 W
WAbolition of Forced Labour Convention, 1957, the full title of which is Convention concerning the Abolition of Forced Labour, 1957, is one of the eight ILO fundamental conventions of the International Labour Organization, which cancels certain forms of forced labour still allowed under the Forced Labour Convention of 1930, such as punishment for strikes and as a punishment for holding certain political views.
 W
WThe African Economic Community (AEC) is an organization of African Union states establishing grounds for mutual economic development among the majority of African states. The stated goals of the organization include the creation of free trade areas, customs unions, a single market, a central bank, and a common currency thus establishing an economic and monetary union.
 W
WThe African Charter on Human and Peoples' Rights is an international human rights instrument that is intended to promote and protect human rights and basic freedoms in the African continent.
 W
WThe African Development Bank Group or Banque Africaine de Développement (BAD) is a multilateral development finance institution headquartered in Abidjan, Ivory Coast, since September 2014. The AfDB is a financial provider to African governments and private companies investing in the regional member countries (RMC).
 W
WThe Convention on International Civil Aviation, also known as the Chicago Convention, established the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a specialized agency of the UN charged with coordinating international air travel. The Convention establishes rules of airspace, aircraft registration and safety, security, and sustainability, and details the rights of the signatories in relation to air travel. The Convention also contains provisions pertaining to taxation.
 W
WThe United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The Convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.
 W
WThe International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966, and in force from 23 March 1976 in accordance with Article 49 of the covenant. Article 49 allowed that the covenant would enter into force three months after the date of the deposit of the thirty-fifth instrument of ratification or accession. The covenant commits its parties to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial. As of September 2019, the Covenant has 173 parties and six more signatories without ratification. Notable holdouts are People's Republic of China and Cuba. North Korea tried to withdraw.
 W
WThe First Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights is an international treaty establishing an individual complaint mechanism for the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR). It was adopted by the UN General Assembly on 16 December 1966, and entered into force on 23 March 1976. As of May 2020, it had 35 signatories and 116 states parties. Two of the ratifying states—Jamaica and Trinidad and Tobago—have denounced the protocol.
 W
WThe Common Fund for Commodities (CFC) is an intergovernmental financial institution established within the framework of the United Nations. It is a vestige of the proposed New International Economic Order. The CFC finances commodity development projects in developing states.
 W
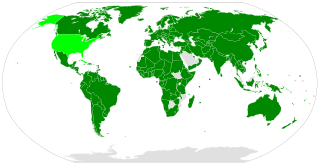
WThe World Customs Organization (WCO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. The WCO works on customs-related matters including the development of international conventions, instruments, and tools on topics such as commodity classification, valuation, rules of origin, collection of customs revenue, supply chain security, international trade facilitation, customs enforcement activities, combating counterfeiting in support of Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), illegal drug enforcement, combating counterfeiting of medicinal drugs, illegal weapons trading, integrity promotion, and delivering sustainable capacity building to assist with customs reforms and modernization. The WCO maintains the international Harmonized System (HS) goods nomenclature, and administers the technical aspects of the World Trade Organization (WTO) Agreements on Customs Valuation and Rules of Origin.
 W
WThe International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 16 December 1966 through GA. Resolution 2200A (XXI), and came in force from 3 January 1976. It commits its parties to work toward the granting of economic, social, and cultural rights (ESCR) to the Non-Self-Governing and Trust Territories and individuals, including labour rights and the right to health, the right to education, and the right to an adequate standard of living. As of July 2020, the Covenant has 171 parties. A further four countries, including the United States, have signed but not ratified the Covenant.
 W
WThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, fiat panis, translates to "let there be bread". It was founded in October 1945.
 W
WThe First Geneva Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of the Wounded in Armies in the Field, held on 22 August 1864, is the first of four treaties of the Geneva Conventions. It defines "the basis on which rest the rules of international law for the protection of the victims of armed conflicts." After the first treaty was adopted in 1864, it was significantly revised and replaced in 1906, 1929, and finally 1949. It is inextricably linked to the International Committee of the Red Cross, which is both the instigator for the inception and enforcer of the articles in these conventions.
 W
WThe Second Geneva Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked Members of Armed Forces at Sea is one of the four treaties of the Geneva Conventions. The Geneva Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked Members of Armed Forces at Sea was first adopted in 1949, it replaced the Hague Convention (X) of 1907. It adapts the main protective regime of the First Geneva Convention to combat at sea.
 W
WThe Third Geneva Convention, relative to the treatment of prisoners of war, is one of the four treaties of the Geneva Conventions. The Geneva Convention relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War was first adopted in 1929, but significantly revised at the 1949 conference. It defines humanitarian protections for prisoners of war. There are 196 state parties to the Convention.
 W
WThe Geneva Convention relative to the Protection of Civilian Persons in Time of War, more commonly referred to as the Fourth Geneva Convention and abbreviated as GCIV, is one of the four treaties of the Geneva Conventions. It was adopted in August of 1950. While the first three conventions dealt with combatants, the Fourth Geneva Convention was the first to deal with humanitarian protections for civilians in a war zone. There are currently 196 countries party to the 1949 Geneva Conventions, including this and the other three treaties.
 W
WIndigenous and Tribal Populations Convention, 1957 is an International Labour Organization Convention within the United Nations that was established in 1957. Its primary focus is to recognize and protect the cultural, religious, civil and social rights of indigenous and tribal populations within an independent country, and to provide a standard framework for addressing the economic issues that many of these groups face.
 W
WThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) is an international financial institution, established in 1944 and headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, that is the lending arm of World Bank Group. The IBRD offers loans to middle-income developing countries. The IBRD is the first of five member institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The initial mission of the IBRD in 1944, was to finance the reconstruction of European nations devastated by World War II. The IBRD and its concessional lending arm, the International Development Association (IDA), are collectively known as the World Bank as they share the same leadership and staff.
 W
WThe International Convention on Load Lines (CLL), was signed in London on 5 April 1966, amended by the 1988 Protocol and further revised in 2003. The convention pertains specifically to a ship's load line, a marking of the highest point on a ship's hull that can safely meet the surface of the water; a ship that is loaded to the point where its load line is underwater and no longer visible has exceeded its draft and is in danger because its capacity has been exceeded.
 W
WThe International Development Association (IDA) is an international financial institution which offers concessional loans and grants to the world's poorest developing countries. The IDA is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C. in the United States. It was established in 1960 to complement the existing International Bank for Reconstruction and Development by lending to developing countries which suffer from the lowest gross national income, from troubled creditworthiness, or from the lowest per capita income. Together, the International Development Association and International Bank for Reconstruction and Development are collectively generally known as the World Bank, as they follow the same executive leadership and operate with the same staff.
 W
WThe International Finance Corporation (IFC) is an international financial institution that offers investment, advisory, and asset-management services to encourage private-sector development in less developed countries. The IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C. in the United States.
 W
WThe International Fund for Agricultural Development is an international financial institution and a specialised agency of the United Nations that works to address poverty and hunger in rural areas of developing countries. It is the only multilateral development organization that focuses solely on rural economies and food security.
 W
WThe International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice through setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and oldest specialised agency of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.
 W
WThe International Maritime Organization is a specialised agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating shipping. The IMO was established following agreement at a UN conference held in Geneva in 1948 and the IMO came into existence ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959. Headquartered in London, United Kingdom, the IMO currently has 174 member states and three associate members.
 W
WThe International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries "working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world." Formed in 1944, started on 27 December 1945, at the Bretton Woods Conference primarily by the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes, it came into formal existence in 1945 with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international monetary system. It now plays a central role in the management of balance of payments difficulties and international financial crises. Countries contribute funds to a pool through a quota system from which countries experiencing balance of payments problems can borrow money. As of 2016, the fund had XDR 477 billion.
 W
WThe International Organization for Migration (IOM) is an intergovernmental organization that provides services and advice concerning migration to governments and migrants, including internally displaced persons, refugees, and migrant workers. In September 2016, IOM became a related organization of the United Nations. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration (ICEM) to help resettle people displaced by World War II. As of 2021, the International Organization for Migration has 173 member states and nine observer states.
 W
WThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization (ITSO) is an intergovernmental organization charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.
 W
WThe United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. As of June 2016, 167 countries and the European Union are parties.
 W
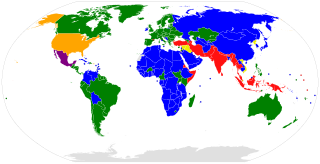
WA World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of great natural beauty. As of July 2021, a total of 1,154 World Heritage Sites exist across 167 countries. With 58 selected areas, Italy is the country with the most sites on the list.
 W
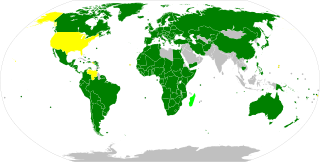
WProtocol I is a 1977 amendment protocol to the Geneva Conventions relating to the protection of victims of international conflicts, where "armed conflicts in which peoples are fighting against colonial domination, alien occupation or racist regimes" are to be considered international conflicts. It reaffirms the international laws of the original Geneva Conventions of 1949, but adds clarifications and new provisions to accommodate developments in modern international warfare that have taken place since the Second World War.
 W
WThe Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees, also known as the 1951 Refugee Convention or the Geneva Convention of 28 July 1951, is a United Nations multilateral treaty that defines who a refugee is, and sets out the rights of individuals who are granted asylum and the responsibilities of nations that grant asylum. The Convention also sets out which people do not qualify as refugees, such as war criminals. The Convention also provides for some visa-free travel for holders of refugee travel documents issued under the convention.
 W
WThe Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees is a key treaty in international refugee law. It entered into force on 4 October 1967, and 146 countries are parties.
 W
WThe Southern African Development Community (SADC) is an inter-governmental organization headquartered in Gaborone, Botswana. Its goal is to further regional socio-economic cooperation and integration as well as political and security cooperation among 16 countries in southern Africa.
 W
WThe United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) is a specialised agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, the sciences, and culture. It has 193 member states and 11 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental, and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate.
 W
WThe UNESCO 1970 Convention on the Means of Prohibiting and Preventing the Illicit Import, Export and Transfer of Ownership of Cultural Property is an international treaty. The treaty, signed to combat the illegal trade in cultural items, was signed on 14 November 1970, and came into effect on 24 April 1972. As of August 2021, 141 states have ratified the treaty.
 W
WThe Charter of the United Nations is the foundational treaty of the United Nations, an intergovernmental organization. It establishes the purposes, governing structure, and overall framework of the UN system, including its six principal organs: the Secretariat, the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Trusteeship Council.
 W
WThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that assists countries in economic and industrial development. It is headquartered at the UN Office in Vienna, Austria, with a permanent presence in over 60 countries. As of April 2019, UNIDO comprises 170 member states, which together set the organization's policies, programs, and principles through the biannual General Conference.
 W
WThe Vienna Convention on Consular Relations is an international treaty that defines a framework for consular relations between sovereign states. It codifies many consular practices that originated from state custom and various bilateral agreements between states.
 W
WThe Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations of 1961 is an international treaty that defines a framework for diplomatic relations between independent countries. It specifies the privileges of a diplomatic mission that enable diplomats to perform their function without fear of coercion or harassment by the host country. This forms the legal basis for diplomatic immunity. Its articles are considered a cornerstone of modern international relations. As of June 2020, it has been ratified by 193 states.
 W
WThe Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is an international treaty adopted in 1979 by the United Nations General Assembly. Described as an international bill of rights for women, it was instituted on 3 September 1981 and has been ratified by 189 states. Over fifty countries that have ratified the Convention have done so subject to certain declarations, reservations, and objections, including 38 countries who rejected the enforcement article 29, which addresses means of settlement for disputes concerning the interpretation or application of the Convention. Australia's declaration noted the limitations on central government power resulting from its federal constitutional system. The United States and Palau have signed, but not ratified the treaty. The Holy See, Iran, Somalia, and Tonga are not signatories to CEDAW.
 W
WThe World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide.
 W
WThe World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
 W
WThe World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is the United Nations specialized agency entrusted with the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism, having its headquarters in Madrid, Spain. It is the leading international organization in the field of tourism, which promotes tourism as a driver of economic growth, inclusive development and environmental sustainability and offers the sector leadership and support in advancing knowledge and tourism policies worldwide. It serves as a global forum for tourism policy issues and a practical source of tourism research and knowledge. It encourages the implementation of the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism to maximize the contribution of tourism to socio-economic development, while minimizing its possible negative impacts, and is committed to promoting tourism as an instrument in achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), geared towards eliminating poverty and fostering sustainable development and peace worldwide.