 W
WAestus is a hypergolic liquid rocket engine used on an upper stage of Ariane 5 family rockets for the orbital insertion. It features unique design of 132 coaxial injection elements causing swirl mixing of the MMH propellants with Nitrogen tetroxide oxidizer. The pressure-fed engine allows for multiple re-ignitions.
 W
WThe AJ10 is a hypergolic rocket engine manufactured by Aerojet Rocketdyne. It has been used to propel the upper stages of several launch vehicles, including the Delta II and Titan III. Variants were and are used as the service propulsion engine for the Apollo command and service module, in the Space Shuttle Orbital Maneuvering System, and on NASA's Orion spacecraft.
 W
WThe ascent propulsion system (APS) or lunar module ascent engine (LMAE) is a fixed-thrust hypergolic rocket engine developed by Bell Aerosystems for use in the Apollo Lunar Module ascent stage. It used Aerozine 50 fuel, and N2O4 oxidizer. Rocketdyne provided the injector system, at the request of NASA, when Bell could not solve combustion instability problems.
 W
WThe Astris was a liquid rocket engine burning the hypergolic propellant combination of Aerozine 50 and N2O4. A single engine powered Astris third stage of the failed Europa rocket.
 W
WThe SpaceX Draco is a family of hypergolic liquid rocket engines designed and built by SpaceX for use in their space capsules. Two engine types have been built to date: Draco and SuperDraco.
 W
WThe KTDU-80 (Russian: Корректирующе-Тормозная Двигательная Установка, КТДУ) is the latest of a family of integrated propulsion system that KB KhIMMASH has implemented for the Soyuz since the Soyuz-T. It integrates main propulsion, RCS and attitude control in a single system pressure fed from a common dual string redundant pressurized propellant system. The common propellant is UDMH and N2O4 and the main propulsion unit, is the S5.80 main engine. It generates 2.95 kN (660 lbf) of thrust with a chamber pressure of 880 kPa (128 psi) and a nozzle expansion of 153.8 that enables it to achieve a specific impulse of 302 s (2.96 km/s). It is rated for 30 starts with a total firing time of 890 seconds. The integrated system without the pressurization or tanks weighs 310 kg (680 lb); it is 1.2 m (47 in) long with a diameter of 2.1 m (83 in).
 W
WThe KTDU-80 (Russian: Корректирующе-Тормозная Двигательная Установка, КТДУ) is the latest of a family of integrated propulsion system that KB KhIMMASH has implemented for the Soyuz since the Soyuz-T. It integrates main propulsion, RCS and attitude control in a single system pressure fed from a common dual string redundant pressurized propellant system. The common propellant is UDMH and N2O4 and the main propulsion unit, is the S5.80 main engine. It generates 2.95 kN (660 lbf) of thrust with a chamber pressure of 880 kPa (128 psi) and a nozzle expansion of 153.8 that enables it to achieve a specific impulse of 302 s (2.96 km/s). It is rated for 30 starts with a total firing time of 890 seconds. The integrated system without the pressurization or tanks weighs 310 kg (680 lb); it is 1.2 m (47 in) long with a diameter of 2.1 m (83 in).
 W
WThe LR87 was an American liquid-propellant rocket engine used on the first stages of Titan intercontinental ballistic missiles and launch vehicles. Composed of twin motors with separate combustion chambers and turbopump machinery, it is considered a single unit. The LR87 first flew in 1959.
 W
WThe LR91 was an American liquid-propellant rocket engine, which was used on the second stages of Titan intercontinental ballistic missiles and launch vehicles. While the original version - the LR91-3 - ran on RP-1/LOX (as did the companion LR87-3) on the Titan I, the models that propelled the Titan II and later were switched to Aerozine 50/N2O4.
 W
WThe R-4D is a small hypergolic rocket engine, originally designed by Marquardt Corporation for use as a reaction control thruster on vehicles of the Apollo moon program. Today, Aerojet Rocketdyne manufactures and markets modern versions of the R-4D.
 W
WThe RD-119 was a liquid rocket engine, burning liquid oxygen and UDMH in the gas-generator cycle. It has a huge expansion ratio on the nozzle and uses a unique propellant combination to achieve an extremely high isp of 352 s for a semi-cryogenic gas-generator engine. It also has a unique steering mechanism. The engine main nozzle is fixed, and the output of the gas generator is fed into four nozzles on the side of the engine. Instead of using gimbaled verniers to supply vector control, the combustion gases are distributed by an electrically driven system that can control the thrust among the nozzles.
 W
WThe RD-0210 (GRAU Index: 8D411K) is also known as the RD-465. It and its twin, the RD-0211, are rocket engines burning N2O4 and UDMH in an oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. They have single nozzle, possess TVC and are the latest evolution in the RD-0203/4 lineage. They are the engines used on the Proton second stage. The RD-0213 is a fixed nozzle variation that is used on the RD-0212 module of the Proton third stage.
 W
WThe RD-0210 (GRAU Index: 8D411K) is also known as the RD-465. It and its twin, the RD-0211, are rocket engines burning N2O4 and UDMH in an oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. They have single nozzle, possess TVC and are the latest evolution in the RD-0203/4 lineage. They are the engines used on the Proton second stage. The RD-0213 is a fixed nozzle variation that is used on the RD-0212 module of the Proton third stage.
 W
WThe RD-0210 (GRAU Index: 8D411K) is also known as the RD-465. It and its twin, the RD-0211, are rocket engines burning N2O4 and UDMH in an oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. They have single nozzle, possess TVC and are the latest evolution in the RD-0203/4 lineage. They are the engines used on the Proton second stage. The RD-0213 is a fixed nozzle variation that is used on the RD-0212 module of the Proton third stage.
 W
WThe RD-0210 (GRAU Index: 8D411K) is also known as the RD-465. It and its twin, the RD-0211, are rocket engines burning N2O4 and UDMH in an oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. They have single nozzle, possess TVC and are the latest evolution in the RD-0203/4 lineage. They are the engines used on the Proton second stage. The RD-0213 is a fixed nozzle variation that is used on the RD-0212 module of the Proton third stage.
 W
WThe RD-0210 (GRAU Index: 8D411K) is also known as the RD-465. It and its twin, the RD-0211, are rocket engines burning N2O4 and UDMH in an oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. They have single nozzle, possess TVC and are the latest evolution in the RD-0203/4 lineage. They are the engines used on the Proton second stage. The RD-0213 is a fixed nozzle variation that is used on the RD-0212 module of the Proton third stage.
 W
WThe RD-0210 (GRAU Index: 8D411K) is also known as the RD-465. It and its twin, the RD-0211, are rocket engines burning N2O4 and UDMH in an oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. They have single nozzle, possess TVC and are the latest evolution in the RD-0203/4 lineage. They are the engines used on the Proton second stage. The RD-0213 is a fixed nozzle variation that is used on the RD-0212 module of the Proton third stage.
 W
WThe RD-0210 (GRAU Index: 8D411K) is also known as the RD-465. It and its twin, the RD-0211, are rocket engines burning N2O4 and UDMH in an oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. They have single nozzle, possess TVC and are the latest evolution in the RD-0203/4 lineage. They are the engines used on the Proton second stage. The RD-0213 is a fixed nozzle variation that is used on the RD-0212 module of the Proton third stage.
 W
WThe RD-0210 (GRAU Index: 8D411K) is also known as the RD-465. It and its twin, the RD-0211, are rocket engines burning N2O4 and UDMH in an oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. They have single nozzle, possess TVC and are the latest evolution in the RD-0203/4 lineage. They are the engines used on the Proton second stage. The RD-0213 is a fixed nozzle variation that is used on the RD-0212 module of the Proton third stage.
 W
WThe RD-214 (GRAU Index 8D59) was a liquid rocket engine, burning AK-27I (a mixture of 73% nitric acid and 27% N2O4 + iodine passivant and TM-185 (a kerosene and gasoline mix) in the gas generator cycle. As was the case with many V-2 influenced engines, the single turbine was driven by steam generated by catalytic decomposition of H2O2. It also had four combustion chambers and vector control was achieved by refractory vanes protruding into the nozzle's exhaust.
 W
WThe RD-250 (GRAU Index 8D518) is the base version of a dual-nozzle family of liquid rocket engines, burning N2O4 and UDMH in the oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. The RD-250 was developed by OKB-456 for Yangel's PA Yuzhmash ICBM, the R-36 (8K67). Its variations were also used on the Tsyklon-2 and Tsyklon-3 launch vehicles. It was supposed to be used on the Tsyklon-4, but since the cancellation of the project it should be considered as out of production.
 W
WThe RD-250 (GRAU Index 8D518) is the base version of a dual-nozzle family of liquid rocket engines, burning N2O4 and UDMH in the oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. The RD-250 was developed by OKB-456 for Yangel's PA Yuzhmash ICBM, the R-36 (8K67). Its variations were also used on the Tsyklon-2 and Tsyklon-3 launch vehicles. It was supposed to be used on the Tsyklon-4, but since the cancellation of the project it should be considered as out of production.
 W
WThe RD-253 ( Russian: Раке́тный дви́гатель 253, Rocket Engine 253) and its later variants, the RD-275 and RD-275M, are liquid-propellant rocket engines developed in the Soviet Union by Energomash. The engines are used on the first stage of the Proton launch vehicle and use an oxidizer-rich staged combustion cycle to power the turbopumps. The engine burns UDMH/N2O4, which are highly toxic but hypergolic and storable at room temperature, simplifying the engine's design.
 W
WThe RD-250 (GRAU Index 8D518) is the base version of a dual-nozzle family of liquid rocket engines, burning N2O4 and UDMH in the oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. The RD-250 was developed by OKB-456 for Yangel's PA Yuzhmash ICBM, the R-36 (8K67). Its variations were also used on the Tsyklon-2 and Tsyklon-3 launch vehicles. It was supposed to be used on the Tsyklon-4, but since the cancellation of the project it should be considered as out of production.
 W
WThe RD-250 (GRAU Index 8D518) is the base version of a dual-nozzle family of liquid rocket engines, burning N2O4 and UDMH in the oxidizer rich staged combustion cycle. The RD-250 was developed by OKB-456 for Yangel's PA Yuzhmash ICBM, the R-36 (8K67). Its variations were also used on the Tsyklon-2 and Tsyklon-3 launch vehicles. It was supposed to be used on the Tsyklon-4, but since the cancellation of the project it should be considered as out of production.
 W
WThe RD-253 ( Russian: Раке́тный дви́гатель 253, Rocket Engine 253) and its later variants, the RD-275 and RD-275M, are liquid-propellant rocket engines developed in the Soviet Union by Energomash. The engines are used on the first stage of the Proton launch vehicle and use an oxidizer-rich staged combustion cycle to power the turbopumps. The engine burns UDMH/N2O4, which are highly toxic but hypergolic and storable at room temperature, simplifying the engine's design.
 W
WThe RD-253 ( Russian: Раке́тный дви́гатель 253, Rocket Engine 253) and its later variants, the RD-275 and RD-275M, are liquid-propellant rocket engines developed in the Soviet Union by Energomash. The engines are used on the first stage of the Proton launch vehicle and use an oxidizer-rich staged combustion cycle to power the turbopumps. The engine burns UDMH/N2O4, which are highly toxic but hypergolic and storable at room temperature, simplifying the engine's design.
 W
WThe S5.4, was a Russian liquid rocket engine burning TG-02 and AK20F in the gas generator cycle. It was originally used as the braking (deorbit) engine of the Vostok, Voskhod, and Zenit spacecraft, which later switched to solid engines.
 W
WThe S5.92 is a Russian rocket engine, currently used on the Fregat upper stage.
 W
WThe Société d'Études pour la Propulsion par Réaction (SEPR) was a French research and manufacturing company founded in 1944 which specialised in the development of liquid-fuelled rocket engines during the 1950s, 60s, 70s and 80s.
 W
WSuperDraco is a hypergolic propellant rocket engine designed and built by SpaceX. It is part of the SpaceX Draco family of rocket engines. A redundant array of eight SuperDraco engines provides fault-tolerant propulsion for use as a launch escape system for the SpaceX Dragon 2, a passenger-carrying space capsule.
 W
WThe Vikas is a family of liquid fuelled rocket engines conceptualized and designed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre in the 1970s. The design was based on the licensed version of the Viking engine with the chemical pressurisation system. The early production Vikas engines used some imported French components which were later replaced by domestically produced equivalents. It is used in the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) series of expendable launch vehicles for space launch use.
 W
WThe Viking rocket engines were members of a series of bipropellant engines for the first and second stages of the Ariane 1 through Ariane 4 commercial launch vehicles, using storable, hypergolic propellants: dinitrogen tetroxide and UH 25, a mixture of 75% UDMH and 25% hydrazine.
 W
WThe Walter HWK 109-509 was a German liquid-fuel bipropellant rocket engine that powered the Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet and Bachem Ba 349 aircraft. It was produced by Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft (HWK) commencing in 1943, with license production by the Heinkel firm's facilities in Jenbach, Austria.
 W
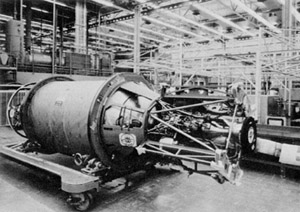
WThe Bell Aerosystems Company XLR81 was an American liquid-propellant rocket engine, which was used on the Agena upper stage. It burned UDMH and RFNA fed by a turbopump in a fuel rich gas generator cycle. The turbopump had a single turbine with a gearbox to transmit power to the oxidizer and fuel pumps. The thrust chamber was all-aluminum, and regeneratively cooled by oxidizer flowing through gun-drilled passages in the combustion chamber and throat walls. The nozzle was a titanium radiatively cooled extension. The engine was mounted on an hydraulic actuated gimbal which enabled thrust vectoring to control pitch and yaw. Engine thrust and mixture ratio were controlled by cavitating flow venturis on the gas generator flow circuit. Engine start was achieved by solid propellant start cartridge.
 W
WThe YF-20 is a Chinese liquid-fuel rocket engine burning N2O4 and UDMH in a gas generator cycle. It is a basic engine which when mounted in a four engine module forms the YF-21. The high altitude variation is known as the YF-22 is normally paired with the YF-23 vernier to form the YF-24 propulsion module for second stages. New versions when used individually for booster applications are called YF-25.
 W
WThe YF-20 is a Chinese liquid-fuel rocket engine burning N2O4 and UDMH in a gas generator cycle. It is a basic engine which when mounted in a four engine module forms the YF-21. The high altitude variation is known as the YF-22 is normally paired with the YF-23 vernier to form the YF-24 propulsion module for second stages. New versions when used individually for booster applications are called YF-25.
 W
WThe YF-20 is a Chinese liquid-fuel rocket engine burning N2O4 and UDMH in a gas generator cycle. It is a basic engine which when mounted in a four engine module forms the YF-21. The high altitude variation is known as the YF-22 is normally paired with the YF-23 vernier to form the YF-24 propulsion module for second stages. New versions when used individually for booster applications are called YF-25.