 W
WAdlertag was the first day of Unternehmen Adlerangriff, which was the codename of a military operation by Nazi Germany's Luftwaffe to destroy the British Royal Air Force (RAF). By June 1940, the Allies had been defeated in Western Europe and Scandinavia. Rather than come to terms with Germany, Britain rejected all overtures for a negotiated peace.
 W
WThe Air battle over the Ore Mountains took place around midday on 11 September 1944 between German and American air forces over the crest of the Ore Mountains near the village of Oberwiesenthal, above the Bohemian market town of Schmiedeberg.
 W
WThe Augsburg Raid, also referred to as Operation Margin, was a bombing raid made by the RAF on the MAN U-boat engine plant in Augsburg undertaken during the daylight hours of 17 April 1942. The mission was assigned to No. 44 (Rhodesia) Squadron and No. 97 Squadron, both of which were equipped with the new Avro Lancaster. The speed of the Lancaster and its large bombload capacity gave reason for optimism that the raid might succeed. It was the first of the attacks upon German industry in Augsburg.
 W
WAxis and Soviet air operations during Operation Barbarossa took place over a six-month period, 22 June – December, 1941. Aviation played a critical role in the fighting on the Eastern Front during this period, in the battles to gain and maintain air superiority or air supremacy, to offer close air support to armies on battlefield, interdicting enemy supply lines, while supplying friendly forces. The Axis air forces were generally better equipped, trained and experienced in executing military tactics and operations. This superiority increased because of the Great Purge in the 1930s and mass expansion of Soviet air forces, which did severe damage to organisational structures.
 W
WThe Battle of Berlin was a series of attacks on Berlin by RAF Bomber Command along with raids on other German cities to keep German defences dispersed. Air Chief Marshal Sir Arthur Harris, AOC-in-C Bomber Command, believed that "We can wreck Berlin from end to end if the USAAF come in with us. It will cost us between 400 and 500 aircraft. It will cost Germany the war".
 W
WOperation Bodenplatte (Baseplate), launched on 1 January 1945, was an attempt by the Luftwaffe to cripple Allied air forces in the Low Countries during the Second World War. The goal of Bodenplatte was to gain air superiority during the stagnant stage of the Battle of the Bulge so that the German Army and Waffen-SS forces could resume their advance. The operation was planned for 16 December 1944, but was delayed repeatedly due to bad weather until New Year's Day, the first day that happened to be suitable.
 W
WThe Bombardment of Mailly-le-Camp was an RAF raid against a German panzer training center located in northern France undertaken during the night of 3/4 May 1944. The mission was a part of the "softening up" campaign Bomber Command conducted prior to the D-Day invasion. The operation was assigned to No. 5 Group, which was joined by No. 1 Group. Estimated a lightly defended target, confusion in the mission plan and communication problems led to the force being held up at the assembly point, where German night fighters slipped in among the bombers. Though the bombers succeeded in destroying the training camp, the victory was achieved at a heavy price.
 W
WThe Minsk Blitz was the heavy bombing of the city of Minsk, the capital of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic within the Soviet Union during the Second World War. On 24 June 1941, three waves of German Luftwaffe bombers, 47 aircraft each, bombed Minsk. The Soviet anti-aircraft defense of the city was poorly organized, and panic ensued. Because the water supply was destroyed, fires could not be put down, and the city was evacuated.
 W
WThe bombing of Obersalzberg was an air raid carried out by the Royal Air Force's Bomber Command on 25 April 1945 during the last days of World War II in Europe. The operation targeted Obersalzberg, a complex of residences and bunkers in Bavaria which had been built for Adolf Hitler and other key members of Germany's leadership. Many buildings in the complex were destroyed, though Hitler's residence and the bunker network were only slightly damaged. Two Allied bombers were shot down with the loss of four airmen, and 31 Germans were killed.
 W
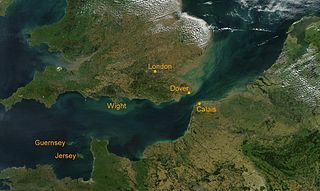
WBattle of Britain Day, 15 September 1940, is the day on which a large-scale aerial battle in the Battle of Britain took place.
 W
WThe Battle of Britain was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defended the United Kingdom (UK) against large-scale attacks by Nazi Germany's air force, the Luftwaffe. It has been described as the first major military campaign fought entirely by air forces. The British officially recognise the battle's duration as being from 10 July until 31 October 1940, which overlaps the period of large-scale night attacks known as the Blitz, that lasted from 7 September 1940 to 11 May 1941. German historians do not accept this subdivision and regard the battle as a single campaign lasting from July 1940 to June 1941, including the Blitz.
 W
WOperation Catechism was a British air raid of World War II that destroyed the German battleship Tirpitz. It was conducted on 12 November 1944 by 29 Royal Air Force heavy bombers that attacked the battleship at its anchorage near the Norwegian city of Tromsø. The ship capsized after being hit by at least two bombs and damaged by the explosions of others, killing between 940 and 1,204 members of the crew; the British suffered no casualties.
 W
WThe German city of Cologne was bombed in 262 separate air raids by the Allies during World War II, all by the Royal Air Force (RAF) but for a single failed post-capture test of a guided missile by the United States Army Air Forces. A total of 34,711 long tons of bombs were dropped on the city by the RAF. 20,000 people died during the war in Cologne due to aerial bombardments.
 W
WThe Combined Bomber Offensive (CBO) was an Allied offensive of strategic bombing during World War II in Europe. The primary portion of the CBO was against Luftwaffe targets which was the highest priority from June 1943 to 1 April 1944. The subsequent highest priority campaigns were against V-weapon installations and petroleum, oil, and lubrication (POL) plants. Additional CBO targets included railyards and other transportation targets, particularly prior to the invasion of Normandy and, along with army equipment, in the final stages of the war in Europe.
 W
WUnternehmen Donnerkeil was the codename for a German military operation of the Second World War. Donnerkeil was designed as an air superiority operation to support the Kriegsmarine's Operation Cerberus, also known as the Channel Dash.
 W
WOperation Frantic was a series of seven shuttle bombing operations during World War II conducted by American aircraft based in Great Britain and southern Italy which then landed at three Soviet airfields in Ukraine. The aircraft in the Ukraine then flew bombing missions en route to their bases in Italy and Great Britain. The operation ran between June and September, 1944.
 W
WOperation Gisela was the codename for a German military operation of the Second World War. Gisela was designed as an aerial intruder operation to support the German air defence system in its night battles with RAF Bomber Command during the Defence of the Reich campaign. It was the last major operation launched by the Luftwaffe Nachtjagdgeschwader during the conflict.
 W
WThe Hardest Day is a Second World War air battle fought on 18 August 1940 during the Battle of Britain between the German Luftwaffe and British Royal Air Force (RAF). On that day, the Luftwaffe made an all-out effort to destroy RAF Fighter Command. The air battles that took place on that day were amongst the largest aerial engagements in history to that time. Both sides suffered heavy losses. In the air, the British shot down twice as many Luftwaffe aircraft as they lost. However, many RAF aircraft were destroyed on the ground, equalising the total losses of both sides. Further large and costly aerial battles took place after 18 August, but both sides lost more aircraft combined on this day than at any other point during the campaign, including 15 September, the Battle of Britain Day, generally considered the climax of the fighting. For this reason, Sunday 18 August 1940 became known as "the Hardest Day" in Britain.
 W
WThe Battle of the Heligoland Bight was the first "named" air battle of the Second World War, which began the longest air campaign of the war, the Defence of the Reich. On 3 September 1939, the United Kingdom declared war on Nazi Germany after the German invasion of Poland, which started the European War. The British did not assist Poland by land or sea but RAF Bomber Command flew several missions against German targets. A number of these air raids were directed at Kriegsmarine warships in German ports to prevent their use in the Battle of the Atlantic. With the front lines static between September 1939 and May 1940, a period known as the "Phoney War" set in, with little fighting on land or in the air.
 W
WOperation Jericho on 18 February 1944 during the Second World War, was an Allied bombing raid, at very low altitude, on Amiens Prison in German-occupied France to blow holes in the prison walls, kill German guards and use shock waves to spring open cell doors. The French Resistance was waiting on the outside to rescue prisoners who got out and spirit them away.
 W
WThe Kammhuber Line was the Allied name given to the German night air defense system established in July 1940 by Colonel Josef Kammhuber. It consisted of a series of control sectors equipped with radars and searchlights and an associated night fighter. Each sector would direct the night fighter into visual range with target bombers.
 W
WThe Kanalkampf was the German term for air operations by the Luftwaffe against the British Royal Air Force (RAF) over the English Channel in July 1940. The air operations over the Channel began the Battle of Britain during the Second World War. By 25 June, the Allies had been defeated in Western Europe and Scandinavia. Britain rejected peace overtures and on 16 July, Adolf Hitler issued Directive 16 to the Wehrmacht, ordering preparations for an invasion of Britain, under the codename Unternehmen Seelöwe.
 W
WOperation EF (1941), also the Raid on Kirkenes and Petsamo took place on 30 July 1941, during the Second World War. After the beginning of Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941, Fleet Air Arm aircraft flew from the aircraft carriers HMS Victorious and Furious to attack merchant vessels in the northern Norwegian port of Kirkenes and the north Finnish port of Liinakhamari in Petsamo.
 W
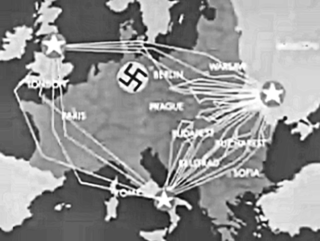
WOperation Kutuzov was the first of the two counteroffensives launched by the Red Army as part of the Kursk Strategic Offensive Operation. It commenced on 12 July 1943, in the Central Russian Upland, against Army Group Center of the German Wehrmacht. The operation was named after General Mikhail Kutuzov, the Russian general credited with saving Russia from Napoleon during the French invasion of Russia in 1812. Operation Kutuzov was one of two large-scale Soviet operations launched as counteroffensives against Operation Citadel. The Operation began on 12 July and ended on 18 August 1943 with the capture of Orel and collapse of the Orel bulge.
 W
WThe Siege of Malta in World War II was a military campaign in the Mediterranean Theatre. From June 1940 to November 1942, the fight for the control of the strategically important island of the British Crown Colony of Malta pitted the air forces and navies of Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany against the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Royal Navy.
 W
WOperation Obviate was an unsuccessful British air raid of World War II which targeted the German battleship Tirpitz. It was conducted by Royal Air Force heavy bombers on 29 October 1944, and sought to destroy the damaged battleship after she moved to a new anchorage near Tromsø in northern Norway.
 W
WOperation Oyster was a bombing raid made by the Royal Air Force (RAF) on 6 December 1942 upon the Philips works at Eindhoven, Netherlands. The Philips company was a major producer of electronics equipment, including vacuum tubes for radio communication. Prior to the Battle of the Netherlands in 1940, Philips was known to be a leading research firm in infrared and radar technology. To ensure accuracy and minimise casualties among the Dutch citizens, the raid had to be undertaken during the day.
 W
WUnternehmen Paula is the German codename given for the Second World War Luftwaffe offensive operation to destroy the remaining units of the Armée de l'Air (ALA), or French Air Force during the Battle of France in 1940. On 10 May the German armed forces (Wehrmacht) began their invasion of Western Europe. By 3 June, the British Army had withdrawn from Dunkirk and the continent in Operation Dynamo, the Netherlands and Belgium had surrendered and most of the formations of the French Army were disbanded or destroyed. To complete the defeat of France, the Germans undertook a second phase operation, Fall Rot, to conquer the remaining regions. In order to do this, air supremacy was required. The Luftwaffe was ordered to destroy the French Air Forces, while still providing support to the German Army.
 W
WOperation Retribution, also known as Operation Punishment, was the April 1941 German bombing of Belgrade, the capital of Yugoslavia, in retaliation for the coup d'état that overthrew the government that had signed the Tripartite Pact. The bombing occurred in the first days of the German-led Axis invasion of Yugoslavia during World War II. The Royal Yugoslav Army Air Force (VVKJ) had only 77 modern fighter aircraft available to defend Belgrade against the hundreds of German fighters and bombers that struck in the first wave early on 6 April. Three days prior, VVKJ Major Vladimir Kren had defected to the Germans, disclosing the locations of multiple military assets and divulging the VVKJ's codes.
 W
WOperation Orator was the code name for the defence of the Allied Arctic convoy PQ 18 by British and Australian air force units based temporarily in North-West Russia, against attack by the German battleship Tirpitz and other Kriegsmarine surface vessels. The wing, known as the Search & Strike Force, was commanded by Group Captain Frank Hopps and its maritime strike element was the Leuchars Wing, comprising No. 144 Squadron, Royal Air Force (RAF) and No. 455 Squadron, Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) equipped with Handley-Page Hampden TB 1 torpedo bombers.
 W
WThe Pointblank directive authorised the initiation of Operation Pointblank, the code name for the primary portion of the Allied Combined Bomber Offensive intended to cripple or destroy the German aircraft fighter strength, thus drawing it away from frontline operations and ensuring it would not be an obstacle to the invasion of Northwest Europe. The Pointblank directive of 14 June 1943 ordered RAF Bomber Command and the U.S. Eighth Air Force to bomb specific targets such as aircraft factories, and the order was confirmed when the Allies met at the Quebec Conference, 1943.
 W
WOperation Steinbock, sometimes called the Baby Blitz, was a strategic bombing campaign by the German Air Force during the Second World War. It targeted southern England and lasted from January to May 1944. Steinbock was the last strategic air offensive by the German bomber arm during the conflict.
 W
WOperation Tidal Wave was an air attack by bombers of the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) based in Libya and Southern Italy on nine oil refineries around Ploiești, Romania on 1 August 1943, during World War II. It was a strategic bombing mission and part of the "oil campaign" to deny petroleum-based fuel to the Axis powers. The mission resulted in "no curtailment of overall product output."
 W
WThe Western Allied Campaign in Romania consisted of war declarations and aerial operations during the Second World War by 8 Western Allied countries against Romania which itself was primarily engaged on the Eastern Front in fighting against the Soviet Union.