 W
WHeinrich Luitpold Himmler was Reichsführer of the Schutzstaffel, and a leading member of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of the Holocaust.
 W
WThe Ahnenerbe operated as a think tank in Nazi Germany between 1935 and 1945. Heinrich Himmler, the Reichsführer-SS, established it as an SS appendage devoted to the task of promoting the racial doctrines espoused by Adolf Hitler and his governing Nazi Party, specifically by supporting the idea that the modern Germans descended from an ancient Aryan race seen as biologically superior to other racial groups. The group comprised scholars and scientists from a broad range of academic disciplines.
 W
WThe Upper Rhine High Command, also incorrectly referred to as Army Group Upper Rhine, was a short-lived headquarters unit of the German Armed Forces (Wehrmacht) created on the Western Front during World War II. The Upper Rhine High Command was formed on 26 November 1944 and deactivated on 25 January 1945. The sole commander of this headquarters unit was Heinrich Himmler.
 W
WHugo Johannes Blaschke was a German dental surgeon notable for being Adolf Hitler's personal dentist from 1933 to April 1945 and for being the chief dentist on the staff of Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler.
 W
WViktor Hermann Brack was a member of the Schutzstaffel (SS) and a convicted Nazi war criminal, who was one of the prominent organisers of the euthanasia programme Action T4; this Nazi initiative resulted in the systematic murder of over 70,000 disabled German and Austrian people. He held various positions of responsibility in Hitler's Chancellery in Berlin. Following his role in the T4 programme, Brack was one of the men identified as responsible for the gassing of Jews in extermination camps, having conferred with Odilo Globočnik about its use in the practical implementation of the Final Solution. Brack was sentenced to death in 1947 and executed by hanging in 1948.
 W
WThe Decent One is a 2014 German-Austrian-Israeli documentary directed by Vanessa Lapa about Heinrich Himmler. The film was based on a cache of letters and diary entries that were purchased by Lapa's parents and published in the German newspaper Die Welt. It premiered at the Berlin International Film Festival and received mixed reviews.
 W
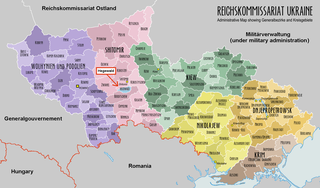
WThe Deutsche Volksliste, a Nazi Party institution, aimed to classify inhabitants of Nazi-occupied territories (1939-1945) into categories of desirability according to criteria systematised by Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler. The institution originated in occupied western Poland. Similar schemes subsequently developed in Occupied France (1940-1944) and in the Reichskommissariat Ukraine (1941-1944).
 W
WHans Otto Georg Hermann Fegelein was a high-ranking commander in the Waffen-SS of Nazi Germany. He was a member of Adolf Hitler's entourage and brother-in-law to Eva Braun through his marriage to her sister Gretl.
 W
WThe Generalplan Ost, abbreviated GPO, was the Nazi German government's plan for the genocide and ethnic cleansing on a vast scale, and colonization of Central and Eastern Europe by Germans. It was to be undertaken in territories occupied by Germany during World War II. The plan was attempted during the war, resulting indirectly and directly in the deaths of millions by shootings, starvation, disease, extermination through labor, and genocide. But its full implementation was not considered practicable during the major military operations, and was prevented by Germany's defeat.
 W
WThe Geheime Staatspolizei, abbreviated Gestapo, was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
 W
WHegewald was a short-lived German colony during World War II, situated near Zhytomyr in Reichskommissariat Ukraine. It was repopulated in late 1942 and early 1943 by ethnically German settlers classified as Volksdeutsche transferred from occupied territories of Poland, Croatia, Bessarabia, and the Soviet Union to an area earmarked for the projected Germanization of the Ukrainian lands. The plans were prepared months in advance by the SS, RKFDV and VoMi, but major problems with supplies occurred right from the region's initial establishment. Heinrich Himmler's original plans to recruit settlers from Scandinavia and the Netherlands were unsuccessful.
 W
WErhard Heiden was an early member of the Nazi Party and the third commander of the Schutzstaffel (SS), the paramilitary wing of the Sturmabteilung. He was appointed head of the SS, an elite subsection of the SA in 1927. At that time the SS numbered less than a thousand men and Heiden found it difficult to cope under the much larger SA. Heiden was not a success in the post, and SS membership dropped significantly under his leadership. He was dismissed from his post in 1929, officially for "family reasons". He was arrested after the Nazis came to power in 1933 and executed that same year.
 W
WHHhH is the debut novel of French author Laurent Binet, published in 2010 by Grasset & Fasquelle. The book recounts Operation Anthropoid, the assassination of Nazi leader Reinhard Heydrich in Prague during World War II. The novel was awarded the 2010 Prix Goncourt du Premier Roman.
 W
WZamość is a historical city in southeastern Poland. It is situated in the southern part of Lublin Voivodeship, about 90 km (56 mi) from Lublin, 247 km (153 mi) from Warsaw. In 2014, the population was 65,149.
 W
WThe ideology of the Schutzstaffel , a paramilitary force and instrument of terror of the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, emphasized a racist vision of "racial purity", primarily based on antisemitism and loyalty to Adolf Hitler and Nazi Germany.
 W
WJulleuchter or Turmleuchter are modern terms used to describe a type of earthenware candle-holder designed and manufactured in Nazi Germany.
 W
WErnst Kaltenbrunner was a high-ranking Austrian SS official during the Nazi era and a major perpetrator of the Holocaust. He was the subsequent Chief of the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA), which included the offices of Gestapo, Kripo, and SD, from January 1943 until the end of World War II in Europe.
 W
WLebensborn e.V. was an SS-initiated, state-supported, registered association in Nazi Germany with the goal of raising the birth rate of Aryan children of persons classified as 'racially pure' and 'healthy' based on Nazi racial hygiene and health ideology. Lebensborn provided welfare to its mostly unmarried mothers, encouraged anonymous births by unmarried women at their maternity homes, and mediated adoption of these children by likewise 'racially pure' and 'healthy' parents, particularly SS members and their families. The Cross of Honour of the German Mother was given to the women who bore the most Aryan children. Abortion was legalised by the Nazis for disabled and non-Germanic children, but strictly punished otherwise.
 W
WOperation Northwind was the last major German offensive of World War II on the Western Front. It began on 31 December 1944 in Rhineland-Palatinate, Alsace and Lorraine in southwestern Germany and northeastern France, and ended on 25 January 1945. The German offensive was an operational failure, with its main objectives not achieved.
 W
WOperation Himmler, also called Operation Konserve or Operation Canned Goods, was a 1939 false flag project planned by Nazi Germany to create the appearance of Polish aggression against Germany. That was then used by the Germans to justify their invasion of Poland.
 W
WOperation Reinhard or Operation Reinhardt was the codename of the secretive German plan in World War II to exterminate Polish Jews in the General Government district of German-occupied Poland. This deadliest phase of the Holocaust was marked by the introduction of extermination camps.
 W
WFranz Pfeffer von Salomon during the Nazi regime known as Franz von Pfeffer, was the first Supreme Leader of the Sturmabteilung (SA) after its re-establishment in 1925. Pfeffer resigned from his SA command in 1930 and was expelled from the Nazi Party in 1941. He died in 1968.
 W
WThe Posen speeches were two speeches made by Heinrich Himmler, the head of the SS of Nazi Germany, on 4 and 6 October 1943 in the town hall of Posen (Poznań), in German-occupied Poland. The recordings are the first known documents in which a member of the Hitler Cabinet spoke of the ongoing extermination of the Jews in extermination camps. They demonstrate that the German government wanted, planned and carried out the Holocaust.
 W
WThe Reich Central Office for the Combating of Homosexuality and Abortion was the central instrument of Nazi Germany for the fight against homosexuality in Nazi Germany and the fight against abortion.
 W
WReichsführer-SS was a special title and rank that existed between the years of 1925 and 1945 for the commander of the Schutzstaffel (SS). Reichsführer-SS was a title from 1925 to 1933, and from 1934 to 1945 it was the highest rank of the SS. The longest-serving and most noteworthy office holder was Heinrich Himmler.
 W
WThe Schutzstaffel was a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, and later throughout German-occupied Europe during World War II. It began with a small guard unit known as the Saal-Schutz made up of party volunteers to provide security for party meetings in Munich. In 1925, Heinrich Himmler joined the unit, which had by then been reformed and given its final name. Under his direction (1929–1945) it grew from a small paramilitary formation during the Weimar Republic to one of the most powerful organizations in Nazi Germany. From the time of the Nazi Party's rise to power until the regime's collapse in 1945, the SS was the foremost agency of security, surveillance, and terror within Germany and German-occupied Europe.
 W
WThe SS Race and Settlement Main Office was the organization responsible for "safeguarding the racial 'purity' of the SS" within Nazi Germany.