 W
W90Y-DOTA-biotin consists of a radioactive substance (yttrium-90) complexed by a chelating agent (DOTA), which in turn is attached to the vitamin biotin via a chemical linker. It is used experimentally in pretargeted radioimmunotherapy. Animal studies have been conducted as well as clinical studies in humans.
 W
WActinium-225 is an isotope of actinium. It undergoes alpha decay to francium-221 with a half-life of 10 days, and is an intermediate decay product in the neptunium series. Except for minuscule quantities arising from this decay chain in nature, 225Ac is entirely synthetic.
 W
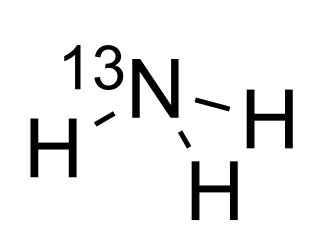
WAmmonia N-13 is a medication for diagnostic positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of the myocardium.
 W
WCopper (64Cu) oxodotreotide or Copper Cu 64 dotatate, sold under the brand name Detectnet, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) for localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in adults.
 W
WDesmethoxyfallypride is a moderate affinity dopamine D2 receptor/D3 receptor antagonist used in medical research, usually in the form of the radiopharmaceuticals desmethoxyfallypride or DMFP(18F) and has been used in human studies as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer.
 W
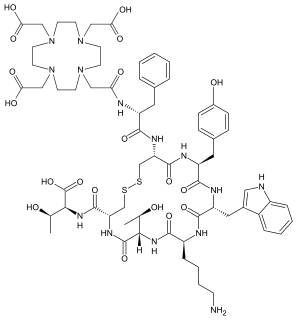
WDOTA-TATE is an eight amino acid long peptide, with a covalently bonded DOTA bifunctional chelator.
 W
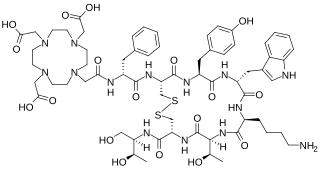
WEdotreotide (USAN, also known as (DOTA0-Phe1-Tyr3) octreotide, DOTA-TOC, DOTATOC) is a substance which, when bound to various radionuclides, is used in the treatment and diagnosis of certain types of cancer. When used therapeutically it is an example of peptide receptor radionuclide therapy.
 W
WFallypride is a high affinity dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist used in medical research, usually in the form of fallypride (18F) as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer in human studies.
 W
WFlortaucipir (18F), sold under the brand name Tauvid, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging to image the brain.
 W
WFluciclovine (18F), also known as anti-1-amino-3-18F-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid, or as Axumin, is a diagnostic agent indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels.
 W
WFluorine-18 (18F) is a fluorine radioisotope which is an important source of positrons. It has a mass of 18.0009380(6) u and its half-life is 109.771(20) minutes. It decays by positron emission 96% of the time and electron capture 4% of the time. Both modes of decay yield stable oxygen-18.
 W
WFluorodeoxyglucose (18F) (INN), or fluorodeoxyglucose F 18, also commonly called fluorodeoxyglucose and abbreviated [18F]FDG, 18F-FDG or FDG, is a radiopharmaceutical, specifically a radiotracer, used in the medical imaging modality positron emission tomography (PET). Chemically, it is 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose, a glucose analog, with the positron-emitting radionuclide fluorine-18 substituted for the normal hydroxyl group at the C-2 position in the glucose molecule.
 W
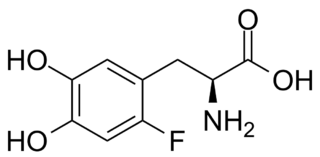
WFluorodopa, also known as FDOPA, is a fluorinated form of L-DOPA primarily synthesized as its fluorine-18 isotopologue for use as a radiotracer in positron emission tomography (PET).
 W
WFluoroestradiol F-18, also known as [18F]16α-fluoroestradiol and sold under the brand name Cerianna, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. It is an analog of estrogen and is used to detect estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer lesions.
 W
WFlutemetamol (18F) is a PET scanning radiopharmaceutical containing the radionuclide fluorine-18, used as a diagnostic tool for Alzheimer's disease.
 W
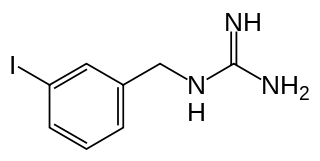
WIobenguane, or MIBG, is an aralkylguanidine analog of the adrenergic neurotransmitter, typically used as a radiopharmaceutical. It acts as a blocking agent for adrenergic neurons. When radiolabeled, it can be used in nuclear medicinal diagnostic and therapy techniques as well as in neuroendocrine chemotherapy treatments.
 W
WIodobenzamide is a pharmaceutical drug used for diagnostic purposes. It is a dopamine antagonist and it can be used by nuclear medicine physicians as a radioactive tracer for SPECT where the radioactive isotope is iodine-123 or iodine-125. The main purpose of a brain study with IBZM is the differentiation of Parkinson's disease from other neurodegenerative diseases such as Lewy Body dementia and multiple system atrophy.
 W
WIodopindolol is a beta-adrenergic selective antagonist tagged with radioisotopic iodine. It has been used to map beta receptors in cellular experiments.
 W
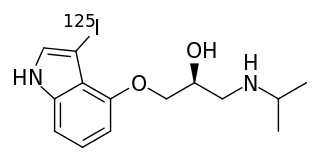
WIofetamine, brand names Perfusamine, SPECTamine), or N-isopropyl-(123I)-p-iodoamphetamine (IMP), is a lipid-soluble amine and radiopharmaceutical drug used in cerebral blood perfusion imaging with single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). Labeled with the radioactive isotope iodine-123, it is approved for use in the United States as a diagnostic aid in determining the localization of and in the evaluation of non-lacunar stroke and complex partial seizures, as well as in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.
 W
WIoflupane (123I) is the international nonproprietary name (INN) of a cocaine analogue which is a neuro-imaging radiopharmaceutical drug, used in nuclear medicine for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and the differential diagnosis of Parkinson's disease over other disorders presenting similar symptoms. During the DaT scan procedure it is injected into a patient and viewed with a gamma camera in order to acquire SPECT images of the brain with particular respect to the striatum, a subcortical region of the basal ganglia. The drug is sold under the brand name Datscan and is manufactured by GE Healthcare, formerly Amersham plc.
 W
WLilotomab is a murine monoclonal antibody against CD37, a glycoprotein which is expressed on the surface of mature human B cells. It was generated at the Norwegian Radium Hospital.
 W
WLutetium (177Lu) chloride, sold under the brand name Lumark among others, is a radioactive compound used for radiolabeling other medicines, either as an anti-cancer therapy or for scintigraphy. It is an isotopomer of lutetium(III) chloride containing the radioactive isotope 177Lu, which undergoes beta decay with a half-life of 6.65 days.
 W
WLutetium (177Lu) oxodotreotide (INN) or 177Lu DOTA-TATE, trade name Lutathera, is a chelated complex of a radioisotope of the element lutetium with DOTA-TATE, used in peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT). Specifically, it is used in the treatment of cancers which express somatostatin receptors.
 W
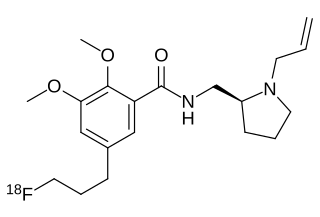
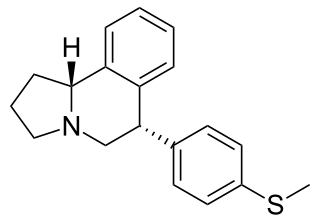
WLY-2459989 is a silent antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor (KOR) that has been developed by Eli Lilly as a radiotracer of the aforementioned receptor, labeled either with carbon-11 or fluorine-18. It possesses high affinity for the KOR and is highly selective for it over the μ-opioid receptor and the δ-opioid receptor. LY-2459989 is a fluorine-containing analogue and follow-up compound of LY-2795050, the first KOR-selective antagonist radiotracer. Relative to LY-2795050, LY-2459989 displays 4-fold higher affinity for the KOR and similar selectivity and also possesses greatly improved central nervous system permeation. The drug appears to possess a short duration of action, with only 25% remaining in serum at 30 minutes post-injection in rhesus monkeys, making it an ideal agent for application in biomedical imaging, for instance in positron emission tomography (PET).
 W
WMcN5652 is a molecule that can be radiolabeled and then used as a radioligand in positron emission tomography (PET) studies. The [11C]-(+)-McN5652 enantiomer binds to the serotonin transporter. The radioligand is used for molecular neuroimaging and for imaging of the lungs.
 W
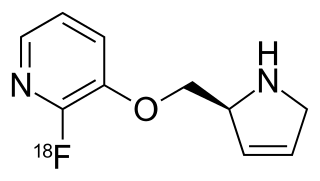
WMefway is a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor antagonist used in medical research, usually in the form of mefway (18F) as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer.
 W
WNifene is a high affinity, selective nicotinic α4β2* receptor partial agonist used in medical research for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, usually in the form of nifene (18F) as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer.
 W
WNuclear Medicine and Biology is a peer-reviewed medical journal published by Elsevier that covers research on all aspects of nuclear medicine, including radiopharmacology, radiopharmacy and clinical studies of targeted radiotracers. It is the official journal of the Society of Radiopharmaceutical Sciences. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2011 impact factor of 3.023.
 W
WOxygen-15 labelled water (also known as 15O-water, [O-15]-H2O, or H215O) is a radioactive variation of regular water, in which the oxygen atom has been replaced by oxygen-15 (15O), a positron-emitting isotope. 15O-water is used as a radioactive tracer for measuring and quantifying blood flow using positron emission tomography (PET) in the heart, brain and tumors.
 W
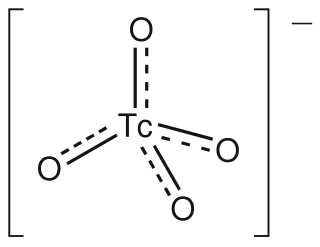
WThe pertechnetate ion is an oxoanion with the chemical formula TcO−4. It is often used as a convenient water-soluble source of isotopes of the radioactive element technetium (Tc). In particular it is used to carry the 99mTc isotope which is commonly used in nuclear medicine in several nuclear scanning procedures.
 W
WPET radiotracer is a type of radioligand that is used for the diagnostic purposes via positron emission tomography imaging technique.
 W
WPiflufolastat F-18, sold under the brand name Pylarify, is a radioactive diagnostic agent used for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. It is given by intravenous injection.
 W
WRadiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents.
 W
WRadiopharmacology is radiochemistry applied to medicine and thus the pharmacology of radiopharmaceuticals. Radiopharmaceuticals are used in the field of nuclear medicine as radioactive tracers in medical imaging and in therapy for many diseases. Many radiopharmaceuticals use technetium-99m (Tc-99m) which has many useful properties as a gamma-emitting tracer nuclide. In the book Technetium a total of 31 different radiopharmaceuticals based on Tc-99m are listed for imaging and functional studies of the brain, myocardium, thyroid, lungs, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, skeleton, blood and tumors.
 W
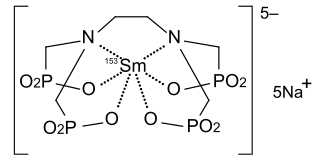
WSamarium (153Sm) lexidronam is a chelated complex of a radioisotope of the element samarium with EDTMP. It is used to treat pain when cancer has spread to the bone.
 W
WSeHCAT is a drug used in a clinical test to diagnose bile acid malabsorption.
 W
WTechnetium is a chemical element with the symbol Tc and atomic number 43. It is the lightest element whose isotopes are all radioactive, none of which is stable other than the fully ionized state of 97Tc. Nearly all available technetium is produced as a synthetic element. Naturally occurring technetium is a spontaneous fission product in uranium ore and thorium ore, the most common source, or the product of neutron capture in molybdenum ores. The silvery gray, crystalline transition metal lies between manganese and rhenium in group 7 of the periodic table, and its chemical properties are intermediate between those of both adjacent elements. The most common naturally occurring isotope is 99Tc, in traces only.
 W
WTechnetium (99mTc) exametazime is a radiopharmaceutical sold under the trade name Ceretec, and is used by nuclear medicine physicians for the detection of altered regional cerebral perfusion in stroke and other cerebrovascular diseases. It can also be used for the labelling of leukocytes to localise intra-abdominal infections and inflammatory bowel disease. Exametazime is sometimes referred to as hexamethylpropylene amine oxime or HMPAO, although correct chemical names are:(NE)-N-[(3R)-3-[[3-[[(2R,3E)-3-hydroxyiminobutan-2-yl]amino]-2,2-dimethylpropyl]amino]butan-2-ylidene]hydroxylamine or 3,3'-( diimino)bis-2-butanone dioxime.
 W
WTechnetium (99mTc) sestamibi (INN) is a pharmaceutical agent used in nuclear medicine imaging. The drug is a coordination complex consisting of the radioisotope technetium-99m bound to six (sesta=6) methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) ligands. The anion is not defined. The generic drug became available late September 2008. A scan of a patient using MIBI is commonly known as a "MIBI scan".
 W
WTechnetium (99mTc) tetrofosmin is a drug used in nuclear medicine cardiac imaging. It is sold under the brand name Myoview. The radioisotope, technetium-99m, is chelated by two 1,2-bis[di-(2-ethoxyethyl)phosphino]ethane ligands which belong to the group of diphosphines and which are referred to as tetrofosmin.
 W
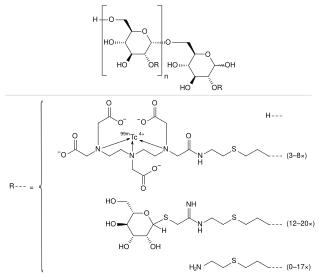
WTechnetium (99mTc) tilmanocept, trade name Lymphoseek, is a radiopharmaceutical diagnostic imaging agent used to locate lymph nodes which may be draining from tumors, and assist doctors in locating lymph nodes for removal during surgery.
 W
WTechnetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99, symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope in the world.
 W
WA technetium-99m generator, or colloquially a technetium cow or moly cow, is a device used to extract the metastable isotope 99mTc of technetium from a decaying sample of molybdenum-99. 99Mo has a half-life of 66 hours and can be easily transported over long distances to hospitals where its decay product technetium-99m is extracted and used for a variety of nuclear medicine diagnostic procedures, where its short half-life is very useful.