 W
W2X Software was a Maltese software company specializing in virtual desktop, application virtualization, application delivery, Remote Desktop Services, remote access and Mobile Device Management. On 25 February 2015, 2X Software was acquired by Parallels, Inc. The 2X products, Remote Application Server and Mobile Device Management, are now included in Parallels' offering.
 W
WandLinux is an Ubuntu-based system using the Linux kernel designed to run a Linux environment natively on Windows systems. It is FOSS being released under the GNU GPL license. It uses the coLinux kernel to run, Xming to run X Window, PulseAudio for sound, and has the option of either using a stripped down version of KDE or Xfce.
 W
WCherryOS was a PowerPC G4 processor emulator for x86 Microsoft Windows platforms, which allowed various Apple Inc. programs to be operated on Windows XP. Announced and made available for pre-orders on October 12, 2004, it was developed by Maui X-Stream (MXS), a startup company based in Lahaina, Hawaii and a subsidiary of Paradise Television. The program encountered a number of launch difficulties its first year, including a poorly-reviewed soft launch in October 2004, wherein Wired Magazine argued that CherryOS used code grafted directly from PearPC, an older open-source emulator. Lead developer Arben Kryeziu subsequently stated that PearPC had provided the inspiration for CherryOS, but "not the work, not the architecture. With their architecture I'd never get the speed."
 W
WCHIP-8 is an interpreted programming language, developed by Joseph Weisbecker. It was initially used on the COSMAC VIP and Telmac 1800 8-bit microcomputers in the mid-1970s. CHIP-8 programs are run on a CHIP-8 virtual machine. It was made to allow video games to be more easily programmed for these computers.
 W
WCooperative Linux, abbreviated as coLinux, is software which allows Microsoft Windows and the Linux kernel to run simultaneously in parallel on the same machine.
 W
WCP-67 was the control program portion of CP/CMS, a virtual machine operating system developed for the IBM System/360-67 by IBM's Cambridge Scientific Center. It was a reimplementation of their earlier research system CP-40, which ran on a one-off customized S/360-40. CP-67 was later reimplemented (again) as CP-370, which IBM released as VM/370 in 1972, when virtual memory was added to the System/370 series. Details on the development and circumstances of CP-67 can be found in the article History of CP/CMS.
 W
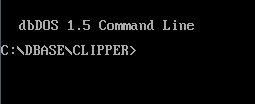
WdbDOS is software developed by dBase for Windows computers with Intel processors. dbDOS allows Intel-based PCs to run DOS Applications, such as dBASE III, dBASE IV, and dBASE V for DOS in an emulated DOS environment. It is an environment configured specifically to allow the various versions of dBASE for DOS to run without any changes to the dBASE executables or the dBASE compiled programs created.
 W
WFlatpak is a utility for software deployment and package management for Linux. It is advertised as offering a sandbox environment in which users can run application software in isolation from the rest of the system.
 W
WGaneti is a virtual machine cluster management tool originally developed by Google. The solution stack uses either Xen, KVM, or LXC as the virtualization platform, LVM for disk management, and optionally DRBD for disk replication across physical hosts or shared storage for external replication. Since 2007 Ganeti is developed and released as free and open-source software. Originally subject to the requirements of the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2, the license was changed to the 2-clause BSD license in version 2.11.6, released September 2014.
 W
WCP-40 was a research precursor to CP-67, which in turn was part of IBM's then-revolutionary CP[-67]/CMS – a virtual machine/virtual memory time-sharing operating system for the IBM System/360 Model 67, and the parent of IBM's VM family. CP-40 ran multiple instances of client operating systems – particularly CMS, the Cambridge Monitor System, built as part of the same effort. Like CP-67, CP-40 and the first version of CMS were developed by IBM's Cambridge Scientific Center (CSC) staff, working closely with MIT researchers at Project MAC and Lincoln Laboratory. CP-40/CMS production use began in January 1967. CP-40 ran on a unique, specially modified IBM System/360 Model 40.
 W
WKernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is a virtualization module in the Linux kernel that allows the kernel to function as a hypervisor. It was merged into the mainline Linux kernel in version 2.6.20, which was released on February 5, 2007. KVM requires a processor with hardware virtualization extensions, such as Intel VT or AMD-V. KVM has also been ported to other operating systems such as FreeBSD and illumos in the form of loadable kernel modules.
 W
WMarionnet is a virtual network laboratory: it allows users to define, configure and run complex computer networks without any need for physical setup. Only a single, possibly even non-networked Linux host machine is required to simulate a whole Ethernet network complete with computers, routers, hubs, switches, cables, and more Support is also provided for integrating the virtual network with the physical host network.
 W
WThe Open Virtualization Alliance (OVA) was a Linux Foundation Collaborative Project committed to foster the adoption of free and open-source software virtualization solutions including KVM, but also software to manage such, e.g. oVirt. The consortium promoted examples of customer successes, encouraged interoperability and accelerated the expansion of the ecosystem of third party solutions around KVM.
Pano Logic was a manufacturer of devices which present virtual desktops to the end user with no local processing power. They describe this concept as "zero client". This is perceived as offering benefits in end-user support and in power provision to desks. OEM versions have been included in displays from some vendors, allowing a single unit to be deployed. The company failed in October 2012. In March 2013, Propalms announced they had acquired the rights to support Panologic customers, and will "help transition the customer base to a new platform".
 W
WParallels Server for Mac is a server-side desktop virtualization product built for the Mac OS X Server platform and is developed by Parallels, Inc., a developer of desktop virtualization and virtual private server software. This software allows users to run multiple distributions of Linux, Windows and FreeBSD server applications alongside Mac OS X Server on Intel-based Apple hardware.
 W
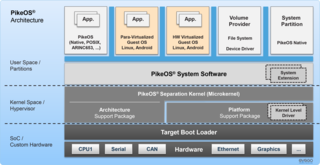
WPikeOS is a commercial, hard real-time operating system (RTOS) that offers a separation kernel based hypervisor with multiple logical partition types for many other operating systems (OS), each called a GuestOS, and applications. It enables users to build certifiable smart devices for the Internet of things (IoT) according to the high quality, safety and security standards of different industries.
 W
WHP ZCentral Remote Boost, formerly known as HP Remote Graphics Software or HP RGS is a client-server remote desktop software developed by HP Inc. and initially launched in 2003. HP RGS enables remote access to high-performance workstations from many different devices including other Workstations, PCs, Windows tablets, MacBooks and thin-clients. The software is targeted at remote access to graphic intensive applications, Video editing and complex 3D models. Collaboration, or screen sharing, between multiple users, remote USB and sound, as well as Windows and Linux are also supported. HP markets RGS for "Real-Time Collaboration", "Workstation-Class Mobility" and "Remote Workers"
 W
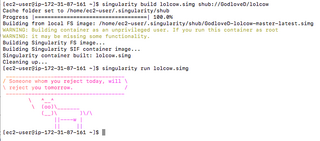
WSingularity is a free, cross-platform and open-source computer program that performs operating-system-level virtualization also known as containerization.
 W
WSmartOS is a free and open-source SVR4 hypervisor based on the UNIX operating system that combines OpenSolaris technology with Linux's KVM virtualization. Its core kernel contributed to the illumos project. It features several technologies: Crossbow, DTrace, KVM, ZFS, and Zones. Unlike other illumos distributions, SmartOS employs NetBSD pkgsrc package management. SmartOS is designed to be particularly suitable for building clouds and generating appliances. It is developed for and by Joyent, but is open-source and free for anyone to use.
 W
WSystancia is a French software company that develops software for desktop and application virtualisation, cloud computing and remote access security solutions. It was founded in 1998 and is located in Sausheim, France.
 W
WTeradici was a privately held software company founded in 2004. In 2021, HP_Inc acquired Teradici. Teradici initially developed a protocol (PCoIP) for compressing and decompressing images and sound when remotely accessing blade servers, and implemented it in hardware. This technology was later expanded to thin clients/zero clients for general Virtual Desktop Infrastructure. Teradici's protocol or hardware is used by HP, Dell-Wyse, Amulet Hotkey, Samsung, Amazon Web Services, Fujitsu, and VMware.
 W
WTurbonomic is an enterprise software company headquartered in Boston, MA. The company's product simulates supply and demand forces in order to efficiently allocate resources such as computing, database, memory and storage. It was updated in 2017 for use with cloud computing platforms.
 W
WA virtual file system (VFS) or virtual filesystem switch is an abstract layer on top of a more concrete file system. The purpose of a VFS is to allow client applications to access different types of concrete file systems in a uniform way. A VFS can, for example, be used to access local and network storage devices transparently without the client application noticing the difference. It can be used to bridge the differences in Windows, classic Mac OS/macOS and Unix filesystems, so that applications can access files on local file systems of those types without having to know what type of file system they are accessing.
 W
WIn computing, the Red Hat Virtual Machine Manager, also known as virt-manager, is a desktop virtual machine monitor.
 W
WVM is a family of IBM virtual machine operating systems used on IBM mainframes System/370, System/390, zSeries, System z and compatible systems, including the Hercules emulator for personal computers.
 W
WVMware Fusion is a software hypervisor developed by VMware for Macintosh computers. VMware Fusion allows Intel-based Macs to run virtual machines with guest operating systems—such as Microsoft Windows, Linux, NetWare, Solaris, or macOS—within the host macOS operating system.
 W
WVMware Server is a discontinued free-of-charge virtualization-software server suite developed and supplied by VMware, Inc.
 W
WVMware ThinApp is an application virtualization and portable application creator suite by VMware that can package conventional applications so that they become portable applications. According to VMware, the product has a success rate of about 90–95 % in packaging applications.
 W
WVMware vSphere is VMware's cloud computing virtualization platform.
 W
WVMware Workstation Pro is a hosted hypervisor that runs on x64 versions of Windows and Linux operating systems ; it enables users to set up virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical machine and use them simultaneously along with the host machine. Each virtual machine can execute its own operating system, including versions of Microsoft Windows, Linux, BSD, and MS-DOS. VMware Workstation is developed and sold by VMware, Inc., a division of Dell Technologies. There is a free-of-charge version, VMware Workstation Player, for non-commercial use. An operating systems license is needed to use proprietary ones such as Windows. Ready-made Linux VMs set up for different purposes are available from several sources.
 W
WVMware Workstation Player, formerly VMware Player, is a virtualization software package for x64 computers running Microsoft Windows or Linux, supplied free of charge by VMware, Inc., a company which was formerly a division of, and whose majority shareholder remains, Dell EMC. VMware Player can run existing virtual appliances and create its own virtual machines. It uses the same virtualization core as VMware Workstation, a similar program with more features, which is not free of charge. VMware Player is available for personal non-commercial use, or for distribution or other use by written agreement. VMware, Inc. does not formally support Player, but there is an active community website for discussing and resolving issues, as well as a knowledge base.
 W
WVyOS is an open source network operating system based on Debian.
 W
WWindows Virtual PC was a virtualization program for Microsoft Windows. In July 2006 Microsoft released the Windows version free of charge. In August 2006, Microsoft announced the Macintosh version would not be ported to Intel-based Macintosh computers, effectively discontinuing the product as PowerPC-based Macintosh computers would no longer be manufactured.