 W
WThe Sukhoi KR-860, earlier named the SKD-717, was a double decker wide-body superjumbo jet aircraft proposed by Russian aerospace company Sukhoi. It was revealed at the 2000 Paris Air Show.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-75 "Checkmate", is a single-engine, fifth-generation stealth fighter aircraft under development by Sukhoi for export and for the Russian Aerospace Forces. The Sukhoi Design Bureau also designates the aircraft as T-75 with marked registration RF-0075.
 W
WThe Sukhoi P-1 was a prototype Soviet interceptor.
 W
WSukhoi-Gulfstream S-21 was a projected Russian-American supersonic business jet.
 W
WThe Sukhoi S-54 was a series of three closely related aircraft proposals; the S-54 trainer aircraft, S-55 light fighter designed for export, and the S-56 carrier-capable light fighter. All members of the family resemble the Sukhoi Su-27 in general form, or the Sukhoi Su-33 more closely, but built around a single Saturn AL-31 engine instead of two, and scaled down accordingly to a smaller layout. The design was offered to several potential customers, including South Africa and India, but was turned down. Development is apparently on hold, awaiting a launch customer.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-1 or I-330 was a prototype Soviet high-altitude fighter aircraft built at the beginning of World War II. An improved version, designated Su-3 (I-360), was also built and tested the following year. Neither version was mass-produced.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-2 was a Soviet reconnaissance and light bomber aircraft used in the early stages of World War II. It was the first airplane designed by Pavel Sukhoi. The basic design received an engine and armament upgrade (Su-4) and was modified for the ground-attack role (ShB).
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-6 was a Soviet ground-attack aircraft developed during World War II. The mixed-power high-altitude interceptor Su-7 was based on the single-seat Su-6 prototype.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-7 is a swept wing, supersonic fighter aircraft developed by the Soviet Union in 1955. Originally, it was designed as a tactical, low-level dogfighter, but was not successful in this role. On the other hand, the soon-introduced Su-7B series became the main Soviet fighter-bomber and ground-attack aircraft of the 1960s. The Su-7 was rugged in its simplicity, but its Lyulka AL-7 engine had such high fuel consumption that it seriously limited the aircraft's payload, as even short-range missions required that at least two hardpoints be used to carry drop tanks rather than ordnance.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-9 was a single-engine, all-weather, missile-armed interceptor aircraft developed by the Soviet Union.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-9 or Самолёт K ;, was an early jet fighter built in the Soviet Union shortly after World War II. The design began in 1944 and was intended to use Soviet-designed turbojet engines. The design was heavily influenced by captured German jet fighters and it was subsequently redesigned to use a Soviet copy of a German turbojet. The Su-9 was slower than competing Soviet aircraft and it was cancelled as a result. A modified version with different engines and a revised wing became the Su-11, but this did not enter production either. The Su-13 was a proposal to re-engine the aircraft with Soviet copies of the Rolls-Royce Derwent turbojet as well as to modify it for night fighting, but neither proposal was accepted.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-11 was an interceptor aircraft used by the Soviet Union in the 1960s.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-12 was a prototype Soviet reconnaissance and artillery spotter aircraft developed during World War II.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-15 is a twinjet supersonic interceptor aircraft developed by the Soviet Union. It entered service in 1965 and remained one of the front-line designs into the 1990s. The Su-15 was designed to replace the Sukhoi Su-11 and Sukhoi Su-9, which were becoming obsolete as NATO introduced newer and more capable strategic bombers.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-15 was a prototype Soviet all-weather interceptor which never reached production. The designation was later reused for an entirely different 1960s interceptor, see Sukhoi Su-15.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-17 is a variable-sweep wing fighter-bomber developed for the Soviet military. Its NATO reporting name is "Fitter". Developed from the Sukhoi Su-7, the Su-17 was the first variable-sweep wing aircraft to enter Soviet service. Two subsequent Sukhoi aircraft, the Su-20 and Su-22, have usually been regarded as variants of the Su-17.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-17 was a prototype Soviet fighter. The name was later reused for an entirely different fighter-bomber, see Sukhoi Su-17.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-24 is a supersonic, all-weather attack aircraft developed in the Soviet Union. The aircraft has a variable-sweep wing, twin-engines and a side-by-side seating arrangement for its crew of two. It was the first of the USSR's aircraft to carry an integrated digital navigation/attack system. It remains in service with the Russian Air Force, Syrian Air Force, Ukrainian Air Force, Azerbaijan Air Force, Iraqi Air Force and various air forces to which it was exported.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-25 Grach is a subsonic, single-seat, twin-engine jet aircraft developed in the Soviet Union by Sukhoi. It was designed to provide close air support for the Soviet Ground Forces. The first prototype made its maiden flight on 22 February 1975. After testing, the aircraft went into series production in 1978 at Tbilisi in the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-26 is a single-seater aerobatic aircraft from the former Soviet Union, powered by a single radial reciprocating engine. The Su-26 has mid-mounted straight wings and fixed landing gear, the main gear mounted on a solid titanium arc.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-27 is a Soviet-origin twin-engine supermaneuverable fighter aircraft designed by Sukhoi. It was intended as a direct competitor for the large United States fourth-generation fighters such as the Grumman F-14 Tomcat and F-15 Eagle, with 3,530-kilometre (1,910 nmi) range, heavy aircraft ordnance, sophisticated avionics and high maneuverability. The Su-27 was designed for air superiority missions, and subsequent variants are able to perform almost all aerial warfare operations. It was designed with the Mikoyan MiG-29 as its complement.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-28 is a downgraded variant of the Su-25UB / Su-25T, with reductions in avionics and aircraft systems, together with the elimination of all weapon-carrying capability. The Su-28 trainer is intended for technical skill, general flight and formation flying training. It is also used as an aerobatic aircraft
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-29 is a Russian two-seat aerobatic aircraft with a 268 kW radial engine. It was designed based on the Su-26 and inherited most of the design and technical features of its predecessor. Due to wide use of composite materials, which make up as much as 60% of the Su-29's aircraft structure, the empty weight is increased by only 50 kg over the single-seat Su-26's empty weight.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-30 is a twin-engine, two-seat supermaneuverable fighter aircraft developed in the Soviet Union by Russia's Sukhoi Aviation Corporation. It is a multirole fighter for all-weather, air-to-air and air-to-surface deep interdiction missions.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-30MKI is a twinjet multirole air superiority fighter developed by Russia's Sukhoi and built under licence by India's Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF). A variant of the Sukhoi Su-30, it is a heavy, all-weather, long-range fighter.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-30MKK is a modification of the Sukhoi Su-30, incorporating advanced technology from the Sukhoi Su-35 variant. The Su-30MKK was developed by Sukhoi in 1997, as a result of a direct Request for tender between the Russian Federation and China. It is a heavy class, all-weather, long-range strike fighter, and like the Sukhoi Su-30, comparable to the American McDonnell Douglas F-15E Strike Eagle. Su-30MK2 is a further improvement to Su-30MKK with upgraded avionics and maritime strike capabilities. The MKK and MK2 are currently operated by the People's Liberation Army Air Force, Indonesian Air Force, Vietnam People's Air Force, Venezuelan Air Force and the Ugandan Air Force.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-30MKM is a supermaneuverable fighter of the Royal Malaysian Air Force. It is a variant of the Su-30 series fighters, with many significant improvements over the original Su-30MK export version. The Su-30MKM was developed by the Sukhoi Design Bureau and is based on the Su-30MKI of the Indian Air Force. Both aircraft have common airframe, thrust vectoring engines and digital fly-by-wire system, however the MKM version differs from the MKI mainly in the composition of the onboard avionics. It can carry up to 8,000 kg (17,637 lb) payload over a 1,296 km un-refueled combat radius.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-31 is a Russian single-engined aerobatic aircraft designed by Sukhoi as a lighter and more powerful version of the Sukhoi Su-29.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-33 is an all-weather carrier-based twin-engine air superiority fighter designed by Sukhoi and manufactured by Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aircraft Production Association, derived from the Su-27 and initially known as the Su-27K. Compared with the Su-27, the Su-33 has a strengthened undercarriage and structure, folding wings and stabilators, all for carrier operations. The Su-33 has canards and its wings are larger than the Su-27 for increased lift. The Su-33 has upgraded engines and a twin nose wheel, and is air refuelable.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-34 is a Soviet-origin Russian twin-engine, twin-seat, all-weather supersonic medium-range fighter-bomber/strike aircraft. It first flew in 1990, intended for the Soviet Air Forces, and it entered service in 2014 with the Russian Air Force.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-35 is the designation for two improved derivatives of the Su-27 air-defence fighter. They are single-seat, twin-engine, supermaneuverable aircraft, designed by the Sukhoi Design Bureau and built by the Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aircraft Plant.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-37 was a single-seat twin-engine aircraft designed by the Sukhoi Design Bureau that served as a technology demonstrator. It allowed for the need to enhance pilot control of the Su-27M, which was a further development of the Su-27. The sole aircraft had originally been built as the eleventh Su-27M (T10M-11) by the Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aircraft Production Association before having its thrust-vectoring nozzles installed. In addition, it was modified with updated flight- and weapons-control systems. The aircraft made its maiden flight in April 1996. Throughout the flight-test program, the Su-37 demonstrated its supermanoeuvrability at air shows, performing manoeuvres such as a 360-degree somersault. The aircraft crashed in December 2002 due to structural failure. The Su-37 did not enter production; despite a report in 1998 which claimed that Sukhoi had built a second Su-37 using the twelfth Su-27M airframe, T10M-11 remained the sole prototype. Sukhoi had instead applied the aircraft's systems to the design bureau's other fighter designs.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-38 is a Russian agricultural aircraft, the first aircraft of this type to be designed and built by the Sukhoi Design Bureau civil aircraft section.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-47 Berkut, also designated S-32 and S-37 during initial development, was an experimental supersonic jet fighter developed by the JSC Sukhoi Company. A distinguishing feature of the aircraft was its forward-swept wing that gave the aircraft excellent agility and maneuverability. While serial production of the type never materialized, the sole aircraft produced served as a technology demonstrator prototype for a number of advanced technologies later used in the 4.5 generation fighter Su-35 and current fifth-generation jet fighter Su-57.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-57 is a single-seat, twin-engine stealth multirole fighter developed by Sukhoi for the Russian Aerospace Forces. The aircraft is the product of the PAK FA fighter programme that would form the basis for a family of stealth combat aircraft. Sukhoi's internal designation for the aircraft is T-50. The Su-57 is the first fighter in Russian military service to feature stealth technology.
 W
WThe Sukhoi Su-80 is a Russian twin-turboprop, twin-boom STOL transport aircraft.
 W
WThe Sukhoi S-70 Okhotnik-B, also referred to as Hunter-B, is a Russian stealth heavy unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) being developed by Sukhoi and Russian Aircraft Corporation MiG as a sixth-generation aircraft project. The drone is based on the earlier Mikoyan Skat, designed by MiG, and encompassing some technologies of the fifth-generation Sukhoi Su-57 fighter jet.
 W
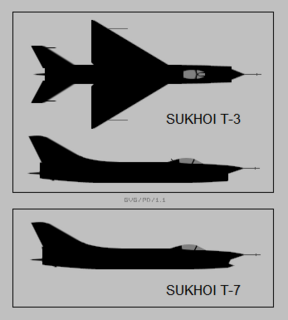
WThe Sukhoi T-3 was a prototype Soviet fighter aircraft.
 W
WThe Sukhoi T-49 was a prototype Soviet fighter aircraft.
 W
WThe Sukhoi T-4, or "Aircraft 100", or "Project 100", or "Sotka" was a Soviet high-speed reconnaissance, anti-ship and strategic bomber aircraft that did not proceed beyond the prototype stage. It is sometimes called the Su-100.