 W
WThe 2S9 NONA is an extremely light-weight self-propelled and air-droppable 120 mm gun-mortar designed in the Soviet Union, which entered service in 1981. The 2S9 chassis is designated the S-120 and based on the aluminium hull of the BTR-D airborne multi-purpose tracked armoured personnel carrier. More generally, the 120 mm mortar is referred to as the Nona, with the 2S9 also known as the Nona-S. Although no figures have been released, it is estimated that well over 1,000 2S9 were built.
 W
WThe 2S31 Vena is a Russian amphibious self-propelled 120 mm mortar system. "2S31" is its GRAU designation.
 W
WThe 4.7-inch gun M1906 was designed and issued by the US Army Ordnance Department beginning in 1906, with the first units receiving the weapon in 1911. It was of the field gun type. It was one of very few pre-war US artillery designs selected for wartime production in World War I, although few of these weapons were delivered to France and used in action. A combination of a limited pre-war munitions industry, the short (19-month) US participation in the war, technical problems with large-scale production, and the ready availability of munitions overseas led to this.
 W
WThe 12 cm 11th Year Type naval gun was a Japanese naval gun and coast defense gun used on submarines, minesweepers, and torpedo boats of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.
 W
WThe 12 cm Minenwerfer M 15 was a medium mortar used by Austria-Hungary in World War I. It was designed by the Army's own Technisches und Administratives Militär-Komitee (TMK) as an enlarged 9 cm Minenwerfer M 14 in 1915. The War Ministry decided to order 50 from the TMK, but the latter preferred only to produce 10 and switch the remaining 40 to the 14 cm Minenwerfer M 15, but no response was made by the Ministry. The TMZ placed an order for the 10 mortars from Teudloff & Dittrich in Vienna at the end of 1915. A follow on order for another hundred was canceled in February 1916.
 W
WThe 12 cm Kanone M 80 was a light siege gun used by Austria-Hungary during World War I. Designed to replace the M 61 series of siege guns the M 80 family of siege guns offered greater range and armor penetration than the older guns. The proven steel-bronze was used for the barrel and the iron carriage lacked any system to absorb recoil other than the traditional recoil wedges placed underneath and behind the wheels of the carriage. These wedges helped to absorb the recoil force and encouraged the wheels to run forward to bring the gun back into battery. Generally a wooden firing platform was constructed for these guns in action to provide a level and smooth surface. Shortly after these guns were adopted a hydraulic recoil cylinder was adapted to absorb the recoil forces. It was attached to the underside of the carriage and the firing platform. For transport the barrel was removed from the carriage by a crane and carried separately.
 W
WThe 12-pounder long gun was an intermediary calibre piece of artillery mounted on warships of the Age of sail. They were used as main guns on the most typical frigates of the early 18th century, on the second deck of fourth-rate ships of the line, and on the upper decks or castles of 80-gun and 120-gun ships of the line. Naval 12-pounders were similar to 12-pound Army guns in the Gribeauval system: the canon lourd de 12 Gribeauval, used as a siege weapon, and the canon de 12 Gribeauval, which was considered a heavy field artillery piece.
 W
WThe 120 KRH 92 is a 120 mm mortar manufactured in Finland.
 W
WThe 120 mm 50 caliber Pattern 1905 was a Russian naval gun developed by Vickers for export in the years before World War I that armed a variety of warships of the Imperial Russian Navy. Guns salvaged from scrapped ships found a second life as coastal artillery, railway artillery and aboard river monitors during the Russian Civil War. It was estimated that there were 110 guns in the Soviet Navy's inventory in 1941. Of these, 39 were in the Baltic Fleet, 20 in the Black sea Fleet, 24 in the Amur Flotilla, 11 in the Pacific Fleet and 6 in the Pinsk flotilla in World War II.
 W
WThe 120 mm howitzer Model 1901 – was a German howitzer used by the Imperial Russian and Romanian Armies during the First World War.
 W
WThe 120 mm Krupp howitzer M1905 was a howitzer used by Turkey, Japan and a few smaller armies including during World War I. After the Ottoman Empires entrance into World War I in 1914 on the side of the Central Powers, it realized that it needed to modernize its artillery. The Model 1905 was a "stock gun" from Krupp that could be supplied to customers from parts on hand, on short notice and with minor alterations to suit the customers' needs. The Model 1905 was a conventional artillery piece for its time, except for a lack of a Gun shield for the crew. The lack of a Gun shield was not a major liability, as most artillery quickly moved into concealed positions after the first few months of war.
 W
WThe 120 mm Gun M1 was the United States Army's standard super-heavy anti-aircraft gun during World War II and the Korean War, complementing the smaller and more mobile M2 90 mm gun in service. Its maximum altitude was about 60,000 ft (18,000 m), which earned it the nickname stratosphere gun.
 W
W120 mm Schneider-Canet M1897 long gun was a heavy artillery piece manufactured by the French company Schneider-Creusot. It was a slow firing gun without a recoil mechanism but with significant range and weight of the shell.
 W
WThe M1943 Mortar also known as the SAMOVAR is a Soviet 120 millimeter calibre smoothbore mortar first introduced in 1943 as a modified version of the M1938 mortar. It virtually replaced the M1938 as the standard weapon for mortar batteries in all Soviet infantry battalions by the late 1980s, though the armies of the Warsaw Pact utilised both in their forces.
 W
WThe 120mm 45 caliber Pattern 1892 was a Russian naval gun developed in the years before the Russo-Japanese War that armed a variety of warships of the Imperial Russian Navy during the Russo-Japanese War and World War I. Guns salvaged from scrapped ships found a second life on river gunboats of the Soviet Navy during the Russian Civil War and as coastal artillery and railway artillery during World War II. It was estimated that in 1941 there were 35 still in service.
 W
WAMOS or Advanced Mortar System is a Finno-Swedish 120 mm automatic twin barrelled, breech loaded mortar turret. AMOS has been fitted to a wide range of armoured vehicles, such as the Sisu Pasi, Patria AMV and Combat Vehicle 90. The Swedish Navy originally planned to fit AMOS to the CB90 assault craft, but found that it was too small to carry it. Instead, a project to develop the larger Combat Boat 2010 was launched specifically to carry AMOS. Sweden cancelled its acquisition of the AMOS in 2009 due to budget regulations by recommendations from Genomförandegruppen. In 2016 a new self propelled mortar system called Mjölner based on a CV90 hull was ordered by the Swedish armed forces, it is based on the AMOS and has many visual similarities but is not as advanced.
 W
WThe BL 4.7-inch, 45-calibre gun was a British medium-velocity naval gun introduced in 1918 for destroyers, intended to counter a new generation of heavily armed destroyers that Germany was believed to be developing.
 W
WThe Bofors 120 mm automatic gun was a dual purpose naval gun. It was initially used aboard Halland-class destroyers and Colombian Navy 7 de Agosto (D-06) and 20 de Julio (D-05). The guns also were used on the Dutch Holland-class and Friesland class destroyers, and later the Tromp-class frigates.
 W
WThe Canon de 12 cm L mle 1931 was a medium field gun made and used by Belgium in World War II. Captured guns were taken into Wehrmacht service after the surrender of Belgium in May 1940 as the 12 cm K 370(b) where it was generally used on coast defense duties.
 W
WThe Cardom "Hatchet", is an Israeli 81 mm/120 mm Recoil Mortar System (RMS), manufactured by Soltam Systems. It is used by the US Army, the Israel Defence Forces, NATO countries, and others. The Cardom is an autonomous, computerized system for mounting on light and medium armored carriers. The system provides accurate and effective fire support.
 W
WThe Dragon Fire 120 mm heavy mortar was designed and produced by the French company TDA Armaments that was picked up by the US Marine Corps for its EFSS requirement. It is a fully automated mortar capable of using rifled or smoothbore 120 mm ammunition. Like all mortars, it is a high-angle-of-fire weapon used for indirect fire support. Dragon Fire is also expected to be effective in a counter-battery role.
 W
WThe Gonzalez Hontoria de 12 cm mod 1883 was a Spanish naval gun developed in the late 1800s that armed a variety of warships of the Spanish Navy during the Spanish–American War.
 W
WThe IMI 120 mm gun is an L44 smoothbore tank gun designed and produced by Israeli Military Industries (IMI). It is widely confused as a licensed production of the Rheinmetall L44 tank gun, however it was developed by IMI from 1983 to 1988, to meet the requirements of the Israel Defense Forces' Merkava Mark III main battle tank, i.e. a narrower mount like in the M-60, both tanks designed around a 105mm gun.
 W
WItalian 120 millimetre naval guns were standard main armament on Italian destroyers and were widely used on various other ships and coastal artillery. The 50-calibre guns used a charge of 9.7 kilograms (21 lb) of smokeless powder to push a 23.49-kilogram (51.8 lb) projectile to a velocity of 950 metres per second (3,100 ft/s). Velocity was later reduced to 920 metres per second (3,000 ft/s), which gave a maximum range of 19.6 kilometres (12.2 mi) at 45° elevation or 18.2 kilometres (11.3 mi) at 35° elevation. Variants of similar designs were built by Ansaldo, OTO, Vickers, Schneider, Canet and Armstrong. Older and shorter-barreled guns have different ballistics as noted below.
 W
WM120 Rak is a self-propelled gun equipped with an automatically loaded 120 mm mortar mounted on a tracked (SMG 120 / M120G) and wheeled chassis, designed by Huta Stalowa Wola (HSW). It is produced in Poland, and used by Polish Land Forces. Serial production and the first delivery started in 2017.
 W
WThe 120-PM-38 or M1938 was a 120 mm Soviet mortar that was used in large numbers by the Red Army during World War II. Although a conventional design its combination of light weight, mobility, heavy firepower and range saw its features widely copied by successive generations of mortars.
 W
WThe Obusier de 120 mm C mle 1897 Schneider-Canet was a howitzer built by the French arms company Schneider-Creusot and used by Serbia during the Balkan Wars and World War I.
 W
WThe Obusier de 120 mm modèle 1915 Tir Rapide or quick loading 120 mm Howitzer Model 1915 was a French howitzer designed and built by the Schneider company and used by a number of nations during the First World War.
 W
WThe Obusier de 120 mm C modèle 1890 - was a French howitzer designed by Captain Louis Henry Auguste Baquet and employed by the French army during the First World War. It was one of the first modern howitzers equipped with a recoil system.
 W
WThe Peigné-Canet-Schneider mle 1897 gun carriage was a railway gun carriage designed and built during the late 1800s. Two types of guns were mounted on these carriages and both the French Army and US Army used them during World War I. They were retired soon after World War I.
 W
WThe PLL-05 is a Chinese self-propelled gun-mortar in use by Chinese mechanised infantry formations. Conceptually it is similar to the Russian 2S23 "Nona-SVK" three of which China purchased for evaluation; at one time it was reported that China would purchase 100 of the Russian vehicles however this failed to occur, nor does it appear that there was a formal transfer of technology to China. The Chinese system features a longer barreled weapon mounted on the Type 92 variant of the WZ551 armored personnel carrier.
 W
WThe QF 4.7 inch Gun Mark V originated as a 4.7 in (120 mm) 45-calibre naval gun designed by the Elswick Ordnance Company for export customers and known as the Pattern Y.
 W
WThe QF 4.7 inch Gun Mark VIII was a British naval anti-aircraft gun designed in the 1920s for the Royal Navy. This was the largest caliber fixed ammunition gun ever in service in the RN, though the round was considerably shorter and lighter than the round for the QF 4.5-inch Mk I – V naval gun. It was carried in powered HA XII mountings on the two Nelson-class battleships, two of the three Courageous-class aircraft carriers, the minelayer HMS Adventure, and the Australian seaplane tender HMAS Albatross.
 W
WThe 4.7 inch QF Mark IX and Mark XII were 45-calibre, 4.7-inch (120 mm) naval guns which armed the majority of Royal Navy and Commonwealth destroyers in World War II, and were exported to many countries after World War II as the destroyers they were mounted on were sold off.
 W
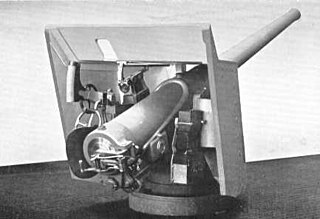
WThe 4.7 inch QF Mark XI was a 50-calibre, 4.7-inch (120 mm) naval gun deployed on Royal Navy (RN) and Allied destroyers during World War II.
 W
WThe QF 4.7-inch Gun Mks I, II, III, and IV were a family of British quick-firing 4.724-inch (120 mm) naval and coast defence guns of the late 1880s and 1890s that served with the navies of various countries. They were also mounted on various wheeled carriages to provide the British Army with a long range gun. They all had a barrel of 40 calibres length.
 W
WRazm is an Iranian 120 mm heavy mortar unveiled in 2010 and produced by Iran's Defense Industries Organization. It is a long range mortar with range of 16 km with rocket-assisted munitions and can be used alongside tube artillery. To achieve this range, Razm uses an unusually long barrel, and is very heavy. The overall design of the mortar is similar to that of 120 mm HM 16.
 W
WThe Rheinmetall 12 cm leFH 08 was a howitzer used by Norway in World War II. It was known in Norwegian service as the 12 cm felthaubits/m09. Captured guns were given a German designation after the Invasion of Norway as the 12 cm leFH 375(n). Two batteries of Artillerie-Abteilung 477, which served in Finland during the war, were equipped with 12 cm Norwegian howitzers, which might have included these guns.
 W
WThe Rheinmetall Rh-120 is a 120 mm smoothbore tank gun designed and produced by the West German Rheinmetall-DeTec AG company, developed in response to Soviet advances in armor technology and development of new armored threats. Production began in 1974, with the first version of the gun, known as the L/44 as it was 44 calibers long, used on the German Leopard 2 tank and soon produced under license for the American M1A1 Abrams and other tanks. The 120-millimeter (4.7 in) gun has a length of 5.28 meters (17.3 ft), and the gun system weighs approximately 3,317 kilograms (7,313 lb).
 W
WThe RML 40-pounder gun was a British rifled muzzle-loading siege and fortification gun designed in 1871. It was intended to supersede the RBL 40-pounder Armstrong gun after the British military reverted to rifled muzzle-loading artillery until a more satisfactory breech-loading system than that of the Armstrong guns was developed.
 W
WThe Royal Ordnance L11A5, officially designated Gun 120 mm Tk L11, is a 120 mm L/55 rifled tank gun design. It was the first of NATO's 120mm Main Battle Tank guns which became the standard calibre for Western tanks in the later period of the Cold War. By 2005, a total of 3,012 L11 guns were produced. List price was US $227,000 (1990).
 W
WThe L30A1, officially designated Gun 120 mm Tk L30, is a 120 mm rifled tank gun used by the British Army and Royal Army of Oman. It is an improved production model of the Royal Ordnance L11 series of rifled tank guns.
 W
WThe Type 3 12 cm AA gun was an anti-aircraft gun used in quantity by the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II.The Type 3 number was designated for the year the gun was accepted, 2603 in the Japanese imperial year calendar, or 1943 in the Gregorian calendar. It replaced the earlier Type 88 75 mm AA Gun in Japanese service.
 W
WThe Type 10 or 12 cm/45 10th Year Type naval gun was a Japanese 120 mm calibre dual purpose anti-aircraft and coastal defense gun used during the Second World War. It was derived from the 12 cm/45 3rd Year Type naval gun. The Type 10 number was designated for the year the gun was accepted,the 10th year of Emperor Taishō's reign, 1927 in the Gregorian calendar. It served as the secondary armament on a number of Japanese aircraft carriers and cruisers and as the main armament on smaller ships, in single or twin mountings.