 W
WThe 22mm rifle grenade is inserted over the firing mechanism on the front of rifles that are equipped with the appropriate spigot-type launcher, either in the form of an integral flash suppressor or a detachable adapter. As with most rifle grenades, it is propelled by a blank cartridge inserted into the chamber of the rifle. A 22mm grenade can range from powerful anti-tank rounds to simple finned tubes with a fragmentation hand grenade attached to the end. The "22mm" refers to the diameter of the base tube which fits over the spigot of the launcher, not the diameter of the warhead section, which is much wider.
 W
WThe AC 58 is an anti-armour rifle grenade used by the French Army. Its official French Army designation is Grenade à fusil antichar de 58 mm Mle F1 PAB.
 W
WThe APAV 40 is a 40 mm dual purpose rifle grenade used by the French Army.
 W
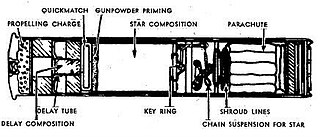
WThe Fallschirm Leuchtpatrone or "parachute light cartridge" in English was a non-lethal star shell that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Fallschirm Leuchtpatrone was designed to be fired from a Kampfpistole flare gun.
 W
WThe Gewehr-Granatpatrone 40 or GGP/40 for short was a shaped charge rifle grenade used by German forces during the Second World War. It was originally developed for Luftwaffe Fallschirmjäger units to provide them with a light and portable anti-tank weapon.
 W
WThe Gewehr-Panzergranate was a shaped charge rifle grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
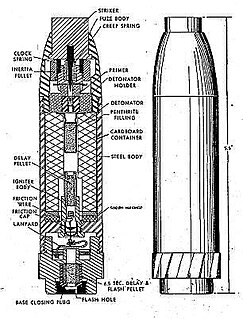
WThe Gewehr-Sprenggranate was a high-explosive rifle grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Große Gewehr-Panzergranate was a shaped charge rifle grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Grosse Panzergranate 46 & 61 were shaped charge rifle grenades that were developed by Germany and used by the Waffen-SS during World War II.
 W
WThe Hales rifle grenade is the name for several rifle grenades used by British forces during World War I. All of these are based on the No. 3 design.
 W
WThe Spanish munitions company Instalaza made two models of rifle grenade during the 1960s. As well as being used by the Spanish Army, the Portuguese Army also used them in the colonial wars that took place in its colonies in Africa.
 W
WThe Kampfpistole or "combat pistol" in English was a flare gun introduced into German service during 1939 and served throughout World War II.
 W
WThe Leuchtpistole 34 or flare gun in English was introduced into German service before World War II and served throughout World War II.
 W
WThe Leuchtpistole 42 or flare gun in English was introduced into German service in 1943 and served throughout World War II.
 W
WThe M1 grenade projection adapter was an expedient rifle grenade used by the American military in World War II, Korea, and Vietnam. It consisted of an add-on 22 mm stabilizer tube and fins that converted a hand-grenade into a rifle grenade. It supplanted the M17 rifle grenade, and was eventually made obsolete by the 40 mm M79 grenade launcher.
 W
WThe M9 rifle grenade was a U S anti-tank rifle grenade used during World War II. It was derived as a lighter version of the M10 grenade which was too heavy to be fired to an effective distance from a rifle.
 W
WThe M17 is a rifle grenade that was used by the United States during World War II.
 W
WThe M31 HEAT is a fin-stabilized anti-tank rifle grenade designed in the late 1950s to replace the Belgian ENERGA rifle grenade which was adopted by the US Army and US Marines as an emergency stop-gap measure during the Korean War. Like the ENERGA, it has a nose-initiated, based-detonated HEAT warhead, but unlike the ENERGA, the mechanical impact fuse system is replaced with a less complex and more reliable piezo-electric fuse system which also allows higher angles of impact, up to 65 degrees.
 W
WThe Modèle 1952 34mm HE rifle grenade was in French service from 1952 to 1978. It was used alongside the APAV40 rifle grenade in French service. It was propelled by being mounted atop a rifle's 22 mm grenade launching adapter, and being launched by a ballistite (blank) cartridge.
 W
WYugoslavia manufactured two types of rifle grenade, both with the nomenclature of M60. The M60 anti-personnel rifle grenade bore a resemblance to the French M52 rifle grenade. The M60 anti-tank rifle grenade bore a resemblance to the STRIM 65, also of French origin. It could penetrate 200mm of armour.
 W
W"Mills bomb" is the popular name for a series of British hand grenades. They were the first modern fragmentation grenades used by the British Army and saw widespread use in the First and Second World Wars.
 W
WThe Nebelpatrone or "fog cartridge" in English was a non-lethal smoke grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Nebelpatrone was designed to be fired from a Kampfpistole flare gun.
 W
WThe Grenade, Rifle No. 68 / Anti-Tank was a British anti-tank rifle grenade used during the Second World War and was one of the first operational weapons to utilise the shaped charge principle.
 W
WThe Panzerwurfkörper 42 was a HEAT grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Panzerwurfkörper 42 was designed to be fired from a Leuchtpistole or flare gun in English.
 W
WThe Propaganda-Gewehrgranate was a non-lethal rifle grenade designed to deliver propaganda leaflets that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II.
 W
WThe Schiessbecher grenade launcher or Gewehrgranatgerät was used by German forces in World War II. The device was introduced as of 1942 and based on rifle grenade launcher models designed during World War I. The Schiessbecher was intended to replace all previous rifle grenade launcher models.
 W
WThe SIMON is an Israeli bullet-trap rifle grenade designed to breach through doors, developed by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems. It is intended for use with 5.56 mm rifles such as the M4 carbine.
 W
WThe Sprengpatrone or "explosive cartridge" in English was a rifle grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Sprengpatrone was designed to be fired from a Kampfpistole flare gun.
 W
WThe STRIM 40 is an anti-personnel rifle grenade of French design and manufacture.
 W
WThe STRIM 65 is an anti-tank rifle grenade that the French Army used from 1961 to 1978, under the designation 65 AC 28. This and the older 73mm Modèle 1950 were the standard anti-tank munitions in French service. A 22 mm grenade launching adapter mounted atop the rifle's barrel held the grenade until the firing of a ballistite (blank) cartridge provided the propulsive force to launch the grenade.
 W
WThe Type 06 rifle grenade is a rifle grenade used by the JGSDF. It can be launched from the Howa Type 89 or Howa Type 64 rifles without other attachments.
 W
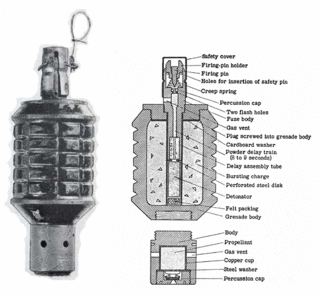
WThe Type 91 Hand Grenade was an improved version of the Type 10 fragmentation hand grenade/rifle grenade of the Imperial Japanese Army. Although superseded as a hand-thrown weapon by the Type 97 by the start of World War II it was still used by units in the Second Sino-Japanese War and by reserve forces, as well as the Japanese Navy's Special Naval Landing Forces.
 W
WThe Type 100 grenade discharger was introduced in 1939 as a grenade launcher for the Type 38 and Type 99 Arisaka Rifles. It launches standard Type 91 and Type 99 hand-grenades. The launcher is somewhat unusual in that rather than using the more common cup designs it is a gas trap system, meaning that it incorporates a barrel extension which taps off excess propellant gases to launch the grenade from a cup offset from the barrel. This has the advantage that standard rifle cartridges could be used along with the standard hand-grenades which simplified logistics, at the expense of increased weight and decreased efficiency. The effective range is approximately 100 yards (91 m).
 W
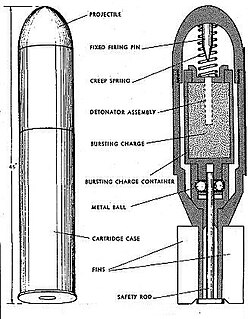
WThe Viven-Bessières rifle grenade, named after its inventors ·, also known as "VB grenade", and officially referred to as the "Viven-Bessières shell" in the French Army instruction manual, was an infantry weapon in use with the French Army from 1916 onwards.
 W
WThe Wurfgranate Patrone 326 was a small grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Wurfgranate Patrone 326 was designed to be fired from a Leuchtpistole or flare gun in English.
 W
WThe Wurfkörper 361 was a grenade that was developed by Germany and used by the Wehrmacht during World War II. The Wurfkörper 361 was designed to be fired from a Leuchtpistole or flare gun in English.