientology began using various legal tactics to stop distribution of unpublished documents written by L. Ron Hubbard. The Church of Scientology is often accused of barratry through the filing of SLAPP suits. The official church response is that its litigious nature is solely to protect its copyrighted works and the unpublished status of certain documents.
 W
WThe Principality of Sealand is an unrecognized micronation that claims HM Fort Roughs, an offshore platform in the North Sea approximately 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) off the coast of Suffolk, as its territory. Roughs Tower is a Maunsell Sea Fort that was built by the British during World War II. Since 1967, the decommissioned Roughs Tower has been occupied and claimed as a sovereign state by the family and associates of Paddy Roy Bates. Bates seized Roughs Tower from a group of pirate radio broadcasters in 1967 with the intention of setting up his own station there. Sealand was invaded by mercenaries in 1978, but was able to repel the attack.
 W
WUnited States v. Graham, 846 F. Supp. 2d 384, was a Maryland District Court case in which the Court held that historical cell site location data is not protected by the Fourth Amendment. Reacting to the precedent established by the recent Supreme Court case United States v. Jones in conjunction with the application of the third party doctrine, Judge Richard D. Bennett, found that "information voluntarily disclosed to a third party ceases to enjoy Fourth Amendment protection" because that information no longer belongs to the consumer, but rather to the telecommunications company that handles the transmissions records. The historical cell site location data is then not subject to the privacy protections afforded by the Fourth Amendment standard of probable cause, but rather to the Stored Communications Act, which governs the voluntary or compelled disclosure of stored electronic communications records.
 W
WThe Video Privacy Protection Act (VPPA) is a bill that was passed by the United States Congress in 1988 as Pub.L. 100–618 and signed into law by President Ronald Reagan. It was created to prevent what it refers to as "wrongful disclosure of video tape rental or sale records [or similar audio visual materials, to cover items such as video games and the future DVD format]." Congress passed the VPPA after Robert Bork's video rental history was published during his Supreme Court nomination. It makes any "video tape service provider" that discloses rental information outside the ordinary course of business liable for up to $2500 in actual damages.
 W
WA warrant canary is a method by which a communications service provider aims to inform its users that the provider has been served with a government subpoena despite legal prohibitions on revealing the existence of the subpoena. The warrant canary typically informs users that there has not been a court-issued subpoena as of a particular date. If the canary is not updated for the period specified by the host or if the warning is removed, users are to assume that the host has been served with such a subpoena. The intention is for a provider to warn users of the existence of a subpoena passively while possibly "technically" not violating a court order not to do so.