 W
WOn June 1, 1990, Presidents George H.W. Bush and Mikhail Gorbachev signed the bilateral U.S.–Soviet Chemical Weapons Accord; officially known as the "Agreement on Destruction and Non-production of Chemical Weapons and on Measures to Facilitate the Multilateral Convention on Banning Chemical Weapons". This pact was signed during a summit meeting in Washington D.C.
 W
WThe Anglo-German Naval Agreement (AGNA) of 18 June 1935 was a naval agreement between the United Kingdom and Germany regulating the size of the Kriegsmarine in relation to the Royal Navy.
 W
WThe Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. For the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all of the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude. The treaty entered into force in 1961 and currently has 54 parties. The treaty sets aside Antarctica as a scientific preserve, establishes freedom of scientific investigation, and bans military activity on the continent. The treaty was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War. Since September 2004, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat headquarters has been located in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
 W
WThe Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty (1972—2002) was an arms control treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union on the limitation of the anti-ballistic missile (ABM) systems used in defending areas against ballistic missile-delivered nuclear weapons. Under the terms of the treaty, each party was limited to two ABM complexes, each of which was to be limited to 100 anti-ballistic missiles.
 W
WThe Arms Trade Treaty (ATT) is a multilateral treaty that regulates the international trade in conventional weapons.
 W
WThe Biological Weapons Convention (BWC), or Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention (BTWC), is a disarmament treaty that effectively bans biological and toxin weapons by prohibiting their development, production, acquisition, transfer, stockpiling and use. The treaty's full name is the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production and Stockpiling of Bacteriological (Biological) and Toxin Weapons and on their Destruction.
 W
WThe list of parties to the Biological Weapons Convention encompasses the states which have signed and ratified or acceded to the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC), a multilateral treaty outlawing biological weapons.
 W
WChemical arms control is the attempt to limit the use or possession of chemical weapons through arms control agreements. These agreements are often motivated by the common belief "that these weapons ...are abominable", and by a general agreement that chemical weapons do "not accord with the feelings and principles of civilized warfare."
 W
WThe Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), officially the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production, Stockpiling and Use of Chemical Weapons and on their Destruction, is an arms control treaty administered by the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), an intergovernmental organization based in The Hague, The Netherlands. The treaty entered into force on 29 April 1997, and prohibits the large-scale use, development, production, stockpiling and transfer of chemical weapons and their precursors, except for very limited purposes. The main obligation of member states under the convention is to effect this prohibition, as well as the destruction of all current chemical weapons. All destruction activities must take place under OPCW verification.
 W
WThe Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) is a multilateral treaty that bans all nuclear tests, for both civilian and military purposes, in all environments. It was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 10 September 1996, but has not entered into force, as eight specific nations have not ratified the treaty.
 W
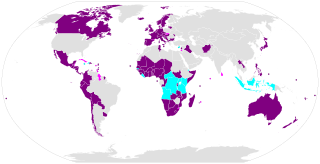
WThe contracting states to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) are the states that have signed and ratified the international agreement banning all nuclear explosions in all environments. Technically they will not be "parties" until the treaty enters into force, at which point these states will also be Member States of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO), which comes into existence upon entry into force of the treaty. Non-contracting states are also listed, including those that are signatories and those are not. States Signatories are Members of the CTBTO Preparatory Commission.
 W
WThe Convention on Cluster Munitions (CCM) is an international treaty that prohibits all use, transfer, production, and stockpiling of cluster bombs, a type of explosive weapon which scatters submunitions ("bomblets") over an area. Additionally, the Convention establishes a framework to support victim assistance, clearance of contaminated sites, risk reduction education, and stockpile destruction. The convention was adopted on 30 May 2008 in Dublin, and was opened for signature on 3 December 2008 in Oslo. It entered into force on 1 August 2010, six months after it was ratified by 30 states. As of July 2021, a total of 123 States have joined the Convention – 110 States Parties and 13 Signatories.
 W
WEuropean Security Treaty is proposition made by Russian president Dmitry Medvedev for new security agreement between Europe, CIS countries and United States.
 W
WThe Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany, or the Two Plus Four Agreement, was negotiated in 1990 between the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic, and the Four Powers which occupied Germany at the end of World War II in Europe: France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In the treaty, the Four Powers renounced all rights they held in Germany, allowing a reunited Germany to become fully sovereign the following year. At the same time, the two German states agreed to confirm their acceptance of the existing border with Poland, and accepted that the borders of Germany after unification would correspond only to the territories then administered by West and East Germany, with the exclusion and renunciation of any other territorial claims.
 W
WThe Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty was an arms control treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union. US President Ronald Reagan and Soviet General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev signed the treaty on 8 December 1987. The US Senate approved the treaty on 27 May 1988, and Reagan and Gorbachev ratified it on 1 June 1988.
 W
WThe Lahore Declaration was a bilateral agreement and governance treaty between India and Pakistan. The treaty was signed on 21 February 1999, at the conclusion of a historic summit in Lahore, and ratified by the parliaments of both countries the same year.
 W
WParties to the Chemical Weapons Convention encompasses the states that have ratified or acceded to the Chemical Weapons Convention, a multilateral treaty outlawing the production, stockpiling, and use of chemical weapons. In addition, these states are members of the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW).
 W
WThe London Naval Treaty, officially the Treaty for the Limitation and Reduction of Naval Armament, was an agreement between the United Kingdom, Japan, France, Italy, and the United States that was signed on 22 April 1930. Seeking to address issued not covered in the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty, which had created tonnage limits for each nation's surface warships, the new agreement regulated submarine warfare, further controlled cruisers and destroyers, and limited naval shipbuilding.
 W
WThe Second London Naval Treaty was an international treaty signed as a result of the Second London Naval Disarmament Conference held in London, the United Kingdom. The conference started on 9 December 1935 and treaty was signed by the participating nations on 25 March 1936.
 W
WThe Mutual and Balanced Force Reductions (MBFR) talks were a series of negotiations held in Vienna between NATO and Warsaw Pact countries between 1973 and 1989.
 W
WNew START is a nuclear arms reduction treaty between the United States and the Russian Federation with the formal name of Measures for the Further Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms. It was signed on 8 April 2010 in Prague, and, after ratification, entered into force on 5 February 2011. It is expected to last until 5 February 2026, having been extended in 2021.
 W
WThe Non-nuclear aggression agreement is a bilateral and nuclear weapons control treaty between the two South Asian states, India and Pakistan, on the reduction of nuclear arms and pledged not to attack or assist foreign powers to attack on each's nuclear installations and facilities. The treaty was drafted in 1988, and signed by the Prime Minister Benazir Bhutto and her Indian counterpart, Rajiv Gandhi on 21 December 1988; it entered into force on January 1991.
 W
WThe list of parties to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty encompasses the states which have signed and ratified or acceded to the international agreement limiting the spread of nuclear weapons.
 W
WThe Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is an international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy, and to further the goal of achieving nuclear disarmament and general and complete disarmament. Between 1965 and 1968, the treaty was negotiated by the Eighteen Nation Committee on Disarmament, a United Nations-sponsored organization based in Geneva, Switzerland.
 W
WThe Convention on the Prohibition of the Use, Stockpiling, Production and Transfer of Anti-Personnel Mines and on their Destruction, known informally as the Ottawa Treaty, the Anti-Personnel Mine Ban Convention, or often simply the Mine Ban Treaty, aims at eliminating anti-personnel landmines (AP-mines) around the world. To date, there are 164 state parties to the treaty. One state has signed but not ratified the treaty, while 32 UN states, including China, Russia, and the United States have not; making a total of 33 United Nations states not party.
 W
WThe Outer Space Treaty, formally the Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies, is a treaty that forms the basis of international space law. The treaty was opened for signature in the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union on 27 January 1967, and entered into force on 10 October 1967. As of February 2021, 111 countries are parties to the treaty, while another 23 have signed the treaty but have not completed ratification. In addition, the Republic of China in Taiwan, which is currently recognized by 14 UN member states, ratified the treaty prior to the United Nations General Assembly's vote to transfer China's seat to the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1971.
 W
WThe Partial Test Ban Treaty (PTBT) is the abbreviated name of the 1963 Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests in the Atmosphere, in Outer Space and Under Water, which prohibited all test detonations of nuclear weapons except for those conducted underground. It is also abbreviated as the Limited Test Ban Treaty (LTBT) and Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (NTBT), though the latter may also refer to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), which succeeded the PTBT for ratifying parties.
 W
WThe list of parties to the Partial Test Ban Treaty encompasses the states who have signed and ratified or acceded to the international agreement prohibiting all test detonations of nuclear weapons except underground.
 W
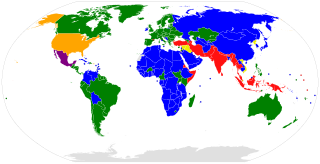
WThe list of parties to the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons encompasses the states which have signed and ratified or acceded to the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, a multilateral treaty outlawing nuclear weapons.
 W
WProtocol I is a 1977 amendment protocol to the Geneva Conventions relating to the protection of victims of international conflicts, where "armed conflicts in which peoples are fighting against colonial domination, alien occupation or racist regimes" are to be considered international conflicts. It reaffirms the international laws of the original Geneva Conventions of 1949, but adds clarifications and new provisions to accommodate developments in modern international warfare that have taken place since the Second World War.
 W
WThe Rush–Bagot Treaty or Rush–Bagot Disarmament was a treaty between the United States and Great Britain limiting naval armaments on the Great Lakes and Lake Champlain, following the War of 1812. It was ratified by the United States Senate on April 16, 1818, and was confirmed by Canada, following Confederation in 1867.
 W
WThe Seabed Arms Control Treaty is a multilateral agreement between the United States, Soviet Union, United Kingdom, and 91 other countries banning the emplacement of nuclear weapons or "weapons of mass destruction" on the ocean floor beyond a 12-mile (22.2 km) coastal zone. It allows signatories to observe all seabed "activities" of any other signatory beyond the 12-mile zone to ensure compliance.
 W
WSTART I was a bilateral treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union on the reduction and the limitation of strategic offensive arms. The treaty was signed on 31 July 1991 and entered into force on 5 December 1994. The treaty barred its signatories from deploying more than 6,000 nuclear warheads and a total of 1,600 intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and bombers.
 W
WSTART II was a bilateral treaty between the United States and Russia on the Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms. It was signed by US President George H. W. Bush and Russian President Boris Yeltsin on 3 January 1993, banning the use of multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicles (MIRVs) on intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Hence, it is often cited as the De-MIRV-ing Agreement. Despite negotiations, it never entered into effect. It was ratified by the US Senate on 26 January 1996 with a vote of 87–4. Although Russia ratified START II on 14 April 2000, it withdrew from the treaty on 14 June 2002 in response to US withdrawal from the ABM Treaty.
 W
WThe Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT) were two rounds of bilateral conferences and corresponding international treaties involving the United States and the Soviet Union. The Cold War superpowers dealt with arms control in two rounds of talks and agreements: SALT I and SALT II.
 W
WThe Treaty Between the United States of America and the Russian Federation on Strategic Offensive Reductions (SORT), also known as the Treaty of Moscow, was a strategic arms reduction treaty between the United States and Russia that was in force from June 2003 until February 2011 when it was superseded by the New START treaty. At the time, SORT was positioned as "represent[ing] an important element of the new strategic relationship" between the two countries with both parties agreeing to limit their nuclear arsenal to between 1,700 and 2,200 operationally deployed warheads each. It was signed in Moscow on 24 May 2002. After ratification by the U.S. Senate and the State Duma, SORT came into force on 1 June 2003. It would have expired on 31 December 2012 if not superseded by New START. Either party could have withdrawn from the treaty upon giving three months written notice to the other.
 W
WThe Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW), or the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty, is the first legally binding international agreement to comprehensively prohibit nuclear weapons with the ultimate goal being their total elimination. It was adopted on 7 July 2017, opened for signature on 20 September 2017, and entered into force on 22 January 2021.
 W
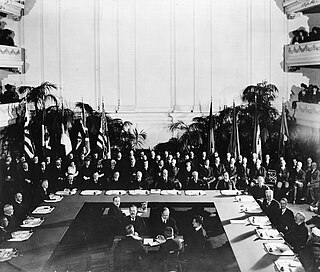
WThe Treaty of Versailles was the most important of the peace treaties that brought World War I to an end. The Treaty ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919 in the Palace of Versailles, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which had directly led to the war. The other Central Powers on the German side signed separate treaties. Although the armistice, signed on 11 November 1918, ended the actual fighting, it took six months of Allied negotiations at the Paris Peace Conference to conclude the peace treaty. The treaty was registered by the Secretariat of the League of Nations on 21 October 1919.
 W
WThe Washington Naval Treaty, also known as the Five-Power Treaty, was a treaty signed during 1922 among the major Allies of World War I, which agreed to prevent an arms race by limiting naval construction. It was negotiated at the Washington Naval Conference, held in Washington, D.C., from November 1921 to February 1922, and it was signed by the governments of Great Britain, the United States, France, Italy, and Japan. It limited the construction of battleships, battlecruisers and aircraft carriers by the signatories. The numbers of other categories of warships, including cruisers, destroyers, and submarines, were not limited by the treaty, but those ships were limited to 10,000 tons displacement each.
 W
WThe Wassenaar Arrangement on Export Controls for Conventional Arms and Dual-Use Goods and Technologies is a multilateral export control regime (MECR) with 42 participating states including many former Comecon countries established in 1996.
 W
WA variety of treaties and agreements have been enacted to regulate the use, development and possession of various types of weapons of mass destruction (WMD). Treaties may regulate weapons use under the customs of war, ban specific types of weapons, limit weapons research, limit allowable weapons stockpiles and delivery systems or regulate civilian use of weapon precursors. The history of weapons control has also included treaties to limit effective defense against weapons of mass destruction in order to preserve the deterrent doctrine of mutual assured destruction as well as treaties to limit the spread of nuclear technologies geographically.
 W
WThe list of parties to weapons of mass destruction treaties encompasses the states which have signed and ratified, succeeded, or acceded to any of the major multilateral treaties prohibiting or restricting weapons of mass destruction (WMD), in particular nuclear, biological, or chemical weapons.