 W
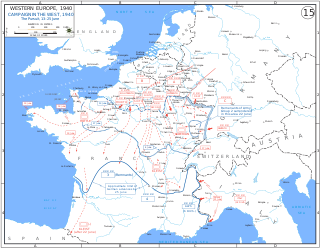
WThe Battle of France, also known as the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France, Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands during the Second World War. On 3 September 1939, France had declared war on Germany, following the German invasion of Poland. In early September 1939, France began the limited Saar Offensive. By mid-October, the French had withdrawn to their start lines. The Germans invaded Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands on 10 May, Italy entered the war on 10 June 1940 and German forces defeated the Allies on 25 June. France and the Low Countries were conquered, ending land operations on the Western Front until the Normandy landings on 6 June 1944.
 W
WThe Battle of Abbeville took place from 27 May to 4 June 1940, near Abbeville during the Battle of France in the Second World War. On 20 May, the 2nd Panzer Division advanced 56 miles (90 km) to Abbeville on the English Channel, overran the 25th Infantry Brigade of the 50th (Northumbrian) Infantry Division and captured the town at 8:30 p.m. Only a few British survivors managed to retreat to the south bank of the Somme and at 2:00 a.m. on 21 May, the III Battalion, Rifle Regiment 2 reached the coast, west of Noyelles-sur-Mer.
 W
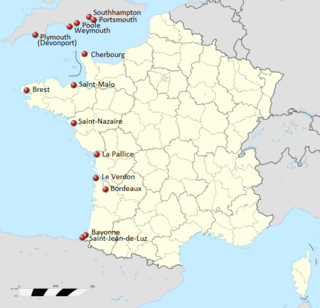
WOperation Aerial was the evacuation of Allied forces and civilians from ports in western France from 15 to 25 June 1940 during the Second World War. The evacuation followed the Allied military collapse in the Battle of France against Nazi Germany. Operation Dynamo, the evacuation from Dunkirk and Operation Cycle, an embarkation from Le Havre, finished on 13 June. British and Allied ships were covered from French bases by five Royal Air Force (RAF) fighter squadrons and assisted by aircraft based in England, to lift British, Polish and Czech troops, civilians and equipment from Atlantic ports, particularly from St Nazaire and Nantes.
 W
WThe Armistice of 22 June 1940 was signed at 18:36 near Compiègne, France, by officials of Nazi Germany and the Third French Republic. It did not come into effect until after midnight on 25 June.
 W
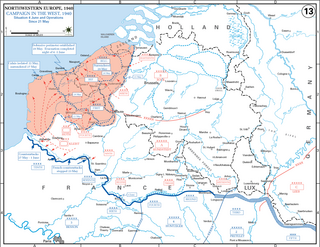
WThe Battle of Arras took place on 21 May 1940, during the Battle of France in the Second World War. Following the German invasion of the Low Countries on 10 May, French and British forces advanced into Belgium. The German campaign plan Fall Gelb had evolved into a decoy operation in the Netherlands and Belgium, with the main effort through the Ardennes. German units crossed the Meuse without waiting for reinforcements at the Battle of Sedan. Instead of consolidating bridgeheads on the west bank of the Meuse, the Germans began an advance down the Somme river valley towards the English Channel.
 W
WThe Battle of Boulogne in 1940 was the defence of the port of Boulogne-sur-Mer by French, British and Belgian troops in the Battle of France during the Second World War. The battle was fought at the same time as the Siege of Calais, just before Operation Dynamo, the evacuation of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) from Dunkirk. After the Franco-British counter-attack at the Battle of Arras on 21 May, German units were held ready to resist a resumption of the attack on 22 May. General der Panzertruppe (Lieutenant-General) Heinz Guderian, the commander of XIX Corps, protested that he wanted to rush north up the Channel coast to capture Boulogne, Calais and Dunkirk. An attack by part of XIX Corps was not ordered until 12:40 p.m. on 22 May, by which time the Allied troops at Boulogne had been reinforced from England by most of the 20th Guards Brigade.
 W
WThe siege of Calais (1940) was a battle for the port of Calais during the Battle of France. The siege was fought at the same time as the Battle of Boulogne, just before Operation Dynamo, the evacuation of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) through Dunkirk. After the Franco-British counter-attack at the Battle of Arras, German units were held back to be ready to resist a resumption of the counter-attack on 22 May, despite the protests of General Heinz Guderian, the commander of the XIX Armee Korps, who wanted to rush north up the Channel coast to capture Boulogne, Calais and Dunkirk. An attack by part of the XIX Armee Korps was not authorised until 12:40 a.m. on the night of 21/22 May.
 W
WOperation Cycle is the name of the evacuation of Allied troops from Le Havre, in the Pays de Caux of Upper Normandy from 10–13 June 1940, towards the end of the Battle of France, during the Second World War. The operation was preceded by the better known rescue of 338,226 British and French soldiers from Dunkirk in Operation Dynamo (26 May – 4 June). On 20 May, the Germans had captured Abbeville at the mouth of the Somme and cut off the main Allied armies in the north. South of the river, the Allies improvised defences and made local counter-attacks, to dislodge the Germans from bridgeheads on the south bank and re-capture river crossings for an advance northwards to regain contact with the armies in northern France and Flanders.
 W
WThe French Demarcation line was the boundary line marking the division of Metropolitan France into the territory occupied and administered by the German Army in the northern and western part of France and the Zone libre in the south during World War II. It was created by the Armistice of 22 June 1940 after the fall of France in May 1940.
 W
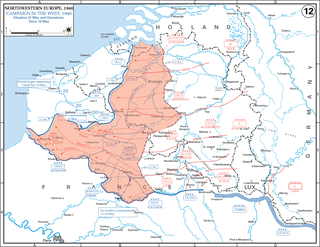
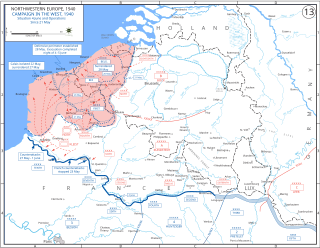
WThe Dunkirk evacuation, codenamed Operation Dynamo and also known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, or just Dunkirk, was the evacuation of Allied soldiers during World War II from the beaches and harbour of Dunkirk, in the north of France, between 26 May and 4 June 1940. The operation commenced after large numbers of Belgian, British, and French troops were cut off and surrounded by German troops during the six-week Battle of France. In a speech to the House of Commons, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill called this "a colossal military disaster", saying "the whole root and core and brain of the British Army" had been stranded at Dunkirk and seemed about to perish or be captured. In his "We shall fight on the beaches" speech on 4 June, he hailed their rescue as a "miracle of deliverance".
 W
WThe Battle of Dunkirk was fought around the French port of Dunkirk (Dunkerque) during the Second World War, between the Allies and Nazi Germany. As the Allies were losing the Battle of France on the Western Front, the Battle of Dunkirk was the defence and evacuation of British and other Allied forces to Britain from 26 May to 4 June 1940.
 W
WA Franco-British Union is a concept for a union between the two independent sovereign states of the United Kingdom and France. Such a union was proposed during certain crises of the 20th century; it has some historical precedents.
 W
WThe Franco-Italian Armistice, or Armistice of Villa Incisa, signed on 24 June 1940, in effect from 25 June, ended the brief Italian invasion of France during the Second World War.
 W
WThe Battle of the Grebbeberg was a major engagement during the Battle of the Netherlands, which was a part of the World War II Operation Fall Gelb in 1940.
 W
WHaddock Force was the name given to a number of Royal Air Force bombers dispatched to airfields in southern France to bomb northern Italian industrial targets, once Italy declared war, which was thought to be imminent. Italy entered the Second World War on 10 June 1940 and the plan was put into effect but at first, the local French authorities prevented the RAF Vickers Wellington bombers from taking off. Armstrong Whitworth Whitleys flying from England via the Channel Islands made the first raid on the night of 11/12 June 1940.
 W
WThe Battle for The Hague was a battle fought on 10 May 1940 during the German invasion of the Netherlands. German Fallschirmjäger units were dropped in and around The Hague in order to capture Dutch airfields and the city itself.
 W
WThe Historiography of the Battle of France describes how the German victory over French and British forces in the Battle of France had been explained by historians and others. Many people in 1940 found the fall of France unexpected and earth shaking. Alexander notes that Belgium and the Netherlands fell to the German army in a matter of days and the British were soon driven back to the British Isles,But it was France's downfall that stunned the watching world. The shock was all the greater because the trauma was not limited to a catastrophic and deeply embarrassing defeat of her military forces – it also involved the unleashing of a conservative political revolution that, on 10 July 1940, interred the Third Republic and replaced it with the authoritarian, collaborationist Etat Français of Vichy. All this was so deeply disorienting because France had been regarded as a great power....The collapse of France, however, was a different case.
 W
WThe Italian invasion of France, also called the Battle of the Alps, was the first major Italian engagement of World War II and the last major engagement of the Battle of France.
 W
WThe Koningshooikt—Wavre Line, abbreviated to KW Line and often known as the Dyle Line after the Dijle (Dyle) river, was a 60 kilometres (37 mi)-long fortified line of defence prepared by the Belgian Army between Koningshooikt and Wavre which was intended to protect Brussels from a possible German invasion. Construction on the KW Line began in September 1939 after World War II had begun but while Belgium itself remained a neutral state. It was subsequently extended southwards from Wavre towards Namur. The line itself consisted of bunkers, anti-tank ditches, and barricades including so-called Cointet-elements and played a key role in Allied strategy during the German invasion of Belgium in May 1940. However, its role in the actual fighting was ultimately minimal. In 2009 an inventory of surviving emplacements was begun.
 W
WJosé Félix de Lequerica y Erquiza was a Spanish lawyer, diplomat and politician who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs between 1944 and 1945.
 W
WThe Manstein Plan is one of the names used to describe the war plan of the German Army during the Battle of France in 1940. The original invasion plan was an awkward compromise devised by General Franz Halder, the chief of Oberkommando des Heeres staff that satisfied no one. Documents with details of the plan fell into Belgian hands during the Mechelen incident of 10 January 1940 and the plan was revised several times, each giving more emphasis to an attack by Army Group A through the Ardennes, which progressively reduced the offensive by Army Group B through the Low Countries to a diversion.
 W
WThe Battle of Montcornet, on 17 May 1940 took place during the Battle of France. The French 4e Division cuirassée, attacked the German-held village of Montcornet with over 200 tanks. The French drove off the Germans but later had to retreat due to lack of support and the intervention of the Luftwaffe.
 W
WThe German invasion of the Netherlands was a military campaign part of Case Yellow, the German invasion of the Low Countries and France during World War II. The battle lasted from 10 May 1940 until the surrender of the main Dutch forces on 14 May. Dutch troops in the province of Zealand continued to resist the Wehrmacht until 17 May when Germany completed its occupation of the whole country.
 W
WUnternehmen Paula is the German codename given for the Second World War Luftwaffe offensive operation to destroy the remaining units of the Armée de l'Air (ALA), or French Air Force during the Battle of France in 1940. On 10 May the German armed forces (Wehrmacht) began their invasion of Western Europe. By 3 June, the British Army had withdrawn from Dunkirk and the continent in Operation Dynamo, the Netherlands and Belgium had surrendered and most of the formations of the French Army were disbanded or destroyed. To complete the defeat of France, the Germans undertook a second phase operation, Fall Rot, to conquer the remaining regions. In order to do this, air supremacy was required. The Luftwaffe was ordered to destroy the French Air Forces, while still providing support to the German Army.
 W
WFall Rot was the plan for a German military operation after the success of Fall Gelb, the Battle of France, an invasion of the Benelux countries and northern France. The Allied armies had been defeated and pushed back in the north to the Channel coast, which culminated in the Dunkirk evacuation. The operation to complete the conquest of France by the German Army began on 5 June 1940. Fall Rot began with a preliminary attack over the river Somme on the Channel Coast to the Seine, beginning on 5 June and the main offensive by Army Group A on 9 June further east over the river Aisne.
 W
WThe Battle of Rotterdam was a Second World War battle fought during the Battle of the Netherlands. Fought between 10 and 14 May 1940, it was a German attempt to seize the Dutch city. It ended in a German victory, following the Rotterdam Blitz.
 W
WOperation Royal Marine was a military operation in May 1940 of the Second World War, during the Battle of France. The British floated fluvial mines down rivers which flowed into Germany from France. The plan was to destroy German bridges, barges and other water transport. After several postponements insisted on by the French government, fearful of German retaliation, the operation began on 10 May 1940, when the German offensive in the west began.
 W
WThe Saar Offensive was a French ground invasion of Saarland, Germany, during the early stages of World War II, from 7 to 16 September 1939. The plans called for roughly 40 divisions, including one armoured division, three mechanised divisions, 78 artillery regiments and 40 tank battalions to assist Poland, which was then under invasion, by attacking Germany's understrength western front. Although 30 divisions advanced to the border, the assault never happened. When the quick victory in Poland allowed Germany to reinforce its lines with homecoming troops, the offensive was stopped. The French forces eventually withdrew amid a German counter-offensive on 17 October.
 W
WThe Battle of Saumur occurred during the last stages of the Battle of France during World War II, when officer cadets from the Cavalry School at Saumur, led by superintendent Colonel Charles Michon, made a defensive stand along the Loire River at Saumur, Gennes, and Montsoreau. For two days the Cavalry School, and other assorted units which had fallen back before the German Wehrmacht advance, held off a German attack. Since the battle occurred after the message by Marshal Pétain which called for an end to fighting, the event is often considered one of the first acts of the French Resistance.
 W
WThe Battle of Sedan or Second Battle of Sedan took place in the Second World War during the Battle of France in 1940. It was part of the German Wehrmacht's operational plan codenamed Fall Gelb for an offensive through the hilly and forested Ardennes, to encircle the Allied armies in Belgium and north-eastern France. German Army Group A crossed the Meuse with the intention of capturing Sedan and pushing northwards towards the Channel coast, to trap the Allied forces that were advancing east into Belgium, as part of the Allied Dyle Plan.
 W
WThe siege of Lille, or Lille pocket, took place during the Battle of France in the Second World War. The siege around the city of Lille took place between the French IV Corps and V Corps of the First Army and four German infantry divisions supported by three panzer divisions.
 W
WStrange Defeat is a book written in the summer of 1940 by French historian Marc Bloch. The book was published in 1946; in the meanwhile, Bloch had been tortured and executed by the Gestapo in June 1944 for his participation in the French resistance. An English translation was published by W. W. Norton in 1968.