 W
WThe Al-Khalid is a main battle tank jointly developed by Pakistan and China during the 1990s, based on the Chinese Type 90-IIM tank. The original prototype was developed by China North Industries Corporation (Norinco) under the name MBT-2000, and Norinco also offered the tank for export. Around 310 Al Khalid MBTs had been produced by 2014. The Bangladesh Army ordered 44 MBT-2000s from China in 2011. The Norinco-made MBT-2000 is also used by the Royal Moroccan Army. It was trialled by the Peruvian Army for possible acquisition, but was not purchased due to financial problems.
 W
WThe AMX-13 is a French light tank produced from 1952 to 1987. It served with the French Army, as the Char 13t-75 Modèle 51, and was exported to more than 26 other nations. Named after its initial weight of 13 tonnes, and featuring a tough and reliable chassis, it was fitted with an oscillating turret built by GIAT Industries with revolver type magazines, which were also used on the Austrian SK-105 Kürassier. Including prototypes and export versions, there are over a hundred variants including self-propelled guns, anti-aircraft systems, APCs, and ATGM versions.
 W
WThe AMX 50 or AMX-50 was a French heavy tank designed in the immediate post Second World War period. It was proposed as, in succession, the French medium, heavy, and main battle tank, incorporating many advanced features. It was cancelled in the late 1950s however, due to unfavourable economic and political circumstances after serious delays in development.
 W
WThe "Armata" Universal Combat Platform is a Russian advanced next generation modular heavy military tracked vehicle platform. The Armata platform is the basis of the T-14, the T-15, a combat engineering vehicle, an armoured recovery vehicle, a heavy armoured personnel carrier, a tank support combat vehicle and several types of self-propelled artillery, including the 2S35 Koalitsiya-SV under the same codename based on the same chassis. It is also intended to serve as the basis for artillery, air defense, and NBC defense systems. The new "Armata" tank platform is meant to replace the older Russian MBTs and APCs that are currently used by the Russian military.
 W
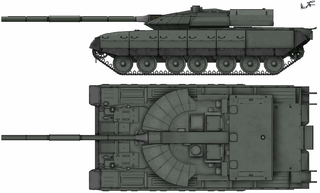
WThe Black Eagle tank, was a presumed prototype main battle tank produced in the Russian Federation. It was thought to have been developed by the KBTM design bureau in Omsk in the late 1990s. A production version of this tank has never been publicly demonstrated. The Black Eagle has been cancelled, with all production and development halted.
 W
WThe Falcon Turret is a low-profile main battle tank turret under development by King Abdullah II Design and Development Bureau in Jordan, with technical assistance from South Africa.
 W
WThe K2 Black Panther is a next generation South Korean main battle tank designed by the South Korean Agency for Defense Development and manufactured by Hyundai Rotem. Developed as a modern main battle tank that will replace most of the remaining M48 Patton tanks and complement the K1 series of main battle tanks currently fielded by the South Korean military, the K2 Black Panther combines an auto-loaded 55 calibre 120 mm main gun, advanced composite armour along with hard and soft-kill active protection systems.
 W
WKarrar is an Iranian third generation main battle tank. The tank was announced on 12 March 2017. At the announcement, it was stated that it possessed an electro-optical fire control system, a laser rangefinder, ballistic computer and could fire at both stationary and mobile targets in day or night.
 W
WThe Leclerc tank is a main battle tank (MBT) built by GIAT, now Nexter of France. It was named in honour of General Philippe Leclerc de Hauteclocque, who led the French element of the drive towards Paris while in command of the Free French 2nd Armoured Division in World War II. The designation "AMX-56" – while very popular – is incorrect.
 W
WThe Lorraine 40t was a prototype French medium tank of the Cold War.
 W
WThe M-84AS is a modernized version of the M-84 main battle tank produced by Yugoimport SDPR in Serbia. M-84AS is sometimes referred to as M-84AB1 and M-2001.
 W
WThe M-84AS1 and M-84AS2 is a new series of modernized version of the M-84 main battle tank designed by Military Technical Institute Belgrade and produced by Tehnički remontni zavod Čačak in Serbia. First prototype version designated M-84AS1 was presented in 2017. and later versions of AS1 and AS2 with numerous improvements over first variant was presented in 2020. Latest variant's AS1 and AS2 incorporates newly developed modular Explosive reactive armour, modern Battlefield management system and fire controls system, Remote controlled weapon station and numerous other new subsystems. AS1 and AS2 are developed in parallel and differs in number of same modernized subsystems implemented and some specific turret modification regarding RCWS and commander hatch and equipment implementation and represents two slightly different modernization versions of same M-84 tank with latter AS2 probably to be used as it becomes available firstly as platoon commander tank.
 W
WThe M-95 Degman is a prototype Croatian main battle tank, developed by the Đuro Đaković company. The Đuro Đaković factory is best known for its principal role in the production of M-84 in the Yugoslav era.
 W
WThe United Defense M8 Armored Gun System was an American light tank that was intended to replace the M551A1 Sheridan in the 82nd Airborne Division, as well as being expected to replace TOW-equipped Humvees in the 2nd Armored Cavalry Regiment. The M8 project was eventually canceled in 1997. Its role in the 2nd ACR was eventually taken by the M1128 Mobile Gun System, but a modernized version of the vehicle is in trials with the US Army once more.
 W
WThe Main Ground Combat System (MGCS) is a project by France and Germany since 2012 to replace their currently deployed Leclerc and Leopard 2 main battle tanks (MBTs). In 2016, the program was in the concept phase which was projected to be completed by 2017.
 W
WObject 478 was a Soviet main battle tank prototype. It was developed by the KMDB of the Malyshev Factory and never put into full production.
 W
WThe "Patagón" tank is a light tank developed in Argentina during the early 2000s, expected to enter service with the Argentine Army. It is based on a SK-105 Kürassier chassis with a refurbished AMX-13 turret. The project was cancelled in late 2008 after five tanks were converted.
 W
WThe PT-91 Twardy ("Tough") is a Polish main battle tank. A development of the T-72M1, it first entered service in 1995. The PT-91 was designed at the OBRUM and is produced by the Bumar Łabędy company, a part of the Bumar Group, a Polish technical military consortium. Changes from the T-72 include a new dual-axis stabilized fire-control system, reactive armour, a more powerful engine, transmission and new automatic loader.
 W
WThe SK-105 Kürassier is an Austrian light tank armed with a rifled 105 mm gun in an oscillating turret. It is estimated that over 700 have been produced.
 W
WThe Spähpanzer SP I.C. was the experimental model of a West German reconnaissance scout light tank with anti-tank components. It was developed from 1956 in order to increase the anti-tank capabilities of reconnaissance tank battalions, but the project eventually declined. There are two blueprint prototype versions of the SP I.C. The single tank built can be seen in the Wehrtechnische Studiensammlung Koblenz.
 W
WThe Stridsvagn 103, also known as the S-Tank, is a Swedish post-World War II main battle tank, designed and manufactured in Sweden. Developed in the 1950s, it was the first main battle tank to use a turbine engine and the only mass-produced tank since World War II to dispense with a turret. It has an unconventional design with a unique gun laying process: it is turretless with a fixed gun traversed by engaging the tracks and elevated by adjusting the hull suspension. The result was a very low-profile design with an emphasis on survivability and heightened crew protection level. Strv 103s formed a major portion of the Swedish armoured forces from the 1960s to the 1990s, when, along with the Centurions, it was replaced by the Leopard 2 variants Stridsvagn 121 and Stridsvagn 122. While most turretless armoured fighting vehicles are classified as assault guns or tank destroyers, the Strv 103 is considered a tank since its designated combat role matched those of other tanks within contemporary Swedish doctrine.
 W
WThe T-14 Armata is a next-generation Russian main battle tank based on the Armata Universal Combat Platform—the first series-produced next-generation tank. The Russian Army initially planned to acquire 2,300 T-14s between 2015 and 2020. Production and fiscal shortfalls delayed this to 2025, and then to the cancellation of the main production run. The test batch of 100 was delivered and deployed to the 2nd Guards Tamanskaya Motor Rifle Division in 2019; tanks will be transferred only after the completion of all state tests.
 W
WThe T-64 is a Soviet second-generation main battle tank introduced in the early 1960s. It was a more advanced counterpart to the T-62: the T-64 served in tank divisions, while the T-62 supported infantry in motorized rifle divisions. It introduced a number of advanced features including composite armor, a compact engine and transmission, and a smoothbore 125-mm gun equipped with an autoloader to allow the crew to be reduced to three so the tank could be smaller and lighter. In spite of being armed and armored like a heavy tank, the T-64 weighed only 38 tonnes.
 W
WThe T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that first entered production in 1971. About 20,000 T-72 tanks have been built, and refurbishment has enabled many to remain in service for decades. The T-72A version introduced in 1979 is considered a second-generation main battle tank. It was widely exported and saw service in 40 countries and in numerous conflicts. The T-72B3 version introduced in 2010 is considered a third-generation main battle tank (MBT).
 W
WThe T-80 is a main battle tank (MBT) designed and manufactured in the Soviet Union. When it entered service in 1976, it was the second MBT in the world to be equipped with a gas turbine engine after the Swedish Strv 103 and the first to use it as a primary propulsion engine. The T-80U was last produced in a factory in Omsk, Russia, while the T-80UD and further-developed T-84 continue to be produced in Ukraine. The T-80 and its variants are in service in Belarus, Cyprus, Egypt, Kazakhstan, Pakistan, Russia, South Korea, and Ukraine. The chief designer of the T-80 was the Soviet engineer Nikolay Popov.
 W
WThe T-84 is a Ukrainian main battle tank (MBT), a development of the Soviet T-80 main battle tank introduced in 1976. The T-84 was first built in 1994 and entered service in the Ukrainian Armed Forces in 1999. The T-84 is based on the diesel-engined T-80 version, the T-80UD. Its high-performance opposed-piston engine makes it one of the fastest MBTs in the world, with a power-to-weight ratio of about 26 horsepower per tonne. The T-84 Oplot is an advanced version incorporating an armoured ammunition compartment in a new turret bustle; ten of these entered Ukrainian service in 2001. The T-84-120 Yatagan is a prototype model intended for export, mounting a 120 mm gun capable of firing standard NATO ammunition and guided missiles.
 W
WThe T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank that entered service in 1993. The tank is a modern variation of the T-72B and incorporates many features found on the T-80U. Originally called the T-72BU, but later renamed to T-90, it is an advanced tank in service with Russian Ground Forces and the Naval Infantry. The T-90 uses a 125 mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard protective measures include a blend of steel and composite armour, smoke grenade dischargers, Kontakt-5 explosive-reactive armour and the Shtora infrared ATGM jamming system. It was designed and built by Uralvagonzavod, in Nizhny Tagil, Russia.
 W
WThe post–Cold War era is the period in world history from the collapse of the Soviet Union on December 25, 1991 to the present. During the Cold War (1947–1991), the Soviet domination of the Warsaw Pact led to effective standardization on a few tank designs. In comparison, France, Germany, the United States, and the United Kingdom had previously developed their own tank designs, but now tried to standardize their designs, while the smaller nations of NATO purchased or adapted these designs.
 W
WThe Type 10 is a next generation main battle tank of JSDF produced by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries for the Japanese Ground Self Defense Force, entering service in 2012. Compared with other currently-serving main battle tanks in the JGSDF, the Type 10 has been equipped with enhancements in its capability to respond to anti-tank warfare and other contingencies.
 W
WThe Type 90 tank is a main battle tank (MBT) of the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force (JGSDF). It was designed and built by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries as a replacement for the Type 61 and to supplement the then current fleet of Type 74 tanks, and entered service in 1990. It is to be superseded by the Type 10 tank.
 W
WThe Type 96 or ZTZ96 is a Chinese second generation main battle tank (MBT). The final evolution of the Type 88 design, the Type 96 entered service with the People's Liberation Army (PLA) in 1997. The later variants of the Type 96 are regarded as near-equivalents to China's third generation MBT.
 W
WThe Type 99 MBT or ZTZ-99 is a Chinese third generation main battle tank (MBT). The vehicle was a replacement for the aging Type 88 introduced in the late 1980s. The Type 99 MBT was China's first mass-produced third generation main battle tank. Combining modular composite armour and tandem-charge defeating ERA, 125 mm smoothbore gun with ATGM-capability, high mobility, digital systems and optics, the Type 99 represents a shift towards rapid modernisation by the PLA.
 W
WZulfiqar (ذوالفقار) is an Iranian main battle tank, conceived by Brigadier General Mir-Younes Masoumzadeh, deputy ground force commander for research and self-sufficiency of the armed forces. It is named after Zulfiqar, the legendary sword of Ali the fourth Caliph and the first Shiite Imam. It's also known as Zolfaqar.