 W
WThe Achaean War of 146 BC was fought between the Roman Republic and the Greek Achaean League, an alliance of Achaean and other Peloponnesian states in ancient Greece. It was the final stage of Rome's conquest of mainland Greece, taking place just after the Fourth Macedonian War.
 W
WThe Aetolian War was fought between the Romans and their Achaean and Macedonian allies, and the Aetolian League and their allies the kingdom of Athamania. The Aetolians had invited Antiochus III the Great to Greece, who came, but after his defeat by the Romans returned to Asia. This left the Aetolians and the Athamanians without any allies. With Antiochus out of Europe the Romans and their allies attacked the Aetolians. After a year of fighting the Aetolians were defeated and forced to pay 1,000 talents of silver to the Romans.
 W
WThe Bastarnae and Peucini were two ancient peoples who between 200 BC and 300 AD inhabited areas north of the Roman frontier on the Lower Danube. The Bastarnae lived in the region between the Carpathian Mountains and the river Dnieper, to the north and east of ancient Dacia. The Peucini occupied the region north of the Danube Delta.
 W
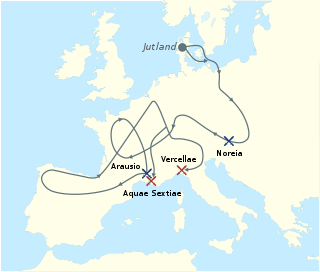
WThe Cimbrian or Cimbric War was fought between the Roman Republic and the Germanic and Celtic tribes of the Cimbri and the Teutons, Ambrones and Tigurini, who migrated from the Jutland peninsula into Roman controlled territory, and clashed with Rome and her allies. The Cimbrian War was the first time since the Second Punic War that Italia and Rome itself had been seriously threatened.
 W
WThe First Punic War was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated.
 W
WThe Galatian War was a war between the Galatian Gauls and the Roman Republic supported by their allies Pergamum in 189 BC. The war was fought in Galatia in central Asia Minor, in present-day Turkey.
 W
WThe Jugurthine War was an armed conflict between the Roman Republic and king Jugurtha of Numidia, a kingdom on the north African coast approximating to modern Algeria. Jugurtha was the nephew and adopted son of Micipsa, King of Numidia, whom he succeeded on the throne, overcoming his rivals through assassination, war, and bribery.
 W
WThe (Second) Latin War was a conflict between the Roman Republic and its neighbors, the Latin peoples of ancient Italy. It ended in the dissolution of the Latin League and incorporation of its territory into the Roman sphere of influence, with the Latins gaining partial rights and varying levels of citizenship.
 W
WThe Latin War was a war fought between the Roman Republic and the Latin League from 498 BC to 493 BC.
 W
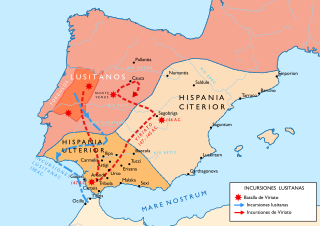
WThe Lusitanian War, called Pyrinos Polemos in Greek, was a war of resistance fought by the Lusitanian tribes of Hispania Ulterior against the advancing legions of the Roman Republic from 155 to 139 BC. The Lusitanians revolted in 155 BC, and again in 146 BC and were pacified. In 154 BC, a long war in Hispania Citerior, known as the Numantine War, was begun by the Celtiberians. It lasted until 133 and is an important event in the integration of what would become Portugal into the Roman and Latin-speaking world.
 W
WThe First Macedonian War was fought by Rome, allied with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate.
 W
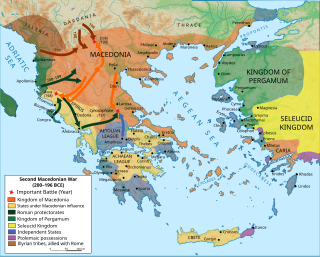
WThe Second Macedonian War was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. During their intervention, although the Romans declared the "freedom of the Greeks" against the rule from the Macedonian kingdom, the war marked a significant stage in increasing Roman intervention in the affairs of the eastern Mediterranean, which would eventually lead to Rome's conquest of the entire region.
 W
WThe Fourth Macedonian War was fought between Macedon, led by the pretender Andriscus, and the Roman Republic. It was the last of the Macedonian Wars, and was the last war to seriously threaten Roman control of Greece until the First Mithridatic War sixty years later.
 W
WThe Macedonian Wars were a series of conflicts fought by the Roman Republic and its Greek allies in the eastern Mediterranean against several different major Greek kingdoms. They resulted in Roman control or influence over Greece and the rest of the eastern Mediterranean basin, in addition to their hegemony in the western Mediterranean after the Punic Wars. Traditionally, the "Macedonian Wars" include the four wars with Macedonia, in addition to one war with the Seleucid Empire, and a final minor war with the Achaean League. The most significant war was fought with the Seleucid Empire, while the war with Macedonia was the second, and both of these wars effectively marked the end of these empires as major world powers, even though neither of them led immediately to overt Roman domination. Four separate wars were fought against the weaker power, Macedonia, due to its geographic proximity to Rome, though the last two of these wars were against haphazard insurrections rather than powerful armies. Roman influence gradually dissolved Macedonian independence and digested it into what was becoming a leading empire. The outcome of the war with the now-deteriorating Seleucid Empire was ultimately fatal to it as well, though the growing influence of Parthia and Pontus prevented any additional conflicts between it and Rome.
 W
WThe First Mithridatic War was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule were led by Mithridates VI of Pontus against Rome and the allied Kingdom of Bithynia. The war lasted five years and ended in a Roman victory which forced Mithridates to abandon all of his conquests and return to Pontus. The conflict with Mithridates VI later resumed in two further Mithridatic Wars.
 W
WThe Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by Rome against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 BC and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus who initiated the hostilities after annexing the Roman province of Asia into its Pontic Empire and committing massacres against the local Roman population known as the Asian Vespers. As Roman troops were sent to recover the territory, they faced an uprising in Greece organized and supported by Mithridates. Mithridates was able to mastermind such general revolts against Rome and played the magistrates of the optimates party off against the magistrates of the populares party in the Roman civil wars. Nevertheless, the first war ended with a Roman victory, confirmed by the Treaty of Dardanos signed by Lucius Sulla and Mithridates. Greece was restored to Roman rule and Pontus was expected to restore the status quo ante bellum in Asia Minor.
 W
WThe Numantine War was the last conflict of the Celtiberian Wars fought by the Romans to subdue those people along the Ebro. It was a twenty-year conflict between the Celtiberian tribes of Hispania Citerior and the Roman government. It began in 154 BC as a revolt of the Celtiberians of Numantia on the Douro. The first phase of the war ended in 151, but in 143, war flared up again with a new insurrection in Numantia.
 W
WAntony's Parthian War was a military campaign by Mark Antony, the eastern triumvir of the Roman Republic, against the Parthian Empire under Phraates IV.
 W
WCaucasian campaign of Pompey was a military campaign led by Pompey that took place in 65 BC and was a consequence of the third Mithridatic War fought over Georgian lands and its neighboring frontiers. Rome sought to expand its influence and establish itself as the overlord of the Middle East. After conquering the Kingdom of Pontus and receiving the subjugation of Tigranes II of Armenia the Romans marched on the Kingdom of Iberia, whose king, Artoces had been an ally of Mithridates VI of Pontus, Rome's premier enemy during the 80's, 70's and early 60's BC.
 W
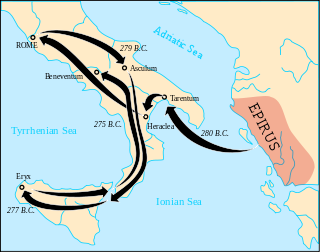
WThe Pyrrhic War was fought by Pyrrhus, the king of Epirus. Pyrrhus was asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to help them in their war with the Roman Republic.
 W
WThe Roman expansion in Italy covers a series of conflicts in which Rome grew from being a small Italian city-state to be the ruler of the Italian peninsula. Roman tradition attributes to the Roman kings the first war against the Sabines and the first conquests around the Alban Hills and down to the coast of Latium. The birth of the Roman Republic after the overthrow of the Etruscan monarch of Rome in 509 BC began a series of major wars between the Romans and the Etruscans. In 390 BC, Gauls from the north of Italy sacked Rome. In the second half of the 4th century BC Rome clashed repeatedly with the Samnites, a powerful tribal coalition of the Apennine region. By the end of these wars, Rome had become the most powerful state in central Italy and began to expand to the north and to the south. The last threat to Roman hegemony came during the Pyrrhic war when Tarentum enlisted the aid of the Greek king Pyrrhus of Epirus to campaign in the South of Italy. Resistance in Etruria was finally crushed in 265-264 BC, the same year the First Punic War began and brought Roman forces outside of the peninsula for the first time.
 W
WThe Roman-Gallic Wars were a series of conflicts between the forces of ancient Rome and various groups identified as Gauls. Among these were the Senones, Insubres, Boii and Gaesatae.
 W
WThe Seleucid War, also known as the War of Antiochos or the Syrian War, was a military conflict between two coalitions led by the Roman Republic and the Seleucid Empire. The fighting took place in modern day southern Greece, the Aegean Sea and Asia Minor.
 W
WThe First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanians.The first of these wars was the result of Rome's intervention to rescue the Campanian city of Capua from a Samnite attack.The second one was the result of Rome's intervention in the politics of the city of Naples and developed into a contest over the control of central and southern Italy.The third war also involved a struggle over the control of this part of Italy.
 W
WThe Second Punic War, which lasted from 218 to 201 BC, was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For seventeen years, the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense material and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse, and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting; and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where the Carthaginian general Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success until moving into Italy; and Africa, where the war was decided.
 W
WThe Battle of Suthul was an episode of the Jugurthine War. The battle was fought in 110 BC between the Roman force led by the legate Aulus Postumius Albinus and the army of Numidia, led by King Jugurtha. In 110 BC, the consul Spurius Postumius Albinus invaded Numidia, but left soon after to prepare elections in Rome. His brother Aulus Postumus Albinus got the leadership of the Roman army, but was easily tricked by Jugurtha, who trapped the Romans near the town of Suthul, which may be the same location as Calama, near modern-day Guelma in Algeria.
 W
WThe Third Punic War was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in modern northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 BC, one of the terms of the peace treaty prohibited Carthage from waging war without Rome's permission. Rome's ally, King Masinissa of Numidia, exploited this to repeatedly raid and seize Carthaginian territory with impunity. In 149 BC Carthage sent an army, under Hasdrubal, against Masinissa, the treaty notwithstanding. The campaign ended in disaster as the Battle of Oroscopa ended with a Carthaginian defeat and the surrender of the Carthaginian army. Anti-Carthaginian factions in Rome used the illicit military action as a pretext to prepare a punitive expedition.
 W
WThe Laconian War of 195 BC was fought between the Greek city-state of Sparta and a coalition composed of Rome, the Achaean League, Pergamum, Rhodes, and Macedon.