 W
WAeronautical earth station is – according to Article 1.82 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «An earth station in the fixed-satellite service, or, in some cases, in the aeronautical mobile-satellite service, located at a specified fixed point on land to provide a feeder link for the aeronautical mobile-satellite service.»
 W
WAeronautical station is – according to Article 1.81 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A land station in the aeronautical mobile service. In certain instances, an aeronautical station may be located, for example, on board ship or on a platform at sea.»
 W
WAircraft earth station is – according to Article 1.84 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A mobile earth station in the aeronautical mobile-satellite service located on board an aircraft.»
 W
WAn amateur radio station is a radio station designed to provide radiocommunications in the amateur radio service for an amateur radio operator. Radio amateurs build and operate several types of amateur radio stations, including fixed ground stations, mobile stations, space stations, and temporary field stations. A slang term often used for an amateur station's location is the shack, named after the small enclosures added to the upperworks of naval ships to hold early radio equipment and batteries.See also
 W
WBase earth station is – according to article 1.72 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «An earth station in the fixed-satellite service or, in some cases, in the land mobile-satellite service, located at a specified fixed point or within a specified area on land to provide a feeder link for the land mobile-satellite service.»
 W
WBase station is – according to the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – a "land station in the land mobile service."
 W
WCoast earth station, also called the coast earth radio station is – according to article 1.76 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «An earth station in the fixed-satellite service or, in some cases, in the maritime mobile-satellite service, located at a specified fixed point on land to provide a feeder link for the maritime mobile-satellite service.» Each radio station shall be classified by the service in which it operates permanently or temporarily.
 W
WA coast radio station is an on-shore maritime radio station which may monitor radio distress frequencies and relays ship-to-ship and ship-to-land communications.
 W
WAn emergency position-indicating radio beacon (EPIRB) is a type of emergency locator beacon, a portable, battery-powered radio transmitter used in emergencies to locate airplanes, vessels, and persons in distress and in need of immediate rescue. In the event of an emergency, such as a ship sinking or an airplane crash, the transmitter is activated and begins transmitting a continuous radio signal, which is used by search-and-rescue teams to quickly locate the emergency and render aid. The signal is detected by satellites operated by an international consortium of rescue services, COSPAS-SARSAT, which can detect emergency beacons anywhere on Earth transmitting on the COSPAS distress frequency of 406 MHz. The consortium calculates the position of the beacon and quickly passes the information to the appropriate local first responder organization, which performs the search and rescue. The basic purpose of this system is to help rescuers find survivors within the so-called "golden day" during which the majority of survivors can usually be saved. The feature distinguishing a modern EPIRB, often called GPIRB, from other types of emergency beacon is that it contains a GPS receiver and broadcasts its position, usually accurate within 100 m (330 ft), to facilitate location. Previous emergency beacons without a GPS can only be localized to within 2 km (1.2 mi) by the COSPAS satellites.
 W
WA feeder link is – according to Article 1.115 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as:A radio link from an earth station at a given location to a space station, or vice versa, conveying information for a space radiocommunication service other than for the fixed-satellite service. The given location may be at a specified fixed point, or at any fixed point within specified areas.
 W
WAtmospheric satellite or pseudo-satellite is a marketing term for an aircraft that operates in the atmosphere at high altitudes for extended periods of time, in order to provide services conventionally provided by an artificial satellite orbiting in space.
 W
WIn aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is 200 feet (61 m) over the ground, within a 1⁄2 mile of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically improves the weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Later versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes.
 W
WInstrument landing system glide path, commonly referred to as a glide path (G/P) or glide slope (G/S), is "a system of vertical guidance embodied in the instrument landing system which indicates the vertical deviation of the aircraft from its optimum path of descent", according to Article 1.106 of the ITU Radio Regulations.
 W
WAn instrument landing system localizer, or simply localizer (LOC), is a system of horizontal guidance in the instrument landing system, which is used to guide aircraft along the axis of the runway.
 W
WA land earth station is – according to Article 1.70 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «An earth station in the fixed-satellite service or, in some cases, in the mobile-satellite service, located at a specified fixed point or within a specified area on land to provide a feeder link for the mobile-satellite service.»
 W
WLand mobile earth station is – according to Article 1.74 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A mobile earth station in the land mobile-satellite service capable of surface movement within the geographical limits of a country or continent.»See also
 W
WLand station is – according to Article 1.69 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A radio station in the mobile service not intended to be used while in motion.»
 W
WA marker beacon is a particular type of VHF radio beacon used in aviation, usually in conjunction with an instrument landing system (ILS), to give pilots a means to determine position along an established route to a destination such as a runway.
 W
WMobile earth station is – according to Article 1.68 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «An earth station in the mobile-satellite service intended to be used while in motion or during halts at unspecified points.»
 W
WMobile radio station is – according to Article 1.67 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A station in the mobile service intended to be used while in motion or during halts at unspecified points.»
 W
WPort station is – according to Article 1.80 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) RR – defined as «A coast station in the port operations service.»
 W
WA Primary radar is a conventional radar sensor that illuminates a large portion of space with an electromagnetic wave and receives back the reflected waves from targets within that space. The term thus refers to a radar system used to detect and localize potentially non-cooperative targets. It is specific to the field of air traffic control where it is opposed to the secondary radar which receives additional information from the target's transponder.
 W
WRadar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (range), angle, or velocity of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the object(s). Radio waves from the transmitter reflect off the object and return to the receiver, giving information about the object's location and speed.
 W
WRadar beacon is – according to article 1.103 of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as "A transmitter-receiver associated with a fixed navigational mark which, when triggered by a radar, automatically returns a distinctive signal which can appear on the display of the triggering radar, providing range, bearing and identification information." Each station shall be classified by the service in which it operates permanently or temporarily.
 W
WRadio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1932, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories observed radiation coming from the Milky Way. Subsequent observations have identified a number of different sources of radio emission. These include stars and galaxies, as well as entirely new classes of objects, such as radio galaxies, quasars, pulsars, and masers. The discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation, regarded as evidence for the Big Bang theory, was made through radio astronomy.
 W
WIn navigation, a radio beacon is a kind of beacon, a device that marks a fixed location and allows direction-finding equipment to find relative bearing. Radio beacons transmit a radio signal that is picked up by radio direction-finding systems on ships, aircraft and vehicles to determine the direction to the beacon.
 W
WRadio direction-finding station is – according to article 1.91 of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A radiodetermination station using radio direction-finding.»
 W
Wradiolocation land station is – according to article 1.90 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A radio station in radiolocation service not intended to be used while in motion.»
 W
WRadionavigation land station is – according to article 1.88 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A radio station in the radionavigation service not intended to be used while in motion.»
 W
WSatellite emergency position-indicating radiobeacon station is – according to article 1.94 of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «An earth station in the mobile-satellite service the emissions of which are intended to facilitate search and rescue (SAR) operations.»
 W
WSatellite link is – according to article 1.113 of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A radio link between a transmitting earth station and a receiving earth station through one satellite. A satellite link comprises one up-link and one down-link.»
 W
WSatellite radio system is – according to article 1.111 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A space system using one or more artificial earth satellites.»
 W
WSecondary surveillance radar (SSR) is a radar system used in air traffic control (ATC), that unlike primary radar systems that measure the bearing and distance of targets using the detected reflections of radio signals, relies on targets equipped with a radar transponder, that reply to each interrogation signal by transmitting encoded data such as an identity code, the aircraft's altitude and further information depending on its chosen mode. SSR is based on the military identification friend or foe (IFF) technology originally developed during World War II, therefore the two systems are still compatible. Monopulse secondary surveillance radar (MSSR), Mode S, TCAS and ADS-B are similar modern methods of secondary surveillance.
 W
WShip earth station is – according to Article 1.78 of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A mobile earth station in the maritime mobile-satellite service located on board ship.»
 W
WA ship station is a radio station located on board a sea vessel. The ITU Radio Regulations define it as "A mobile station in the maritime mobile service located on board a vessel which is not permanently moored, other than a survival craft station."
 W
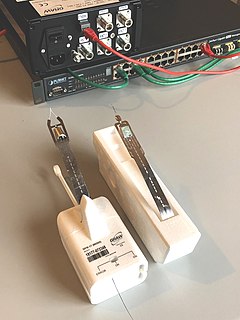
WA radiosonde is a battery-powered telemetry instrument carried into the atmosphere usually by a weather balloon that measures various atmospheric parameters and transmits them by radio to a ground receiver. Modern radiosondes measure or calculate the following variables: altitude, pressure, temperature, relative humidity, wind, cosmic ray readings at high altitude and geographical position (latitude/longitude). Radiosondes measuring ozone concentration are known as ozonesondes.
 W
WSpace radio station is a radio station located on an object travelling beyond the major portion of the Earth's atmosphere. Each station shall be classified by the service in which it operates permanently or temporarily. However, most spacecraft communicate by this means.
 W
WSpace radio system is – according to article 1.110 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «Any group of cooperating earth stations and/or space stations employing space radiocommunication for specific purposes.»
 W
WStandard frequency and time signal station is – according to article 1.95 of the International Telecommunication Union´s (ITU) ITU Radio Regulations (RR) – defined as «A radio station in the standard frequency and time signal service.»