 W
WAcetrizoic acid is a pharmaceutical drug that was used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging. It was applied in form of its salt, sodium acetrizoate, but is no longer in clinical use.
 W
WBarium sulfate (or sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula BaSO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium and materials prepared from it. The white opaque appearance and its high density are exploited in its main applications.
 W
WBarium sulfate suspension, often simply called barium, is a contrast agent used during X-rays. Specifically it is used to improve visualization of the gastrointestinal tract on plain X-ray or computed tomography. It is taken by mouth or used rectally.
 W
WDiatrizoate, also known as amidotrizoate, is a contrast agent used during X-ray imaging. This includes visualizing veins, the urinary system, spleen, and joints, as well as computer tomography. It is given by mouth, injection into a vein, injection into the bladder, through a nasogastric tube, or rectally.
 W
WDiodone was a radiocontrast agent used in urography. It was usually formulated as a salt with diethanolamine.
 W
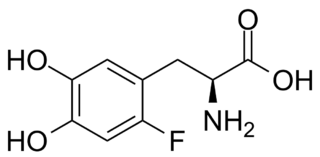
WFluorodopa, also known as FDOPA, is a fluorinated form of L-DOPA primarily synthesized as its fluorine-18 isotopologue for use as a radiotracer in positron emission tomography (PET).
 W
WFlutemetamol (18F) is a PET scanning radiopharmaceutical containing the radionuclide fluorine-18, used as a diagnostic tool for Alzheimer's disease.
 W
WIobenzamic acid is a pharmaceutical drug used as an X-ray contrast agent.
 W
WIobitridol is a pharmaceutical drug used as a radiocontrast agent in X-ray imaging. It is injected into blood vessels, joints, or body cavities such as the uterus, and filtered out by the kidneys. Its most common adverse effect is nausea. Severe allergic reactions are rare.
 W
WIocarmic acid is a pharmaceutical drug used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging in the 1970s and 80s. Uses included imaging of the uterus and Fallopian tubes. It was applied in form of its salt, meglumine iocarmate.
 W
WIocetamic acid is a pharmaceutical drug taken by mouth and used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging of the gall bladder.
 W
WIodamide is a pharmaceutical drug used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging. Its uses include imaging of the uterus and Fallopian tubes.
 W
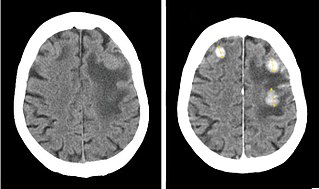
WIodinated contrast is a form of intravenous radiocontrast agent containing iodine, which enhances the visibility of vascular structures and organs during radiographic procedures. Some pathologies, such as cancer, have particularly improved visibility with iodinated contrast.
 W
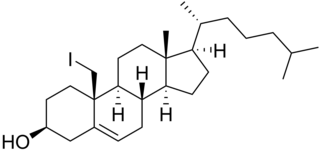
WIodocholesterol, or 19-iodocholesterol, also as iodocholesterol (131I) (INN), is a derivative of cholesterol with an iodine atom in the C19 position and a radiopharmaceutical. When the iodine atom is a radioactive isotope, it is used as an adrenal cortex radiocontrast agent in the diagnosis of patients suspected of having Cushing's syndrome, hyperaldosteronism, pheochromocytoma, and adrenal remnants following total adrenalectomy.
 W
WIodoxamic acid is an organoiodine compound used as a radiocontrast agent. It features both a high iodine content as well as several hydrophilic groups.
 W
WIoflupane (123I) is the international nonproprietary name (INN) of a cocaine analogue which is a neuro-imaging radiopharmaceutical drug, used in nuclear medicine for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and the differential diagnosis of Parkinson's disease over other disorders presenting similar symptoms. During the DaT scan procedure it is injected into a patient and viewed with a gamma camera in order to acquire SPECT images of the brain with particular respect to the striatum, a subcortical region of the basal ganglia. The drug is sold under the brand name Datscan and is manufactured by GE Healthcare, formerly Amersham plc.
 W
WIoglicic acid is a pharmaceutical drug that was used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging, in form of its salt meglumine ioglicate. Uses included imaging of the brain, the aorta and femoral arteries, and the urinary system.
 W
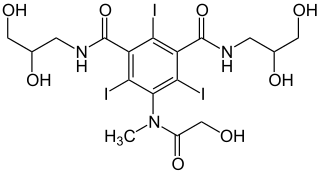
WIohexol, sold under the trade name Omnipaque among others, is a contrast agent used for X-ray imaging. This includes when visualizing arteries, veins, ventricles of the brain, the urinary system, and joints, as well as during computed tomography. It is given by mouth, injection into a vein, or into a body cavity.
 W
WIomeprol is a pharmaceutical drug used as a radiocontrast agent in X-ray imaging. It is sold under the trade names Imeron and Iomeron.
 W
WIopamidol (INN), sold under the brand name Isovue among others, is a nonionic, low-osmolar iodinated contrast agent, developed by Bracco Diagnostics.
 W
WIopanoic acid is an iodine-containing radiocontrast medium used in cholecystography. Both iopanoic acid and ipodate sodium are potent inhibitors of thyroid hormone release from thyroid gland, as well as of peripheral conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3). These compounds inhibit 5'deiodinase (5'DID-1 and 5'DID-2) enzymes, which catalyse T4-T3 conversion in the thyroid cell, liver, kidney, skeletal muscle, heart, brain, pituitary. This accounts for the dramatic improvement in both subjective and objective symptoms of hyperthyroidism, particularly when they are used as an adjunctive therapy with thioamides (propylthiouracil, carbimazole). They can be used in the treatment of patients with severe thyrotoxicosis (thyroid storm) and significant morbidity (e.g., myocardial infarction, or stroke) for rapid control of elevated plasma triiodothyronine concentrations. The use of iopanoic acid for treatment of thyrotoxicosis has been discontinued in the United States.
 W
WIopentol is a pharmaceutical drug that was used as a radiocontrast agent for X-ray imaging in Europe.
 W
WIopromide is an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging. It is marketed under the name Ultravist which is produced by Bayer Healthcare. It is a low osmolar, non-ionic contrast agent for intravascular use; i.e., it is injected into blood vessels.
 W
WIopydol is a pharmaceutical drug used as a radiocontrast agent in X-ray imaging.
 W
WIotalamic acid is an iodine-containing radiocontrast agent. It is available in form of its salts, sodium iotalamate and meglumine iotalamate. It can be given intravenously or intravesically.
 W
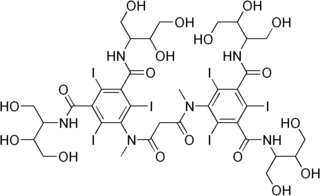
WIotrolan is an iodine-containing radiocontrast agent, a substance used to improve the visibility of body structures on images obtained by X-ray techniques.
 W
WIoversol is an organoiodine compound that is used as a contrast medium. It features both a high iodine content, as well as several hydrophilic groups. It is used in clinical diagnostics including arthrography, angiocardiography and urography.
 W
WIoxaglic acid is pharmaceutical drug used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging. It has low osmolality, typically resulting in fewer side effects than high-osmolality media. It is manufactured by Guerbet, but marketing in the US has been discontinued. As of 2021, it may still be available in some European countries.
 W
WIoxilan is a diagnostic contrast agent. It is injected intravenously before taking X-ray images to increase arterial contrast in the final image. It was marketed in the US under the trade name Oxilan by Guerbet, L.L.C., but has been discontinued in 2017.
 W
WIoxitalamic acid is a pharmaceutical drug used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging. It is used in form of its salts, ioxitalamate sodium and ioxitalamate meglumine.
 W
WIpodate sodium is an iodine-containing radiopaque contrast media used for X-rays. The drug is given orally and the resulting contrast allows for easy resolution of the bile duct and gall bladder.
 W
WMethiodal is a pharmaceutical drug that was used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging. Its uses included myelography ; for this use, cases of adhesive arachnoiditis have been reported, similar to those seen under the contrast medium iofendylate.
 W
WMetrizamide is a non-ionic iodine-based radiocontrast agent. It is also a density gradient medium for the centrifugation of biological particles.
 W
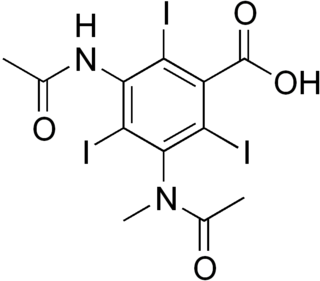
WMetrizoic acid is a pharmaceutical drug that was used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging. Its uses included angiography and urography, but it has been discontinued, at least in the US.
 W
WPropyliodone is a molecule used as a contrast medium in bronchography. It was developed by a team at Imperial Chemical Industries in the late 1930s.
 W
WTechnetium (99mTc) etarfolatide is an investigational non-invasive, folate receptor-targeting companion imaging agent that is being developed by Endocyte. Etarfolatide consists of a small molecule targeting the folate receptor and an imaging agent, which is based on technetium-99m. This companion imaging agent identifies cells expressing the folate receptor, including cancer and inflammatory cells.
 W
WThorotrast is a suspension containing particles of the radioactive compound thorium dioxide, ThO2, that was used as a radiocontrast agent in medical radiography in the 1930s and 1940s. Use in some countries, such as the U.S., continued into the 1950s.