 W
WThe Abingdon Sword is a late Anglo-Saxon iron sword and hilt believed to be from the late 9th or early 10th century; only the first few inches of the blade remain attached to the hilt.
 W
WThe Ballinderry Sword is an iron Viking-style weapon found in a bog on the site of a crannog in Ballinderry, in Rosemount, County Westmeath, Ireland in 1928. It is no. 36 in A History of Ireland in 100 Objects. It was found along with other Viking objects: a longbow, two spearheads, an axe head and a gaming board. The settlement dates from between the late 9th and early 11th century and the collection of artifacts uncovered appears to fit the profile of a wealthy Irish farmer or of a local ruler.
 W
WThe Metropolitan Museum of Art holds a 16th-century combination weapon in its armaments collection. The weapon is an 89 3/4 inch boar spear with two wheellock pistol barrels fused to both flat sides of the spear's head; the intent of this design was to provide the wielder with the extra stopping power of two .41 caliber musket balls that could be fired at targets out of the reach of the spear. Some sources posit that such weapons were instead experimental pieces or curiosities. The 9 lb, German-made weapon was donated to the Met's collection by the Roger's fund in 1904.
 W
WThe Cawood sword is a medieval sword discovered in the River Ouse near Cawood in North Yorkshire in the late 19th century. The blade is of Oakeshott type XII and has inscriptions on both sides. It most likely dates to the early 12th century.
 W
WThe City of London swords are five two-handed ceremonial swords owned by the City of London, namely the Mourning Sword, the Pearl Sword, the State Sword, the Old Bailey Sword and the Mansion House Justice Room Sword. A sixth sword, the Travelling Sword of State, replaces the Sword of State for visits outside the City. They are part of the plate collection of Mansion House, the official residence of the Lord Mayor of London.
 W
WThe Clacton Spear, or Clacton Spear Point, is the tip of a wooden spear discovered in Clacton-on-Sea in 1911. It is 400,000 years old and the oldest known worked wooden implement.
 W
WThe curved saber of San Martín is an historic weapon used by José de San Martín.
 W
WA double-barreled wheellock pistol was crafted by German gunsmith Peter Peck for Charles V in 1540. It is one of the oldest surviving European pistols. It is in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
 W
WThe Gebel el-Arak Knife, also Jebel el-Arak Knife, is an ivory and flint knife dating from the Naqada II period of Egyptian prehistory, showing Mesopotamian influence. The knife was purchased in 1914 in Cairo by Georges Aaron Bénédite for the Louvre, where it is now on display in the Sully wing, room 20. At the time of its purchase, the knife handle was alleged by the seller to have been found at the site of Gebel el-Arak, but it is today believed to come from Abydos.
 W
WThe Gilling sword is an Anglo-Saxon sword, dating from the late 9th to early 10th centuries AD, found by a schoolboy in a river in 1976 and subsequently acquired by the Yorkshire Museum.
 W
WThe Gray's Inn Lane Hand Axe is a pointed flint hand axe, found buried in gravel under Gray's Inn Lane, London, England, by pioneering archaeologist John Conyers in 1679, and now in the British Museum. The hand axe is a fine example from about 350,000 years ago, in the Lower Paleolithic period, but its main significance lies in the role it and the circumstances of its excavation played in the emerging understanding of early human history.
 W
WThe Holy Lance, also known as the Lance of Longinus, the Spear of Destiny, or the Holy Spear, is the supposed lance that pierced the side of Jesus as he hung on the cross during his crucifixion.
 W
WThe Imperial Sword is one of the four most important parts of the Imperial Regalia (Reichskleinodien) of the Holy Roman Empire. During a coronation, it was given to the emperor along with the Imperial Crown (Reichskrone), Imperial Sceptre (Reichszepter), and the Imperial Orb (Reichsapfel). All four parts of the Imperial Regalia are displayed in the Imperial Treasury at the Hofburg Palace in Vienna, Austria.
 W
WJoyeuse was, in medieval legend, the sword wielded by Charlemagne as his personal weapon. The name means "joyous". A sword identified as Joyeuse was used in French royal coronation ceremonies since the 13th century, and is now kept at the Louvre museum.
 W
WThe John F. Kennedy assassination rifle is a long-barrelled firearm that was used to assassinate John F. Kennedy, the 35th President of the United States.
 W
WThe Kris of Knaud, also known as the Keris of Knaud or Knaud's Kris, is the oldest known kris surviving in the world. Given to Charles Knaud, a Dutch physician, by Paku Alam V in the 19th century, the kris is on display at the Tropenmuseum, Royal Tropical Institute in Amsterdam.
 W
WThe sword Lobera was the symbol of power used by Saint Ferdinand III of Castile, instead of the more traditional rod, and so the king will be depicted with orb and sword in hand.
 W
WThe Mainz Gladius or Sword of Tiberius is a famous ancient Roman sword and sheath that was found in the Rhine near Mainz in Germany. Since 1866 it has been part of the British Museum's collection, when it was given to the museum by the philanthropist Felix Slade. A replica of the Mainz Gladius can be found in the Romano-Germanic Central Museum (Mainz). The type of gladius was first introduced to the Romans in 20 BC. Eventually the Mainz Gladius was overtaken in popularity by the Pompeii Gladius.
 W
WThe Mikoyan Project 1.44/1.42 was a technology demonstrator developed by the Mikoyan design bureau. It was the Soviet Union's answer to the U.S.'s Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF), incorporating many fifth-generation jet fighter aspects such as advanced avionics, stealth technology, supermaneuverability, and supercruise. The design's development was a protracted one, characterised by repeated and lengthy postponements due to a chronic lack of funds; the MiG 1.44 made its maiden flight in February 2000, nine years behind schedule, and was cancelled later that year.
 W
WNader Shah's Sword refers to the sword carried by Iranian ruler Nader Shah. It is located in Tehran, Iran. Under later Iranian ruler Fath-Ali Shah Qajar, some fifty years or more later, it was inscribed and embellished. The scabbard of the sword is covered with diamonds. The modern historian Michael Axworthy notes that "Nader used the imagery of the sword to describe himself on a number of occasions".
 W
WThe Narmer macehead is an ancient Egyptian decorative stone mace head. It was found in the “main deposit” in the temple area of the ancient Egyptian city of Nekhen (Hierakonpolis) by James Quibell in 1898. It is dated to the Early Dynastic Period reign of king Narmer whose serekh is engraved on it. The macehead is now kept at the Ashmolean Museum, Oxford.
 W
WThe so-called Sabre of Charlemagne is an early sabre of Hungarian (Magyar) type which has exceptionally been preserved as part of the Aachen regalia of the Holy Roman Empire. Along with the rest of the imperial regalia from both Aachen and Nuremberg, it is now kept in the Hofburg Palace, Vienna.
 W
WThe Sayala Mace or Seyala Mace is a ceremonial mace made of gold plated wood and stone, from Predynastic Egypt. It was found by Cecil Mallaby Firth in 1910–11 at Sayala in Lower Nubia and subsequently kept in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo until it was stolen in 1920. Its later fate is unknown. The mace is especially significant for the detailed depictions of animals on its handle.
 W
WThe Schöningen spears are a set of eight wooden throwing spears from the Palaeolithic Age that were excavated between 1994 and 1998 in the open-cast lignite mine in Schöningen, Helmstedt district, Germany, together with an associated cache of approximately 16,000 animal bones. The excavations took place under the management of Hartmut Thieme of the Lower Saxony State Service for Cultural Heritage (NLD).
 W
WThe Scorpion macehead is a decorated ancient Egyptian macehead found by British archeologists James E. Quibell and Frederick W. Green in what they called the main deposit in the temple of Horus at Hierakonpolis during the dig season of 1897–1898. It measures 25 centimeters long, is made of limestone, is pear-shaped, and is attributed to the pharaoh Scorpion due to the glyph of a scorpion engraved close to the image of a king wearing the White Crown of Upper Egypt.
 W
WThe Seax of Beagnoth is a 10th-century Anglo-Saxon seax. It was found in the inland estuary of the Thames in 1857, and is now at the British Museum in London. It is a prestige weapon, decorated with elaborate patterns of inlaid copper, brass and silver wire. On one side of the blade is the only known complete inscription of the twenty-eight letter Anglo-Saxon runic alphabet, as well as the name "Beagnoth" in runic letters. It is thought that the runic alphabet had a magical function, and that the name Beagnoth is that of either the owner of the weapon or the smith who forged it. Although many Anglo-Saxon and Viking swords and knives have inscriptions in the Latin alphabet on their blades, or have runic inscriptions on the hilt or scabbard, the Seax of Beagnoth is one of only a handful of finds with a runic inscription on its blade.
 W
WThe Seven-Branched Sword is a sword of continental manufacture believed to be identical with the artifact of that name, a present of the king of Baekje that was granted upon a Yamato ruler as a present, which is mentioned in the Nihon Shoki in the fifty-second year of the reign of the semi-mythical Empress Jingū. It is a 74.9 cm (29.5 in) long iron sword with six branch-like protrusions along the central blade. The original sword has been conserved since antiquity in the Isonokami Shrine in Nara Prefecture, Japan and is not on public display. An inscription on the side of the blade is an important source for understanding the relationships between kingdoms of the Korean peninsula and Japan in that period.
 W
WThe Spear of Fuchai is the spear of King Fuchai of Wu, the archrival of King Goujian of Yue. It was unearthed in Jiangling, Hubei in November 1983. The script on it is bird-worm seal script, a variant of seal script that was commonly used in the southern states such as Wu and Yue. The inscription mirrors the text of King Goujian's Sword, except changing the name of the owner and type of weapon. In this case, the text reads, "吴王夫差自作用矛" or "King Fuchai of Wu made for his personal use, this spear."
 W
WThe Suontaka sword was found in what was previously interpreted as a high-status woman's grave at Suontaka Vesitorninmäki, Hattula, Finland in 1968. Based on a study published in 2021, the sword was likely hidden in the grave some time after the burial. The grave dates from the late Nordic Iron Age, c. 1040–1174 AD, and it also included another hiltless sword with silver-inlays that was placed directly on the buried corpse. Ancient DNA analysis found that the individual likely had Klinefelter syndrome, indicated through the presence of XXY chromosomes. The individual had been buried in a female dress with three brooches. According to the authors of the 2021 study, "The overall context of the grave indicates that it was a respected person whose gender identity may well have been nonbinary."
 W
WThe sword of François I is a ceremonial sword made c. 1510–1515 from a blade forged around 1480 and a custom-made handle. It was captured by the Spanish at the Battle of Pavia and brought back to France in 1808 by Murat. It is currently on display at the Musée de l'Armée at Les Invalides, in Paris.
 W
WThe Sword of Islam was a ceremonial melee weapon given in 1937 to Benito Mussolini, who was pronounced as the Protector of Islam.
 W
WThe Sword of Saint Peter is a holy relic held in the Poznań Archdiocesan Museum.
 W
WThe Sword of Saints Cosmas and Damian, also known as the Sword of Essen, is a ceremonial weapon in Essen Abbey. The sword itself dates to the mid 10th century, the gold decoration was added at the close of the 10th or the onset of the 11th century, while the silver mounts with the inscription were added 15th century.
 W
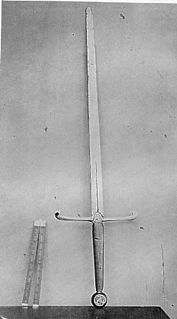
WThe Sword of Stalingrad is a bejewelled ceremonial longsword specially forged and inscribed by command of King George VI of the United Kingdom as a token of homage from the British people to the Soviet defenders of the city during the Battle of Stalingrad. On 29 November 1943, it was presented to Marshal Joseph Stalin by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill at a ceremony during the Tehran Conference, in the presence of President Franklin D. Roosevelt and an honour guard.
 W
WThe Manx Sword of State is a ceremonial sword that represents the Tynwald on the Isle of Man. It represents the duties of the Sovereign of the Isle of Man, and is used every month in Tynwald, and annually during the Tynwald Day ceremony. There have been three swords used for such functions over the years. One is used for the ceremonies; one is housed in a museum; the other was lost in the 18th century. The Sword of State is popularly said to date to the mid 13th century, however it is not unlike 15th-century ceremonial swords used in England, and recent analysis dates it to the 15th century as well.
 W
WThe Sword of Victory or Phra Saeng Khan Chaiyasi is part of the royal regalia of the King of Thailand. The sword represents the military might and power of the king. The hilt has a length of 25.4 centimetres with the blade measuring 64.5 centimetres. When placed in the scabbard the sword has a total length of 101 centimetres and weighs 1.9 kilograms. The swords neck between the blade and the hilt is decorated with a gold inlaid miniature of Vishnu riding the Garuda.
 W
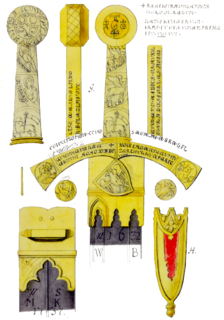
WSzczerbiec is the ceremonial sword used in the coronations of most Polish monarchs from 1320 to 1764. It now is displayed in the treasure vault of the royal Wawel Castle in Kraków, as the only preserved part of the medieval Polish crown jewels. The sword is noted for its hilt, decorated with magical formulae, Christian symbols, and floral patterns, as well as for the narrow slit in the blade which holds a small shield with the coat of arms of Poland. The name of the sword, derived from the Polish word szczerba, may be rendered into English as "the Notched Sword" or "the Jagged Sword", though the edges of its blade are straight and smooth.
 W
WTizona is the name of one of the swords carried by Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar, El Cid, according to the Cantar de Mio Cid. The name of the second sword of El Cid is Colada.
 W
WThe Wallace Sword is an antique two-handed sword purported to have belonged to William Wallace (1270–1305), a Scottish knight who led a resistance to the English occupation of Scotland during the Wars of Scottish Independence. It is said to have been used by William Wallace at the Battle of Stirling Bridge in 1297 and the Battle of Falkirk (1298).