 W
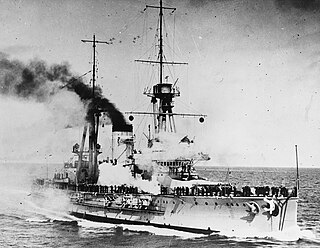
WAlfonso XIII was the second of three España-class dreadnought battleships built in the 1910s for the Spanish Navy. Named after King Alfonso XIII of Spain, the ship was not completed until 1915 owing to a shortage of materials that resulted from the start of World War I the previous year. The España class was ordered as part of a naval construction program to rebuild the fleet after the losses of the Spanish–American War; the program began in the context of closer Spanish relations with Britain and France. The ships were armed with a main battery of eight 305 mm (12 in) guns and were intended to support the French Navy in the event of a major European war.
 W
WAlmirante Cervera was a light cruiser and lead ship of the Almirante Cervera class of the Spanish Navy. She was named after the Spanish admiral Pascual Cervera y Topete, commander of the Spanish naval forces in Cuba during the Spanish–American War. She was part of the Spanish Republican Navy between 1931 and 1936, year in which she became a key player of the Nationalist Fleet in the Spanish Civil War.
 W
WAlmirante Ferrándiz was a Churruca-class destroyer in the Spanish Republican Navy. She took part in the Spanish Civil War on the government side.
 W
WThe Antifascist Worker and Peasant Militias were a militia group founded in the Second Spanish Republic in 1934. Their purpose was to protect leaders of the Communist Party of Spain (PCE) and Unified Socialist Youth (JSU) from the attacks of Fascist militia groups such as the Falange Blueshirts.
 W
WThe Archimede class were a group of four submarines built for the Regia Marina in the early 1930s. The boats fought in the Spanish Civil War and in World War II. Under Spanish colors, these boats were known as the General Mola class, and remained in service until 1959.
 W
WThe Ascaso Column was the third column organized in Barcelona at the beginning of the Spanish Civil War. They left for the Aragon front on 25 July with 2,000 militiamen. They had 4-6 machine guns and 3-4 trucks, transformed into armored tiznaos by a Gavà metallurgist. It was located in the sector of Huesca, and was run by Cristóbal Alvaldetrecu, Gregorio Jover and Domingo Ascaso. Among the participants in the column was José Luis Facerías, later known as one of the libertarian maquis in Catalonia between 1945 and 1953. The internationalist groups "Giustizia e Libertá" and the "Battalion of Death" also joined the Ascaso Column.
 W
WBaleares was a Canarias-class heavy cruiser of the Spanish Navy. The two ships of the class were built upon a British design and were a modified version of the Royal Navy′s County class. Baleares was constructed in Spain by the Vickers-Armstrongs subsidiary Sociedad Española de Construcción Naval, and saw service during the Spanish Civil War, when she was torpedoed and sunk by destroyers of the Spanish Republican Navy during the Battle of Cape Palos.
 W
WThe Basque Auxiliary Navy was a section of the Spanish Republican Navy operating in the Bay of Biscay between 1936 and 1937. It began operations in October 1936 at the behest of the autonomous Basque Government. The main Basque naval base was at Portugalete.
 W
WC-3 was a C-class submarine of the Spanish Republican Navy. C-3 was built by Sociedad Española de Construcción Naval (SECN) in Cartagena, Spain, launched 20 February 1929, and commissioned on 4 May 1929. She took part in the Spanish Civil War on the government side before being sunk by the German submarine U-34 on 12 December 1936.
 W
WCanarias was a heavy cruiser of the Spanish Navy. She was built in Spain by the Vickers-Armstrongs subsidiary Sociedad Española de Construcción Naval upon a British design, and was a modified version of the Royal Navy′s County class. Canarias saw service during the Spanish Civil War.
 W
WSS Cantabria was a Spanish cargo ship which was sunk in a military action of the Spanish Civil War, off the coast of Norfolk 12 miles ENE of Cromer on 2 November 1938. The ship was shelled by the Spanish Nationalist auxiliary cruiser Nadir, which was part of General Franco's navy.
 W
WThe Central Region Army Group, Spanish: Grupo de Ejércitos de la Región Central (GERC), was a military formation of the Spanish Republican Army during the last phase of the Spanish Civil War. It gathered the most powerful section of the republican military and would endure until the 1939 surrender. The GERC was under the command of general José Miaja Menant, the Defence of Madrid hero.
 W
WThe Eastern Region Army Group, Spanish: Grupo de Ejércitos de la Región Oriental (GERO), was a military formation of the Spanish Republican Army during the last phase of the Spanish Civil War. It was established in June 1938 as a response to the splitting in two of the territory under the sovereignty of the Spanish Republic after the Central Region Army Group (GERC), under the command of General Miaja, had been set up in the central-southern region of Spain.
 W
WEuzko Gudarostea was the name of the army commanded by the Basque Government during the Spanish Civil War. It was formed by Basque nationalists, socialists, communists, anarchists and republicans under the direction of lehendakari José Antonio Aguirre and coordinating with the army of the Second Spanish Republic. It fought the troops of Francisco Franco during 1936 and 1937. It surrendered to the Italian Corpo Truppe Volontarie at Santoña, while the rest of the Republican army kept fighting until 1939. This event is called the Santoña Agreement, Pact of Santoña, or Treason of Santoña by some Spanish leftists.
 W
WThe Extremaduran Army, was a military formation of the Spanish Republican Army during the last phase of the Spanish Civil War. It was part of the Central Region Army Group (GERC). The Republican forces deployed at the Extremaduran Front were under its jurisdiction. They guarded the westernmost end of the Republican territory, an area that saw long periods of inactivity between the major battles.
 W
WThe Guardia Mora, officially the Guardia de Su Excelencia el Generalísimo was Francisco Franco's personnel ceremonial escort. it was formed in February 1937 from personnel drawn from the Guardia Civil in Tétouan and the II Tabor of Grupo de Regulares de Tetuan No.1. Their white and red hooded cloak, based on the djellaba, was worn over the white parade uniform of Regulares officers.
 W
WThe British Independent Labour Party sent a small contingent to fight in the Spanish Civil War. The contingent fought alongside the Workers' Party of Marxist Unification (POUM) and included George Orwell, who subsequently wrote about his experiences in his personal account Homage to Catalonia.
 W
WThe Irish Brigade fought on the Nationalist side of Francisco Franco during the Spanish Civil War. The unit was formed wholly of Roman Catholics by the politician Eoin O'Duffy, who had previously organised the banned quasi-fascist Blueshirts and openly fascist Greenshirts in Ireland. Despite the declaration by the Irish government that participation in the war was unwelcome and ill-advised, 700 of O'Duffy's followers went to Spain. They saw their primary role in Spain as fighting for the Roman Catholic Church against the Red Terror of Spanish anticlericalists. They also saw many religious and historical parallels in the two nations, and hoped to prevent communism gaining ground in Spain.
 W
WThe Iron Column was a Valencian anarchist militia column formed during the Spanish Civil War to fight against the military forces of the Nationalist Faction that had rebelled against the Second Spanish Republic.
 W
WJaime I was a Spanish dreadnought battleship, the third and final member of the España class, which included two other ships: España and Alfonso XIII. Named after King James I of Aragon, Jaime I was built in the early 1910s, though her completion was delayed until 1921 owing to a shortage of materials that resulted from the start of World War I the previous year. The class was ordered as part of a naval construction program to rebuild the fleet after the losses of the Spanish–American War in the context of closer Spanish relations with Britain and France. The ships were armed with a main battery of eight 305 mm (12 in) guns and were intended to support the French Navy in the event of a major European war.
 W
WJosé Luis Díez was a Churruca-class destroyer in the Spanish Republican Navy. She took part in the Spanish Civil War on the government side.
 W
WJúpiter-class minelayers was a group of four vessels of the Spanish Republican Navy built during the Spanish Republic. Three of them came into service during the Civil War after joining the rebel side.
 W
WLepanto was a Churruca-class destroyer of the Spanish Republican Navy. She took part in the Spanish Civil War on the side of the government of the Second Spanish Republic. She was named after the Battle of Lepanto.
 W
WMar Negro was an armed merchantman of the Nationalist Spanish Navy during the Spanish Civil War. The cargo ship was launched in 1930 along with her sister ship MV Mar Cantábrico, and after five years with the Compañía Marítima Del Nervión company, she was first requisitioned by the Spanish Republican Navy in 1936. Captured by a group of Nationalist sympathizers from her crew off Algeria in 1937, she entered in service in 1938 after being converted to an auxiliary cruiser.
 W
WThe Perla-class submarines were the third sub-class of the 600 Series of coastal submarines built for the Royal Italian Navy during the 1930s and named after gemstones. Of the ten boats built of this class, only three survived World War II.
 W
WThe Fuerzas Regulares Indígenas, known simply as the Regulares (Regulars), are volunteer infantry units of the Spanish Army, largely recruited in the cities of Ceuta and Melilla. Consisting of indigenous infantry and cavalry recruited in Spanish Morocco, forming part of the Army of Africa and officered by Spaniards, these troops played a significant role in the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939).
 W
WSánchez Barcáiztegui was a Churruca-class destroyer of the Spanish Republican Navy. She took part in the Spanish Civil War on the side of the government of the Second Spanish Republic.
 W
WThe term "Aviación Nacional" or "Fuerza Aérea Nacional" refers to military air units supporting General Franco against the Second Spanish Republic in the Spanish Civil War and includes:The Nationalist side of the Spanish Air Force made up of planes supplied by Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy and by aircraft captured from the Spanish Republican Air Force Condor Legion of Nazi Germany Aviazione Legionaria of Fascist Italy
 W
WThe Spanish Legion, informally known as the Tercio or the Tercios, is a unit of the Spanish Army and Spain's Rapid Reaction Force. It was raised in the 1920s to serve as part of Spain's Army of Africa. The unit, which was established in January 1920 as the Spanish equivalent of the French Foreign Legion, was initially known as the Tercio de Extranjeros, the name under which it began fighting in the Rif War of 1920–1926. Although foreign recruitment spans the Spanish-speaking nations, the majority of recruits are Spaniards. Over the years, the force's name has changed from Tercio de Extranjeros to Tercio de Marruecos, and by the end of the Rif War it became the "Spanish Legion", with several "tercios" as sub-units.
 W
WTerç de Requetès de la Mare de Déu de Montserrat was a battalion-type Carlist infantry unit, forming part of Nationalist troops during the Spanish Civil War. It is known as one of two Catalan units fighting against the Republicans. It is also recognized as the Nationalist unit which recorded the highest KIA ratio of 19%, with corresponding average Nationalist figure estimated at 6%. Its operational history consists mostly of long periods of inactivity or low-intensity skirmishes punctuated by two heavy combat engagements, culminating on August 25, 1937 and August 19, 1938.
 W
WThe Tiradores de Ifni were volunteer indigenous infantry units of the Spanish Army, largely recruited in the enclave of Ifni The tiradores were originally recruited from the Spanish Morocco, forming part of the Army of Africa and mostly officered by Spaniards, these troops played a role in the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939).
 W
WThe Turbine-class destroyer was a group of eight destroyers built for the Regia Marina in the 1920s. The ships played a minor role in the Spanish Civil War of 1936–1937, supporting the Nationalists. All the ships of the class were lost during World War II.
 W
WViriatos, named after the Lusitanian leader Viriathus, was the generic name given to Portuguese volunteers who fought with the Nationalists in the Spanish Civil War. In the first weeks of the war, the Portuguese Army tried to form a Viriatos Legion to aid the Nationalist insurgents in Spain. The Legion was disbanded before any recruitment drive could take place after pro-Republican incidents in Portugal had convinced the government that direct intervention on the side of the Nationalists could cause further unrest.