 W
WIgnacio José de Allende y Unzaga, born Ignacio Allende y Unzaga, was a captain of the Spanish Army in Mexico who came to sympathize with the Mexican independence movement. He attended the secret meetings organized by Josefa Ortiz de Domínguez, where the possibility of an independent New Spain was discussed. He fought along with Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla in the first stage of the struggle, eventually succeeding him in leadership of the rebellion. Allende was captured by Spanish colonial authorities while he was in Coahuila and executed for treason in Chihuahua.
 W
WAntonio Azarola y Gresillón was a Spanish Navy officer, rear admiral of the Spanish Republican Navy. He was executed by firing squad on 4 August 1936 at the Ferrol Naval Base in Galicia, NW Spain, by rebel Navy officers for refusing to join the coup of July 1936 against the Spanish Republic that triggered the Spanish Civil War.
 W
WFrancisca Cualladó Baixauli was a Spanish Catholic seamstress born in Molino de San Isidro, ward of Ruzafa, Valencia, who was executed by firing squad at the Torre Espioca of Benifaió in 1936, during the Spanish Civil War. She was considered a martyr by the Catholic Church, and beatified by Pope John Paul II on 11 March 2001. Her feast day is celebrated on September 19.
 W
WEduardo Barriobero y Herrán was a lawyer and activist in the Confederación Nacional del Trabajo.
 W
WMaría Gertrudis Teodora Bocanegra Mendoza was a woman who fought in the Mexican War of Independence. She was arrested, tortured and executed in 1817.
 W
WJosé Joaquín Justo Camacho Lago was a Neogranadine statesman, lawyer, journalist and professor, who worked for the Independence of the New Granada, what is now Colombia, and participated in the Open Cabildo which declared the Act of Independence, of which he was also a signer. He was executed during the Reign of Terror of Pablo Morillo after the Spanish invasion of New Granada.
 W
WManuel Carrasco i Formiguera, was a Spanish lawyer and Christian democrat Catalan nationalist politician. His execution, by order of Francisco Franco, provoked protests from Catholic journalists such as Joseph Ageorges, the President of the International Federation of Catholic Journalists. Ageorges wrote, "Even more than the death of the Duke of Enghien stained the memory of Napoleon, the death of Carrasco has stained the reputation of Franco". Such protests, in turn, provoked the anger of the Francoist press. His funeral in Paris on 27 April 1938 was attended by many notable people, including Joan Miró, Ossorio y Gallardo, Josep M. de Sagarra, Joaquim Ventalló and Jacques Maritain and his wife Raissa.
 W
WFrancesc de Paula Castelló Aleu was a Spanish Roman Catholic killed during the Spanish Civil War on false accusations of fascism. Castelló was noted for his devout and outgoing nature in addition for his activism in Christian movements such as the Catholic Action; he had friends from these movements and in one met his fiancée though his death broke their soon-to-be union. He worked as a chemist for a time prior to conscription into the armed services on the eve of the civil war.
 W
WRoberto Cofresí y Ramírez de Arellano, better known as El Pirata Cofresí, was a pirate from Puerto Rico. He was born into a noble family, but the political and economic difficulties faced by the island as a colony of the Spanish Empire during the Latin American wars of independence meant that his household was poor. Cofresí worked at sea from an early age which familiarized him with the region's geography, but it provided only a modest salary, and he eventually decided to abandon the sailor's life and became a pirate. He had previous links to land-based criminal activities, but the reason for Cofresí's change of vocation is unknown; historians speculate that he may have worked as a privateer aboard El Scipión, a ship owned by one of his cousins.
 W
WLluís Companys i Jover was a Spanish politician from Catalonia who served as president of Catalonia from 1934 and during the Spanish Civil War.
 W
WIsidoro Diéguez Dueñas was a Spanish bricklayer who joined the Spanish Communist Party, fought in the Spanish Civil War (1936–39) and went into exile. When he returned from Mexico to Portugal he was arrested by the police and handed over to the Spanish authorities, who executed him.
 W
WDomènec Batet i Mestres was a Spanish military man who became general of the Spanish Army.
 W
WFederico Fernández-Cavada was an officer in the Union Army during the American Civil War and a diplomat, as well as commander-in-chief of all the Cuban forces during Cuba's Ten Years' War. Because of his artistic talents, he was assigned to the Hot Air Balloon Unit of the Union Army. From the air he sketched what he observed of enemy positions and movements. On April 19, 1862, Fernández Cavada sketched enemy positions from Thaddeus Lowe's Constitution balloon during the Peninsular Campaign in Virginia.
 W
WFrancisco Ferrer i Guàrdia (1859–1909) was a radical freethinker, anarchist, and educationist behind a network of secular, private, libertarian schools in and around Barcelona. His execution, following a revolt in Barcelona, propelled Ferrer into martyrdom and grew an international movement of radicals and libertarians, who established schools in his model and promoted his schooling approach.
 W
WPedro Felipe Figueredo, mostly known as Perucho was a Cuban poet, musician, and freedom fighter of the 19th century. In the 1860s, he was active in the planning of the Cuban uprising against the Spanish known as the Ten Years' War.
 W
WBebel García García was a Spanish football player and politician from Galicia.
 W
WCeferino Giménez Malla was a Spanish Romani, a Roman Catholic catechist and activist for Spanish Romani causes, considered the patron saint of Romani people in Roman Catholicism. A victim of the Spanish Republican militias during the Civil War, Ceferino Giménez Malla was beatified on May 4, 1997; May 4 is also his feast day.
 W
WManuel Goded Llopis was a Spanish Army general who was one of the key figures in the July 1936 revolt against the democratically elected Second Spanish Republic. Having unsuccessfully led an attempted insurrection in Barcelona, he was captured and executed by the Republican government. Previously, Goded had distinguished himself in the Battle of Alhucemas of the Rif War.
 W
WDon Miguel Gregorio Antonio Ignacio Hidalgo y Costilla y Gallaga Mandarte Villaseñor, more commonly known as Don Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla or Miguel Hidalgo, was a Criollo Catholic priest, leader of the Mexican War of Independence and recognized as the Father of the Nation.
 W
WDon Diego de León y Navarrete was a Spanish military figure. As a young man, he entered the Spanish army as a cavalryman and achieved the rank of captain at the age of 17.
 W
WJorge Tadeo Lozano, Viscount of Pastrana was a Neogranadine scientist, journalist, and politician who presided over the Constituent College of Cundinamarca and was elected President of Cundinamarca in 1811.
 W
WMariano Matamoros y Guridi was a Mexican Roman Catholic priest and revolutionary rebel soldier of the Mexican War of Independence, who fought for independence against Spain in the early 19th century.
 W
WGeneral Martín Francisco Javier Mina y Larrea, nicknamed El Mozo or El Estudiante (Student), was a Spanish lawyer and army officer, who later became a Mexican independence figure.
 W
WJosé María Teclo Morelos Pérez y Pavón was a Mexican Roman Catholic priest and revolutionary rebel leader who led the Mexican War of Independence movement, assuming its leadership after the execution of Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla in 1811. Morelos and Ignacio López Rayón are credited with organizing the war of independence. Under Morelos the Congress of Anáhuac was installed on 13 September 1813, and in 6 November of the same year congress declared the country's independence. On 22 October 1814, a constitution, Decreto Constitucional para la Libertad de la América Mexicana, was drafted by the Congress which declared that Mexico would be a Republic.
 W
WPedro Muñoz Seca was a Spanish comic playwright. He was one of the most successful playwrights of his era. He wrote approximately 300 dramatic works, both sainetes and longer plays, often in collaboration with Pedro Pérez Fernández or Enrique García Álvarez. His most ambitious and best known play is La venganza de Don Mendo ; other major works include La barba de Carrillo and Pepe Conde (1920).
 W
WAntonio Ortega Gutiérrez was a Spanish Republican military officer and acting president of Madrid Football Club between 1937 and 1938 during the Spanish Civil War; directly involved in the defense of Madrid.
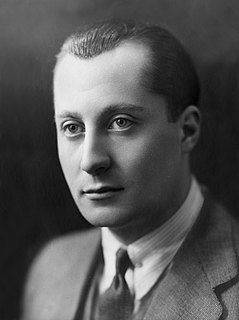 W
WJosé Antonio Primo de Rivera y Sáenz de Heredia, 1st Duke of Primo de Rivera, 3rd Marquess of Estella, often referred to simply as José Antonio, was a Spanish politician who founded the fascist Falange Española, later Falange Española de las JONS.
 W
WApolinario de la Cruz, better known as Hermano Pule, was a Filipino religious leader who founded and led the Cofradía de San José. The cofradía was established in 1832 in response to the racially discriminatory practices of the Catholic Church in the Philippines. During the Spanish colonial period, Catholic religious orders refused to admit native Filipinos as members. In retaliation, Pule established his own religious order that was exclusive for native Filipinos. During its peak, the cofradía had 4,500 to 5,000 members from the provinces of Tayabas, Batangas, and Laguna. Fearing an armed rebellion, the Spanish colonial government sent military forces to suppress the cofradía, an attack that was resisted by Hermano Pule and his followers on October 23, 1841. However, more troops were sent and the cofradía was finally quelled by the colonial military forces on November 1, 1841. Pule was then captured, tried, and executed.
 W
WCayetano Redondo Aceña was a Spanish politician, typographer, journalist and esperantist. A member of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party, he served as Mayor of Madrid from November 1936 to May 1937, during the Spanish Civil War.
 W
WJosé Protasio Rizal Mercado y Alonso Realonda was a Filipino nationalist and polymath during the tail end of the Spanish colonial period of the Philippines. He is considered the national hero of the Philippines. An ophthalmologist by profession, Rizal became a writer and a key member of the Filipino Propaganda Movement, which advocated political reforms for the colony under Spain.
 W
WPolicarpa Salavarrieta, also known as "La Pola", was a Neogranadine seamstress who spied for the Revolutionary Forces during the Spanish Reconquista of the Viceroyalty of New Granada. She was captured by Spanish Royalists and ultimately executed for high treason. The Day of the Colombian Woman is commemorated on the anniversary of her death. She is now considered a heroine of the independence of Colombia.
 W
WMaría Antonia Santos Plata, was a Neogranadine peasant, rebel leader and heroine.
 W
WMaria Silva Cruz was a Spanish anarchist and a hero of the Casas Viejas Uprising in Spain. She was also known as "La Libertaria."
 W
WJose Maria Torrijos y Uriarte, Count of Torrijos, a title granted posthumously by the Queen Governor, also known as General Torrijos, was a Spanish Liberal soldier. He fought in the Spanish War of Independence and after the restoration of absolutism by Ferdinand VII in 1814 he participated in the pronouncement of John Van Halen of 1817 that sought to restore the Constitution of 1812, for which he spent two years in prison until he was released after the triumph of the Riego uprising in 1820. He returned to fight the French when the Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis invaded Spain to restore the absolute power of Ferdinand VII and when those triumphed ending the liberal triennium exiled to England. There he prepared a statement which he himself led, landing on the coast of Málaga from Gibraltar on December 2, 1831, with sixty men accompanying him, but they fell into the trap that had been laid before him by the absolutist authorities and were arrested. Nine days later, on December 11, Torrijos and 48 of his fellow survivors were shot without trial on the beach of San Andres de Málaga, a fact that was immortalized by a sonnet of José de Espronceda entitled To the death of Torrijos and his Companions, Enrique Gil y Carrasco's A la memoria del General Torrijos, and by a famous painting that was painted in 1888 by Antonio Gisbert. "The tragic outcome of his life explains what has happened to history, in all fairness, as a great symbol of the struggle against despotism and tyranny, with the traits of epic nobility and serenity typical of the romantic hero, eternalized in the famous painting by Antonio Gisbert." The city of Málaga erected a monument to Torrijos and his companions in the Plaza de la Merced, next to the birthplace of the painter Pablo Picasso. Under the monument to Torrijos in the middle of the square are the tombs of 48 of the 49 men shot; One of them, British, was buried in the English cemetery (Málaga).
 W
W"Las Trece Rosas" is the name given in Spain to a group of thirteen young women who were executed by a Francoist firing squad just after the conclusion of the Spanish Civil War. Their execution was part of a massive execution campaign known as the "saca de agosto", which included 43 young men.
 W
WAntonio Villavicencio y Verástegui was a statesman and soldier of New Granada, born in Quito, and educated in Spain. He served in the Battle of Trafalgar as an officer in the Spanish Navy with the rank of Second Lieutenant. He was sent as a representative of the Spanish Crown to New Granada, where his arrival was used as an excuse in Santafé de Bogotá to start a revolt; this was known as the Florero de Llorente, which culminated in the proclamation of independence from Spain. After this incident he resigned his office and joined the cause of independence. He was later captured and became the first martyr executed during the reign of terror of Pablo Morillo.
 W
WMartín Zurbano Baras was a Spanish military figure. A guerrilla leader, he is considered a "martyr to Spanish liberty".