 W
WThe Landing at Barcelona was a failed Allied attempt in May 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession to capture the city of Barcelona from its Spanish pro-Bourbon defenders.
 W
WThe siege of Barcelona took place between 14 September and 19 October 1705 during the War of the Spanish Succession when a multinational Grand Alliance army led by Lord Peterborough, supporting the Habsburg pretender to the Spanish throne, captured the city of Barcelona from its Spanish Bourbonic defenders, most of whom then joined the Habsburg army.
 W
WThe Siege of Barcelona took place between 3 and 27 April 1706 during the War of the Spanish Succession when a Franco-Spanish army laid siege to Barcelona in an attempt to recapture the city following its fall to an English-led Allied army the previous year.
 W
WThe siege of Belgrade was a successful attempt by Imperial Habsburg troops under the command of the Elector of Bavaria Maximilian II Emanuel to capture the city of Belgrade from the Ottoman Empire. The capture took place on 6 September 1688, after a month of siege, during the Great Turkish War (1683–1699). By conquering Belgrade, the Imperialists gained an important strategic outpost, as the city had been the Ottoman's chief fortress in Europe, for more than a century and a half. The Turks recaptured it two years later only to lose it again to Eugene of Savoy in 1717.
 W
WThe siege of Belgrade was a successful attempt by Austrian troops under the command of Prince Eugene of Savoy to capture the strategically important city of Belgrade from the Ottoman Empire. It took place during the Seventh Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–1718), barely a year after the Austrian victory at the Battle of Petrovaradin (Peterwardein). The Austrians routed the Ottoman relief army under Grand Vizier Hacı Halil Pasha on 16 August. As a consequence, the Belgrade garrison, deprived of relief, surrendered to the Austrians on 21 August. The Ottoman Sultan Ahmed III sued for peace, resulting in the Treaty of Passarowitz a year later, which completed the transfer of the remainder of Hungary, the Banat and the city of Belgrade into Austrian hands.
 W
WThe capture of Belgrade was the recapture of Belgrade by the Ottoman Empire in 1739.
 W
WThe Siege of Brussels took place between January and February 1746 during the War of the Austrian Succession. A French army under the overall command of Maurice de Saxe, in a bold and innovative winter campaign besieged and captured the city of Brussels, which was then the capital of the Austrian Netherlands, from its Austrian garrison.
 W
WThe Siege of Gaeta was a siege during the War of Polish Succession fought at Gaeta, Italy. The Habsburgs at Gaeta withstood four months of siege from the Bourbon armies under the Duke of Parma.
 W
WIn the Siege of Hüningen, the Austrians captured the city from the French. Hüningen is in the present-day Department of Haut-Rhin, France. Its fortress lay approximately 2.5 miles (4.0 km) north of the Swiss city of Basel and .5 miles (0.80 km) north of the spot where the present-day borders of Germany, France and Switzerland meet. During the time of this siege, the village was part of the Canton of Basel City and the fortress lay in area contested between the German states and the First French Republic.
 W
WThe siege of Kehl lasted from 26 October 1796 to 9 January 1797. Habsburg and Württemberg regulars numbering 40,000, under the command of Maximilian Anton Karl, Count Baillet de Latour, besieged and captured the French-controlled fortifications at the village of Kehl in the German state of Baden-Durlach. The fortifications at Kehl represented important bridgehead crossing the Rhine to Strasbourg, an Alsatian city, a French Revolutionary stronghold. This battle was part of the Rhine Campaign of 1796, in the French Revolutionary War of the First Coalition.
 W
WThe Siege of Kehl was one of the opening moves of the French Rhineland campaign in the War of the Polish Succession, at the fortress town of Kehl in the upper Rhine River valley. A large French army under the command of the Duke of Berwick besieged and captured the fortress, which was lightly garrisoned and in poor condition.
 W
WIn the siege of Khotyn a Habsburg Austrian army led by Prince Josias of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld and an Imperial Russian army commanded by Ivan Saltykov besieged an Ottoman Turkish garrison in the fortress of Khotyn. The Allies eventually forced the surrender of the fortress. The siege was part of the Russo-Turkish War.
 W
WThe siege of Le Quesnoy saw a force made up of Habsburg Austrians and French Royalists led by François Sébastien Charles Joseph de Croix, Count of Clerfayt lay siege to a Republican French garrison commanded by François Goullus. After two and a half week siege, the French capitulated after suffering heavy losses. The War of the First Coalition operation was fought at Le Quesnoy, located near the border with Belgium about 27 kilometres (17 mi) west of Maubeuge.
 W
WThe Siege of Lille saw a Republican French garrison under Jean-Baptiste André Ruault de La Bonnerie hold Lille against an assault by a Habsburg army commanded by Duke Albert of Saxe-Teschen. Though the city was fiercely bombarded, the French successfully withstood the Austrian attack in the action. Because the Austrians were unable to completely encircle the city, the French were able to continuously send in reinforcements. After news of the French victory over the Prussians at Valmy, Albert withdrew his troops and siege cannons. The next battle was at Jemappes in November. The Column of the Goddess monument was completed in 1845 to commemorate the siege.
 W
WThe siege of Luxembourg was a siege by France of the Habsburg-held Fortress of Luxembourg that lasted from 1794 until 7 June 1795, during the French Revolutionary Wars. Although the French army failed to breach the walls of the city, which were renowned as amongst the best in the world, the fortress was forced to surrender after more than seven months.
 W
WIn the siege of Mainz, from 14 April to 23 July 1793, a coalition of Prussia, Austria, and other German states led by the Holy Roman Empire besieged and captured Mainz from revolutionary French forces. The allies, especially the Prussians, first tried negotiations, but this failed, and the bombardment of the city began on the night of 17 June.
 W
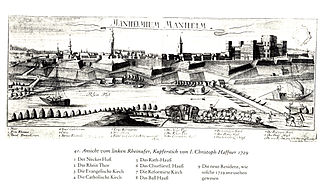
WThe action at Mannheim began in April 1795 when two French armies crossed the Rhine and converged on the confluence of the Main and the Rhine. Initial action at Mannheim resulted in a minor skirmish, but the Bavarian commander negotiated a quick truce with the French and withdrew. On 17 October 1795, 17,000 Habsburg Austrian troops under the command of Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser engaged 12,000 soldiers, led by Jean-Charles Pichegru in the grounds outside the city of Mannheim. In a combination of maneuvers, the Habsburg army forced 10,000 of the French forces to withdraw into the city itself; other French troops fled to join neighboring Republican armies. First Coalition forces then laid siege to Mannheim. Subsequent action at neighboring cities forced the French to withdraw further westward toward France; after a month's siege, the 10,000-strong Republican French garrison now commanded by Anne Charles Basset Montaigu surrendered to 25,000 Austrians commanded by Wurmser. This surrender brought the 1795 campaign in Germany to an end. The battle and siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Situated on the Rhine River at its confluence with the Neckar River, Mannheim lies in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg in modern-day Germany.
 W
WDuring the siege of Mantua, which lasted from 4 July 1796 to 2 February 1797 with a short break, French forces under the overall command of Napoleon Bonaparte besieged and blockaded a large Austrian garrison at Mantua for many months until it surrendered. This eventual surrender, together with the heavy losses incurred during four unsuccessful relief attempts, led indirectly to the Austrians suing for peace in 1797. The siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, which is part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Mantua, a city in the Lombardy region of Italy, lies on the Mincio River.
 W
WThe Siege of Philippsburg was conducted by French forces against forces in the fortress of Philippsburg in the Rhine River valley during the War of the Polish Succession. The Duke of Berwick led 100,000 men up the Rhine Valley in opposition to Austrian forces, of which 60,000 were detached to invest the fortress at Philippsburg, beginning on 1 June 1734. A relief column of 35,000 under the aging Prince Eugene of Savoy was unsuccessful in actually relieving the siege. On 12 June Berwick was killed by a cannonball while inspecting the trenches, and command of the besiegers fell to Marshals d'Asfeld and Noailles. The fortress surrendered one month later, and the garrison withdrew to the fortress of Mainz with the honours of war.
 W
WThe Siege of Pizzighettone was the first major military engagement of the northern Italian campaigns of the War of the Polish Succession. Troops from France and the Kingdom of Sardinia began blockading the Habsburg Milanese fortress at Pizzighettone on 11 November 1733, commencing siege operations on 15 November. On 30 November the commander of the Austrian garrison negotiated a capitulation in which he promised to withdraw toward Mantua on 9 December if no relief arrived. As no reinforcements appeared by that time, the fortress' garrison withdrew with full honors on 9 December.
 W
WThe Siege of Ragusa or Siege of Dubrovnik was fought between local Ragusan insurgents, as well as Austrian Croat troops and the British Royal Navy under Captain William Hoste against a French garrison under Joseph de Montrichard between 19 and 27 January 1814 during the Adriatic campaign of the Napoleonic Wars. The siege was fought on the coast of the Adriatic Sea for possession of the strategically important fortified town of Ragusa.
 W
WThe siege of Temeşvar took place from 31 August to 12 October 1716 during the Austro-Turkish War of 1716-1718. The Habsburg army led by Prince Eugene of Savoy, who had just won a crushing victory at Petrovaradin, managed to capture the fortress of Temeşvar an Ottoman stronghold since 1552, the capital of the Banat and the last Turkish stronghold in Hungary. The garrison capitulated after a 43 days siege. The city remained under military administration until 6 June 1778, when it was handed over to the administration of the Kingdom of Hungary.
 W
WThe Siege of Toulon took place between 29 July to 21 August 1707 during the War of the Spanish Succession, when a combined Savoyard-Imperial army supported by a British naval force, attacked the French base at Toulon.
 W
WThe Siege of Trarbach was conducted during the War of the Polish Succession by French troops against a garrison of troops of the Holy Roman Empire in the fortress at Trarbach in the County of Sponheim, a small principality of the Holy Roman Empire. The French, led by Marshal Belle-Isle, were victorious, and destroyed the fortress.
 W
WThe siege of Turin took place from June to September 1706, during the War of the Spanish Succession, when a French army led by Louis de la Feuillade besieged the Savoyard capital of Turin. The campaign by Prince Eugene of Savoy that led to its relief has been called the most brilliant of the war in Italy. The siege is also famous for the death of Piedmontese hero Pietro Micca.
 W
WThe siege of Vienna, in 1529, was the first attempt by the Ottoman Empire to capture the city of Vienna, Austria. Suleiman the Magnificent, sultan of the Ottomans, attacked the city with over 100,000 men, while the defenders, led by Niklas Graf Salm, numbered no more than 21,000. Nevertheless, Vienna was able to survive the siege, which ultimately lasted just over two weeks, from 27 September to 15 October 1529.
 W
WThe Siege of Ypres saw a Republican French army commanded by Jean-Charles Pichegru invest the fortress of Ypres and its 7,000-man garrison composed of Habsburg Austrians under Paul von Salis and Hessians led by Heinrich von Borcke and Georg von Lengerke. French troops under Joseph Souham fended off three relief attempts by the corps of François Sébastien Charles Joseph de Croix, Count of Clerfayt. Meanwhile, the French besiegers led by Jean Victor Marie Moreau compelled the Coalition defenders to surrender the city. The fighting occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the Wars of the French Revolution. In 1794 Ypres was part of the Austrian Netherlands, but today it is a municipality in Belgium, located about 120 kilometres (75 mi) west of Brussels.