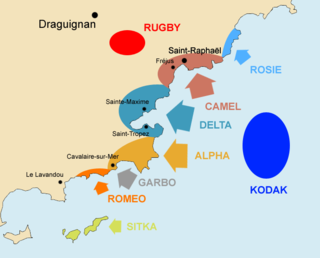
 W
WThe British 2nd Parachute Brigade was part of the Operation Rugby airborne landings in August 1944. The operation was carried out by an ad hoc airborne formation called the 1st Airborne Task Force. Operation Rugby was itself part of the Operation Dragoon invasion of Southern France by the American 7th Army. The airborne task force landed in the River Argens valley with the objective of preventing German reinforcements from reaching the landing beaches. The landings were mainly an American operation and the brigade was the only British Army formation involved.
 W
WThe 6th Airborne Division advance to the River Seine occurred in August 1944, in the later stages of the Battle of Normandy, following the German Army's defeat in the Falaise Pocket, during the Second World War.
 W
WThe Second Battle of the Alps was a military campaign fought between combined German and Italian Social Republic forces, and the re-established French Republic led by Charles de Gaulle.
 W
WThe siege of Breslau, also known as the Battle of Breslau, was a three-month-long siege of the city of Breslau in Lower Silesia, Germany, lasting to the end of World War II in Europe. From 13 February 1945 to 6 May 1945, German troops in Breslau were besieged by the Soviet forces which encircled the city as part of the Lower Silesian Offensive Operation. The German garrison's surrender on 6 May was followed by the surrender of all German forces two days after the battle.
The siege of Budapest or Battle of Budapest was the 50-day-long encirclement by Soviet and Romanian forces of the Hungarian capital of Budapest, near the end of World War II. Part of the broader Budapest Offensive, the siege began when Budapest, defended by Hungarian and German troops, was encircled on 26 December 1944 by the Red Army and the Romanian Army. During the siege, about 38,000 civilians died through starvation or military action. The city unconditionally surrendered on 13 February 1945. It was a strategic victory for the Allies in their push towards Berlin.
 W
WThe German occupation of Czechoslovakia (1938–1945) began with the German annexation of the Sudetenland in 1938, continued with the March 1939 invasion of the Czech lands and creation of the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, and by the end of 1944 extended to all parts of the former Czechoslovakia.
 W
WThe Defence of the Reich is the name given to the strategic defensive aerial campaign fought by the Luftwaffe air arm of the combined Wehrmacht armed forces of Nazi Germany over German-occupied Europe and Nazi Germany during World War II. Its aim was to prevent the destruction of German civilians, military and civil industries by the Western Allies. The day and night air battles over Germany during the war involved thousands of aircraft, units and aerial engagements to counter the Allied strategic bombing campaign. The campaign was one of the longest in the history of aerial warfare and with the Battle of the Atlantic and the Allied Blockade of Germany was the longest of the war. The Luftwaffe fighter force defended the airspace of German-occupied territory against attack, first by RAF Bomber Command and then against the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF).
 W
WThe Siege of Dunkirk in World War II began in September 1944, when Allied units of the Second Canadian Division surrounded the fortified city and port of Dunkirk. The siege lasted until after the official end of the war in Europe. German units within the fortress withstood probing attacks and as the opening of the port of Antwerp was more important, the 21st Army Group commander, Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery, decided to contain but not capture Dunkirk with the 1st Czechoslovak Armoured Brigade. The fortress, commanded by Admiral Friedrich Frisius, eventually surrendered unconditionally to Brigadier General Alois Liška, the commander of the Czechoslovak brigade group, on 9 May 1945, a day after the surrender of Nazi Germany took effect.
 W
WThe Georgian uprising on Texel was an insurrection by the 882nd Infantry Battalion Königin Tamara of the Georgian Legion of the German Army stationed on the German-occupied Dutch island of Texel. The battalion was made up of 800 Georgians and 400 Germans, with mainly German officers. It was one of the last battles in the European theatre.
 W
WThe German invasion of Luxembourg was part of Case Yellow, the German invasion of the Low Countries—Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands—and France during World War II. The battle began on 10 May 1940 and lasted just one day. Facing only light resistance, German troops quickly occupied Luxembourg. The Luxembourgish government, and Grand Duchess Charlotte, managed to escape the country and a government-in-exile was created in London.
 W
WThe fall of Denmark in April 1940 left the Danish colony of Greenland an unoccupied territory of an occupied nation, under the possibility of seizure by the United Kingdom or Canada. To forestall this, the United States acted to guarantee Greenland's position. However, with the entrance of the United States into the war in December 1941, Greenland became a combatant.
 W
WOperation Konrad III was a German military offensive on the Eastern Front of the Second World War. It was the third and most ambitious of the three Konrad Operations and had the objective of relieving the siege of Budapest and recapturing the entire Transdanubia region. Achieving complete surprise, the German offensive began on 18 January 1945. Supported by the Luftwaffe, the IV SS Panzer Corps, the principal German attack formation, overran the Soviet 4th Guards Army in two days, destroying hundreds of Soviet tanks along the way, reached the Danube river on 19 January and recaptured 400 square kilometers of territory in four days. After nine days of combat, and the destruction by the SS of two-thirds of Soviet tanks in the entire 3rd Ukrainian Front, the German offensive was stopped by Soviet reinforcements 25 kilometers short of Budapest on 26 January.
 W
WThe 872-day siege of Leningrad, Russia, resulted from the failure of the German Army Group North to capture Leningrad in the Eastern Front during World War II. The siege lasted from September 8, 1941, to January 27, 1944, and was one of the longest and most destructive sieges in history, devastating the city of Leningrad.
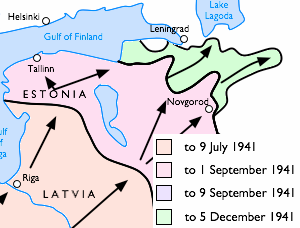 W
WLeningrad strategic defensive operation is the term in Soviet historiography for the defensive operations in the area south of Leningrad by the Red Army and the Soviet Navy during World War II from 10 July to 30 September 1941. The following operations are considered as part of the strategic operation:Kingisepp–Luga defensive 10 July – 23 September 1941 Soltsy–Dno offensive 14–22 July 1941 Tallinn defensive 5– 28 August 1941 Staraya–Russa offensive 8–23 August 1941 Demyansk defensive 6–26 September 1941
 W
WThe siege of Leningrad was a prolonged military blockade undertaken from the south by the Army Group North of Nazi Germany against the Soviet city of Leningrad on the Eastern Front in World War II. The Finnish army invaded from the north, co-operating with the Germans until Finland had recaptured territory lost in the recent Winter War, but refused to make further approaches to the city. Also co-operating with the Germans after August 1942 was the Spanish Blue Division. It was transferred to the southeastern flank of the siege of Leningrad, just south of the Neva near Pushkin, Kolpino and its main intervention was in Krasny Bor in the Izhora River area.
 W
WThe North African campaign of the Second World War took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943. It included campaigns fought in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts and in Morocco and Algeria, as well as Tunisia.
 W
WThe Continuation War, also known as Second Soviet-Finnish war, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany, against the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1941 to 1944, as a part of World War II. In Soviet historiography, the war was called the Finnish Front of the Great Patriotic War. Germany regarded its operations in the region as part of its overall war efforts on the Eastern Front and provided Finland with critical material support and military assistance, including economic aid.
 W
WOperation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 with the Normandy Landings (D-Day). A 1,200-plane airborne assault preceded an amphibious assault involving more than 5,000 vessels. Nearly 160,000 troops crossed the English Channel on 6 June, and more than two million Allied troops were in France by the end of August.
 W
WThe Prague uprising of 1945 was a partially successful attempt by the Czech resistance to liberate the city of Prague from German occupation during World War II. The preceding six years of occupation had fuelled anti-German sentiment and the approach of the Soviet Red Army and the US Third Army offered a chance of success.
 W
WThe Raid on Santorini took place on 24 April 1944 as part of the Mediterranean Campaign in World War II. It was conducted by the British Special Boat Service, against the mixed German and Italian garrison on the island of Santorini (Thera) in the Aegean Sea. The raid was made in tandem with similar operations at the islands of Ios, Mykonos and Amorgos that aimed to destroy Axis naval observation posts and radio stations on the Cycladic islands.
 W
WThe siege of Sevastopol also known as the defence of Sevastopol or the Battle of Sevastopol was a military engagement that took place on the Eastern Front of the Second World War. The campaign was fought by the Axis powers of Germany and Romania against the Soviet Union for control of Sevastopol, a port in the Crimea on the Black Sea. On 22 June 1941 the Axis invaded the Soviet Union during Operation Barbarossa. Axis land forces reached the Crimea in the autumn of 1941 and overran most of the area. The only objective not in Axis hands was Sevastopol. Several attempts were made to secure the city in October and November 1941. A major attack was planned for late November, but heavy rains delayed it until 17 December 1941. Under the command of Erich von Manstein, Axis forces were unable to capture Sevastopol during this first operation. Soviet forces launched an amphibious landing on the Crimean peninsula at Kerch in December 1941 to relieve the siege and force the Axis to divert forces to defend their gains. The operation saved Sevastopol for the time being, but the bridgehead in the eastern Crimea was eliminated in May 1942.
 W
WThe Allied invasion of Sicily, codenamed Operation Husky, was a major campaign of World War II, in which the Allies took the island of Sicily from the Axis powers. It began with a large amphibious and airborne operation, followed by a six-week land campaign, and initiated the Italian Campaign.
 W
WThe Slovak National Uprising was an armed insurrection organized by the Slovak resistance movement during World War II. This resistance movement was represented mainly by the members of the Democratic Party, but also by social democrats and Communists, albeit on a smaller scale. It was launched on 29 August 1944 from Banská Bystrica in an attempt to resist German troops that had occupied Slovak territory and to overthrow the collaborationist government of Jozef Tiso. Although the resistance was largely defeated by German forces, guerrilla operations continued until the Red Army, Czechoslovak Army and Romanian Army liberated Fascist Slovakia in 1945.
 W
WThe spring 1945 offensive in Italy, codenamed Operation Grapeshot, was the final Allied attack during the Italian Campaign in the final stages of the Second World War. The attack into the Lombard Plain by the 15th Allied Army Group started on 6 April 1945 and ended on 2 May with the surrender of German forces in Italy.
 W
WThe surrender of Major General Botho Elster and more than 19,000 German soldiers to the United States Army during World War II took place on 17 September 1944 at Beaugency, France. Elster and his soldiers were attempting to escape from France which was rapidly being freed from occupation by Nazi Germany by Allied military forces. With his escape route to Germany cut off by Allied armies, surrounded by French Resistance fighters, and attacked by Allied air forces, Elster negotiated a surrender to the United States Army. Members of the French Resistance criticized the surrender as it did not give credit to the Resistance for its contribution to Elster's surrender.
 W
WThe Raid on Symi also known as Operation Tenement took place from 13 to 15 July 1944 as part of the Mediterranean Campaign in World War II. The action was a combined operation conducted by two Allied special forces, the British Special Boat Service and the Greek Sacred Band, who raided the German and Italian garrisons at the island of Symi in the Aegean Sea.
 W
WThe siege of Tobruk lasted for 241 days in 1941, after Axis forces advanced through Cyrenaica from El Agheila in Operation Sonnenblume against Allied forces in Libya, during the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) of the Second World War. In late 1940, the Allies had defeated the Italian 10th Army during Operation Compass (9 December 1940 – 9 February 1941) and trapped the remnants at Beda Fomm. During early 1941, much of the Western Desert Force (WDF) was sent to the Greek and Syrian campaigns. As German troops and Italian reinforcements reached Libya, only a skeleton Allied force remained, short of equipment and supplies.
 W
WOperation Waldfest was a Nazi German scorched earth operation and counter measure to French resistance activity in the Vosges mountains of German-occupied France during World War II. It was carried out in two stages, between September and November 1944, by units of the Wehrmacht and Allgemeine SS. The operations aim was to counter the Allied Operation Loyton, to disrupt the local French resistance, the Maquis, to destroy local villages in order to prevent them serving as shelter for Allied forces in the upcoming winter and to deport all men of fighting age in the area to Germany as forced labour.