 W
WThe Battle of Breitenfeld or First Battle of Breitenfeld, was fought at a crossroads near Breitenfeld approximately 8 km north-west of the walled city of Leipzig on 17 September, or 7 September, 1631. It was the Protestants' first major victory of the Thirty Years War.
 W
WBattle on the Elster was the third and last battle between the Salian king Henry IV of Germany and anti-king Rudolf of Rheinfelden, fought on October 14, 1080 near Hohenmölsen on the White Elster river. Rudolf's forces were victorious; however, he was mortally wounded and succumbed to his injuries the next day.
 W
WThe Battle of Courtrai saw Johann von Thielmann's Kingdom of Saxony troops and a few Prussians encounter an Imperial French force under Nicolas Joseph Maison near Kortrijk (Courtrai), a city south-west of Ghent in what is now Belgium. Thielmann attacked only to find himself facing the bulk of Maison's I Corps. The action ended in a rout of the Saxons, most of whom were under fire for the first time.
 W
WThe Crossing of the Düna took place during the Great Northern War on July 19, 1701 near the city of Riga, present-day Latvia. The Swedish king Charles XII was in hot pursuit of king Augustus II the Strong of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Saxony. The crossing was easily made, and the coalition troops were quickly broken and retreated.
 W
WThe Battle of Flarcheim was fought between German king Henry IV and the German anti-king Rudolf of Swabia on January 27, 1080 near Flarchheim.
 W
WThe Battle of Fraustadt was fought on 2 February 1706 (O.S.) / 3 February 1706 / 13 February 1706 (N.S.) between Sweden and Saxony-Poland and their Russian allies near Fraustadt in Poland. During the Battle of Fraustadt on February 3, August II was only 120 km away, with a cavalry force about 8,000 men strong. That was one of the main reasons that Swedish General Rehnskiöld hurried to engage Schulenburg. The battle is an example of a successful pincer movement and was one of Sweden's greatest victories in the Great Northern War.
 W
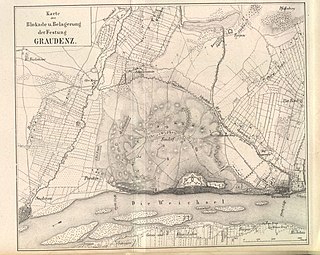
WThe Siege of Graudenz was a siege during the Napoleonic Wars between 22 January and 11 December, 1807. As part of the War of the Fourth Coalition the Prussian fortress at Graudenz in West Prussia was besieged by forces of the French Empire and its allies. The garrison, commanded by General Wilhelm René de l'Homme de Courbière, withheld blockade and siege for some 11 months, long past the formal Peace of Tilsit. The French abandoned the siege after the borders between Prussia and the new Duchy of Warsaw were defined; Graudenz staying a Prussian possession until after World War I.
 W
WThe Battle of Hohenfriedberg or Hohenfriedeberg, now Dobromierz, also known as the Battle of Striegau, now Strzegom, was one of Frederick the Great's most admired victories. Frederick's Prussian army decisively defeated an Austrian army under Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine on 4 June 1745 during the Second Silesian War.
 W
WThe twin battles of Jena and Auerstedt were fought on 14 October 1806 on the plateau west of the river Saale in today's Germany, between the forces of Napoleon I of France and Frederick William III of Prussia. The decisive defeat suffered by the Prussian Army subjugated the Kingdom of Prussia to the French Empire until the Sixth Coalition was formed in 1813.
 W
WThe Battle of Kalisz took place on October 29, 1706 in Kalisz, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Great Northern War. It was a three-hour fight which could have been prevented if Augustus II of Poland had informed the Swedes and Russians of certain matters. At the time, an alliance existed between the Poles, Saxons, and Russians. The battle was fought by Russian cavalry, led by commander Aleksandr Menshikov; against a smaller Swedish force headed by colonel Mardefelt. The Russians played a role of significance here because they needed to support their Saxon allies under Augustus.
 W
WThe Battle of Kesselsdorf was fought on 15 December 1745, between the Kingdom of Prussia and the combined forces of the Archduchy of Austria and the Electorate of Saxony during the part of the War of the Austrian Succession known as the Second Silesian War. The Prussians were led by Leopold I, Prince of Anhalt-Dessau, while the Austrians and Saxons were led by Field Marshal Rutowsky. The Prussians were victorious over the Royal Saxon Army and the Imperial Army of the Holy Roman Emperor.
 W
WThe Battle of Kliszów took place on July 19, 1702, near Kliszów in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Great Northern War. A numerically superior Polish–Saxon army led by Augustus II the Strong, operating from an advantageous defensive position, was defeated by a Swedish army half its size under the command of King Charles XII.
 W
WThe Battle of Leipzig, contemporaneously called the Battle of Leipsic(French: Bataille de Leipsick; German: Völkerschlacht bei Leipzig ; Swedish: Slaget vid Leipzig) and later the Battle of the Nations, was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813 at Leipzig, Saxony.
 W
WThe Battle of Lenzen was a land battle between a Saxon army of the Kingdom of Germany and the armies of the Slavic Redarii and Linonen peoples, that took place on 4 September 929 near the fortified Linonen stronghold of Lenzen in Brandenburg, Germany. The Saxon army, commanded by Saxon magnate Bernhard, destroyed a Slavic Redarii army. It marked the failure of Slavic attempts to resist German king Henry the Fowler's expansionism to the Elbe.
 W
WThe Battle of Minden was a major engagement during the Seven Years' War, fought on 1 August 1759. An Anglo-German army under the overall command of Prussian Field Marshal Ferdinand of Brunswick defeated a French army commanded by Marshal of France, Marquis de Contades. Two years previously, the French had launched a successful invasion of Hanover and attempted to impose an unpopular treaty of peace upon the allied nations of Britain, Hanover and Prussia. After a Prussian victory at Rossbach, and under pressure from Frederick the Great and William Pitt, King George II disavowed the treaty. In 1758, the allies launched a counter-offensive against the French and Saxon forces and drove them back across the Rhine.
 W
WThe Battle of Mühlberg took place near Mühlberg in the Electorate of Saxony in 1547, during the Schmalkaldic War. The Catholic princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V decisively defeated the Lutheran Schmalkaldic League of Protestant princes under the command of Elector John Frederick I of Saxony and Landgrave Philip I of Hesse.
 W
WThe Battle of Nördlingen took place on 6 September NS during the Thirty Years' War. A combined Imperial-Spanish force won a crushing victory over a Swedish-German army.
 W
WThe Siege of Pirna took place in 1756 as part of the Prussian invasion of Saxony during the Third Silesian War.
 W
WThe Battle of Poznań was a battle that took place on August 9, 1704 in Poznań, Poland during the Great Northern War.
 W
WThe Battle of Praga took place on October 25, 1705 near the town of Warsaw, Poland during the fifth year of the Great Northern War. The Swedish army of more than 270 men assisted by approximately 140 soldiers from the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth under the command of Valentin Dahldorf defeated a combined Polish–Saxon–Russian force of about 5,000 men under Michał Serwacy Wiśniowiecki and Aleksandr Menshikov.
 W
WThe Battle of Pułtusk took place on April 21, 1703 in Pułtusk during the Great Northern War. The Swedish army under the command of Charles XII defeated the Saxon army under Adam Heinrich von Steinau.
 W
WThe Battle of Poniec took place on October 28, 1704 in Poniec, Poland, during the Great Northern War. The Swedish Army under Charles XII unsuccessfully dislodged the Saxon Army under Johann Matthias von der Schulenburg through several cavalry charges. The Saxons had deployed in a massive square formation near the village of Janiszewo, west of Poniec.
 W
WIn the Rhine campaign of 1796, two First Coalition armies under the overall command of Archduke Charles outmaneuvered and defeated two French Republican armies. This was the last campaign of the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars.
 W
WThe Battle of Saalfeld took place on 10 October 1806, at which a French force of 12,800 men commanded by Marshal Jean Lannes defeated a Prussian-Saxon force of 8,300 men under Prince Louis Ferdinand. The battle took place in Thuringia in what was the Ernestine duchy of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. The battle was the second clash in the Prussian Campaign of the War of the Fourth Coalition.
 W
WThe Saxon Rebellion or Rebellion of the Saxons, also commonly called the Saxon Uprising, refers to the struggle between the Salian dynasty ruling the Holy Roman Empire and the rebel Saxons during the reign of Henry IV. The conflict reached its climax in the period from summer 1073 until the end of 1075, in a rebellion that involved several clashes of arms.
 W
WThe Battle of Schleiz took place on October 9, 1806 in Schleiz, Germany between a Prussian-Saxon division under Bogislav Friedrich Emanuel von Tauentzien and a part of Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte's I Corps under the command of Jean-Baptiste Drouet, Comte d'Erlon. It was the first clash of the War of the Fourth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars. As Emperor Napoleon I of France's Grande Armée advanced north through the Frankenwald it struck the left wing of the armies belonging to the Kingdom of Prussia and the Electorate of Saxony, which were deployed on a long front. Schleiz is located 30 kilometers north of Hof and 145 kilometers southwest of Dresden at the intersection of Routes 2 and 94.
 W
WThe Siege of Montmédy was a battle of the Franco-Prussian War at the small commune of Montmédy, in the Meuse, it was besieged by the army of the German coalition. Defended by the 57th Line Infantry Regiment, the Garde Mobile and elements of other units, it surrendered on December 14, 1870.
 W
WThe Battle of Sievershausen occurred on 9 July 1553 near the village of Sievershausen, where the forces of the Hohenzollern margrave Albert Alcibiades of Brandenburg-Kulmbach fought against the united troops of Elector Maurice of Saxony and Duke Henry V of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel. With 4,000 men killed, including the Saxon elector and two of Henry's sons, it was one of the bloodiest battles on Lower Saxon territory. Margrave Albert was defeated.
 W
WThe Battle of Soor was a battle between Frederick the Great's Prussian army and an Austro-Saxon army led by Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine during the Second Silesian War. The battle occurred in the vicinity of Soor, also known as Hajnice, in the modern day Czech Republic. The battle started with a failed Austrian surprise attack on the outnumbered Prussians. Despite initial setbacks the Prussian army managed to defeat the Austrians, due to an unexpected attack from a reserve regiment that refused to follow Frederick's orders.
 W
WThe Battle of Wagram was a military engagement of the Napoleonic Wars that ended in a costly but decisive victory for Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte's French and allied army against the Austrian army under the command of Archduke Charles of Austria-Teschen. The battle led to the breakup of the Fifth Coalition, the Austrian and British-led alliance against France.
 W
WThe Battle of Warsaw was fought on 31 July 1705 near Warsaw, Poland, during the Great Northern War. The battle was part of a power struggle for the Polish–Lithuanian throne. It was fought between Augustus II the Strong and Stanisław Leszczyński and their allies. Augustus II entered the Northern war as elector of Saxony and king of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and had formed an alliance with Denmark–Norway and Russia. Stanisław Leszczyński had seized the Polish throne in 1704, with the support of the Swedish army of Charles XII of Sweden. The struggle for the throne forced the Polish nobility to pick sides; the Warsaw Confederation supported Leszczyński and Sweden, and the Sandomierz Confederation supported Augustus II and his allies. The conflict resulted in the Polish civil war of 1704–1706.
 W
WThe Battle of Wittstock took place during the Thirty Years' War (1618-1648). It was fought on 24 September or 4 October 1636. A Swedish-allied army commanded jointly by Johan Banér and Alexander Leslie, later 1st Earl of Leven decisively defeated a combined Imperial-Saxon army, led by Count Melchior von Hatzfeld and the Saxon Elector John George I.