 W
WThe Attack on Marstrand was a successful Dano-Norwegian siege of the Swedish town of Marstrand and Carlsten fortress which took place between July 10 and July 16, 1719 during the end of the Great Northern War.
 W
WSack of Baturyn, sometimes also referred to as the Slaughtering in Baturyn, was a part of series of punishing raids conducted by the Russian Imperial Army against Mazepa and Cossack state. On 2 November 1708, upon the sack of Baturyn, its entire civil population was exterminated, while the "Hetman Residence" was completely obliterated.
 W
WThe Crossing of the Düna took place during the Great Northern War on July 19, 1701 near the city of Riga, present-day Latvia. The Swedish king Charles XII was in hot pursuit of king Augustus II the Strong of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Saxony. The crossing was easily made, and the coalition troops were quickly broken and retreated.
 W
WThe battle of Erastfer took place on 29 December 1701 (O.S.) / 30 December 1701 / 9 January / 1702 (N.S.) near Erastfer in eastern Swedish Livonia between a Russian force of around 13,000 regulars along with 6,000 irregulars led by general Boris Sheremetev and a Swedish force of about 3,470 men, under the command of Wolmar Anton von Schlippenbach. The Swedes were defeated, with a loss of 1,000 men killed and captured along with all their artillery pieces. The Russians sustained about 1,000 killed along with another 2,000 wounded. It was the first significant Russian victory in the Great Northern War. Before invading Ingria, Peter the Great secured Poland's continued participation in the war against Sweden by promising King Augustus II of Poland, 20,000 Russian troops, 100,000 pounds of gunpowder, and 100,000 rubles per year over three years.
 W
WThe Siege of Fredriksten was an attack on the Norwegian fortress of Fredriksten in the city of Fredrikshald, (now Halden) by King Charles XII of Sweden. While inspecting his troops' lines, Charles XII was killed by a projectile. The Swedes broke off the siege, and the Norwegians held the fortress. Along with the Treaty of Nystad three years later, the death of Charles XII marked the end of the imperial era in Sweden, and the beginning of the Age of Liberty in that country.
 W
WThe Battle of Fraustadt was fought on 2 February 1706 (O.S.) / 3 February 1706 / 13 February 1706 (N.S.) between Sweden and Saxony-Poland and their Russian allies near Fraustadt in Poland. During the Battle of Fraustadt on February 3, August II was only 120 km away, with a cavalry force about 8,000 men strong. That was one of the main reasons that Swedish General Rehnskiöld hurried to engage Schulenburg. The battle is an example of a successful pincer movement and was one of Sweden's greatest victories in the Great Northern War.
 W
WThe Battle of Gadebusch or Wakenstädt was Sweden's final great victory in the Great Northern War. It was fought by the Swedes to prevent the loss of the city of Stralsund to Danish and Saxon forces.
 W
WThe Battle of Gemauerthof was a battle in the Great Northern War, fought south of Riga near Jelgava, in present-day Latvia in July 1705. The Swedish forces under Adam Ludwig Lewenhaupt fought a Russian army under Boris Sheremetyev. The Swedes, exhausted after forced marching, went to camp and were cooking supper when the news came of a large Russian army with 16 artillery pieces nearby. The Swedes, who themselves had 17 artillery pieces quickly deployed into battle formation and, encouraged by General Lewenhaupt, attacked the Russians. Although suffering severe setbacks on their right flank, the assault continued. On the left, the Swedish cavalry charged and broke the Russians. The infantry in the centre fired carefully at point-blank range and then charged, pushing their foes back in disorder. The battle ended in a confused melee, which was eventually won by the Swedes. The Russian cavalry withdrew while the infantry was destroyed by a combined-arms assault leaving 5,000 men dead, wounded or captured. The Swedes were victorious, but the victory was only symbolic. In August, the Russians conquered Courland.
 W
WThe battles at Göta älv were a series of battles and sieges which took place in and around the Gothenburg area between 1717 and 1719, between the Swedish Empire and Denmark-Norway, during the Great Northern War.
 W
WThe Battle of Grodno (1706) refers to the battle during the Great Northern War. Grodno was a city of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth at this time.
 W
WThe successful Landing on Groß Stresow by Prussian, Danish and Saxon troops took place on 15 November 1715 on the island of Rügen, Germany during the Great Northern War. The landing was followed with cavalry assaults from the Swedish defences on the island, commanded by Charles XII king of Sweden who despite the huge numerical disadvantage of - one up against five - chose to attack the fortified camp. The Swedes managed to get past the "Cheval de frise" and break through, but were then rapidly repulsed and routed after taking heavy casualties.
 W
WThe Battle of Helsingborg was the last major engagement of the Great Northern War to take place on Swedish soil, and resulted in a decisive victory of a Swedish force of 14,000 men under the command of Magnus Stenbock against a Danish force of equal strength under the command of Jørgen Rantzau, ensuring that Denmark's final effort to regain the Scanian territories that it had lost to Sweden in 1658 failed. The battle was fought on March 10, 1710, in the province of Scania, just outside the city of Helsingborg, and directly on the Ringstorp heights just north-east of the city.
 W
WThe Battle of Holowczyn or Holofzin or Golovchin was fought between the Russian forces, and the Swedish army, led by Charles XII of Sweden, only 26 years of age at the time. Despite difficult natural obstacles and superior enemy artillery, the Swedes were able to achieve surprise and defeat the numerically superior Russian forces, who were separated from each other, had no overall command and could not coordinate their actions, so that only 8,000-9,000 of them could take part in the fighting. Reportedly, it was Charles' favourite victory.
 W
WThe Landing at Humlebæk took place on August 4, 1700, in the Swedish invasion of Denmark during the Great Northern War 1700-1721. It was the first offensive during the war by the Swedish army, and it was directly led by Charles XII of Sweden commanding the right flank and Arvid Horn together with Carl Gustav Rehnskiöld at the left. The Swedes were victorious and utterly routed the Danish forces led by Jens Rostgaard.
 W
WBattle of Hummelshof took place on July 19, 1702 (O.S.) near the small town Hummelshof in Swedish Livonia. It was the second significant Russian victory in the Great Northern War.
 W
WThe Battle of Jakobstadt was a battle fought in the Great Northern War. It took place on 25 July 1704 (O.S.) / 26 July 1704 / 5 August 1704 (N.S.) between a Swedish army under Adam Ludwig Lewenhaupt and a combined Lithuanian/Russian force under Great Hetman Michał Serwacy Wiśniowiecki at the town of Jēkabpils in the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia. The Swedes were victorious.
 W
WThe Battle of Kalisz took place on October 29, 1706 in Kalisz, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Great Northern War. It was a three-hour fight which could have been prevented if Augustus II of Poland had informed the Swedes and Russians of certain matters. At the time, an alliance existed between the Poles, Saxons, and Russians. The battle was fought by Russian cavalry, led by commander Aleksandr Menshikov; against a smaller Swedish force headed by colonel Mardefelt. The Russians played a role of significance here because they needed to support their Saxon allies under Augustus.
 W
WThe Battle of Kletsk took place on 30 April 1706, in- and outside the city of Kletsk, Belarus during Charles XII's Polish campaign of 1701–1706, in the Great Northern War. The Swedish forces were led by Carl Gustaf Creutz who defeated a larger Russian–Cossack force under the command of Semjon Nepljujev and Danylo Apostol. Many of the Russian and Cossack regiments participating in the battle were wiped out and ceased to exist as fighting units.
 W
WThe Battle of Kliszów took place on July 19, 1702, near Kliszów in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth during the Great Northern War. A numerically superior Polish–Saxon army led by Augustus II the Strong, operating from an advantageous defensive position, was defeated by a Swedish army half its size under the command of King Charles XII.
 W
WThe Battle of Koporye took place on October 8, 1708 close to Koporye, in the Swedish Empire during the Ingrian campaign in the Great Northern War. A Swedish force consisting of 1,800 men under the command of generals Carl Gustaf Armfeldt and Anders Erik Ramsay attacked a numerically stronger enemy of between 2,000 and 3,000 Russian forces. The battle ended in a Swedish victory with about 600 killed Russians and only 70 dead for the Swedish force. After some further campaigning, the Swedish–Finland army under the command of Georg Lybecker decided to evacuate his troops, having failed with his objectives.
 W
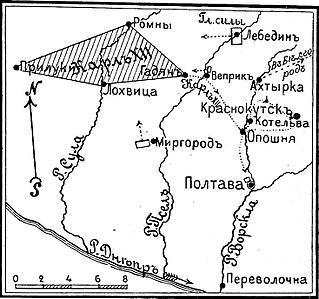
WThe Battle of Krasnokutsk–Gorodnoye took place on February 20–22, 1709, in the Swedish campaign of Russia during the Great Northern War 1700-1721. The Swedish troops were directly led by Charles XII King of Sweden who persecuted a force of Russians commanded by Karl Evald von Rönne from the minor battle of Krasnokutsk to the town Gorodnoye where a new battle took place. The Swedes were victorious but cancelled their offensive when the night fell.
 W
WThe Battle of Lemberg on September 6, 1704, was a successful Swedish assault on the town of Lemberg (Lviv), in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, during the Great Northern War.
 W
WThe Battle of Lesnaya was one of the major battles of the Great Northern War. It took place on September 28, 1708 (O.S.) / September 29, 1708 / October 9, 1708 (N.S.) between a Russian army of between 26,500 and 29,000 men commanded by Peter I of Russia, Mikhail Mikhailovich Golitsyn, Aleksandr Danilovich Menshikov, Christian Felix Bauer and Nikolai Grigorovitj von Werden and a Swedish army of about 12,500 men commanded by Adam Ludwig Lewenhaupt and Berndt Otto Stackelberg, at the village of Lesnaya, located close to the border between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia. The Swedes were escorting a supply column of more than 4,500 wagons for their main army in Ukraine.
 W
WThe Battle of Molyatichi, also known as the Battle of Dobroye, took place on August 31, 1708 at Molyatichi during the Great Northern War. The Russian army of Peter the Great under the command of Mikhail Golitsyn successfully attacked the avatgarde of the Swedish Army of Charles XII under Carl Gustaf Roos. The fighting occurred in the swamp between the rivers Belaya Natopa and Chernaya Natopa. The Swedish forces were surprised by the Russian attack in the morning fog and withdrew to the main Swedish army. The swampy landscape prevented the Russian cavalry to cut off the Swedish way of retreat. Since the attack of the main body of the Swedish army was not part of the Russian intentions at that moment, the Russians pulled back. The Swede chronists noted the grown fighting skills of the Russians. Together with the following Battle of Lesnaya, the battle of Malatitze caused Charles XII to abort his advance to Central Russia.
 W
WThe Battle of Napue was fought on February 19, 1714 (O.S.) / March 2, 1714 (N.S.) at the villages of Napue and Laurola in the Isokyrö parish of the Swedish Empire between the Swedish Empire and the Tsardom of Russia. It was the final land battle of the Finnish campaign in the Great Northern War. The Swedish detachment, consisting almost entirely of Finnish troops, were defeated by the numerically superior Russian force. As a result, all of Finland fell under Russian military occupation for the rest of the War; a seven-year period of hardship known in Finland as the Great Wrath. The Kyrö Distillery Company named its Napue rye gin after the battle in 2014.
 W
WThe Battle of Narva on 30 November [O.S. 19 November] 1700 was an early battle in the Great Northern War. A Swedish relief army under Charles XII of Sweden defeated a Russian siege force three to four times its size. Previously, Charles XII had forced Denmark–Norway to sign the Treaty of Travendal. Narva was not followed by further advances of the Swedish army into Russia; instead, Charles XII turned southward to expel August the Strong from Livonia and Poland-Lithuania. Tsar Peter the Great of Russia took Narva in a second battle in 1704.
 W
WThe siege of Narva, also known as the Second Battle of Narva, was the second Russian siege of Swedish Narva during the Great Northern War from 27 June to 9 August 1704.
 W
WThe Siege of Nöteborg was one of the first sieges of the Great Northern War, when Russian forces captured the Swedish fortress of Nöteborg in October 1702. Peter the Great had assembled a force of 20,000 men for this task, and marched for ten days to his destination. About 12,000 of these men were positioned on the banks of the Neva river, where they camped until 6 October (N.S.). On that day, after giving command of the main force to Boris Sheremetev, he moved toward Nöteborg. After the Swedish commander, Wilhelm von Schlippenbach, refused to give up the fort immediately, the Russians began bombarding it. A final Russian assault on the fort was tactically unsuccessful, resulting in heavy casualties, but forced the fort's defenders to surrender on 22 October 1702. After taking control, Peter immediately began reconstructing the fort for his own purposes, renaming it Shlisselburg.
 W
WThe Battle of Petschora took place on February 23, 1701 near the village of Pechory, Russia during the second year of the Great Northern War. The Swedish army of about 2,100 men assisted by approximately 2,000 peasants under the command of Jacob Spens defeated a Russian force of about 6,000 men.
 W
WThe Battle of Poltava was the decisive victory of Peter the Great over the Swedish Empire forces under Swedish king Charles XII, in one of the battles of the Great Northern War.
 W
WThe Battle of Poznań was a battle that took place on August 9, 1704 in Poznań, Poland during the Great Northern War.
 W
WThe Battle of Praga took place on October 25, 1705 near the town of Warsaw, Poland during the fifth year of the Great Northern War. The Swedish army of more than 270 men assisted by approximately 140 soldiers from the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth under the command of Valentin Dahldorf defeated a combined Polish–Saxon–Russian force of about 5,000 men under Michał Serwacy Wiśniowiecki and Aleksandr Menshikov.
 W
WThe Battle of Pułtusk took place on April 21, 1703 in Pułtusk during the Great Northern War. The Swedish army under the command of Charles XII defeated the Saxon army under Adam Heinrich von Steinau.
 W
WThe Battle of Poniec took place on October 28, 1704 in Poniec, Poland, during the Great Northern War. The Swedish Army under Charles XII unsuccessfully dislodged the Saxon Army under Johann Matthias von der Schulenburg through several cavalry charges. The Saxons had deployed in a massive square formation near the village of Janiszewo, west of Poniec.
 W
WThe Battle of Reinbek, or Skirmish of Reinbek, on May 30, 1700 was a small engagement at the river of Bille near Reinbek in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, as a consequence of the Danish invasion of Holstein-Gottorp, earlier that year.
 W
WThe Sieges of Riga were two sieges which took place on February 22 and June 15, 1700 in Riga during the Great Northern War. The Swedish garrison of about 4,000 men under the command of Erik Dahlberg successfully repulsed the Saxons until the main Swedish army under Charles XII of Sweden arrived to sweep the Saxons away in the battle of Riga which ended the period of sieges for the year.
 W
WThe Battle of Saladen was a battle that took place on 19 March 1703 near Saločiai, Lithuania during the Great Northern War. The Swedes won the battle.
 W
WThe Siege of Stralsund was a battle during the Great Northern War. The Swedish Empire defended her Swedish Pomeranian port of Stralsund against a coalition of Denmark-Norway, the Electorate of Saxony and the Tsardom of Russia, which was joined by the Kingdom of Prussia during the siege.
 W
WThe Battle of Strömstad took place on July 19, 1717 at Strömstad during the Great Northern War. The Swedish army of about 1,800 men under the command of Johan Giertta defeated the Danish fleet of several larger vessels and perhaps 4,000 men under Peder Tordenskjold. Peter tried to destroy the stocks of supplies Sweden had gathered for the upcoming invasion of Norway. In the battle about 200 Swedes were either dead or wounded and about 350 Norwegians.
 W
WThe siege of Thorn was set during the Great Northern War, between Sweden and Saxony from May to October 14, 1703. The Swedish army was commanded by Charles XII of Sweden and the Saxon by General von Kanitz. The siege ended with a victory for Sweden, and the whole garrison surrendered to the Swedes.
 W
WDuring the Great Northern War, the fortress of Tönning (Tønning) in the territory of Holstein-Gottorp, an ally of the Swedish Empire, was besieged twice. Denmark-Norway was forced to lift the first siege in 1700, but a combined force of the anti-Swedish coalition successfully besieged and took Tönning in 1713–1714.
 W
WThe Battle of Tryszki, Tryškiai or Triski, on December 14, 1701, was a small engagement between Swedish forces under Charles XII of Sweden and Polish–Lithuanian forces under Grzegorz Antoni Ogiński, in the town of Tryszki (Tryškiai), Samogitia. After the Crossing of the Düna Charles went into an alliance with the Sapieha family to gain his support in dethroning Augustus II the Strong from the Polish throne, in exchange for protection from rival families in Samogitia, such as the Ogiński family. After initial engagements between Swedish forces and those loyal to Grzegorz Antoni Ogiński, the Swedish king personally takes command of the troops and engages Grzegorz at the town of Tryszki; after a brief encounter, Grzegorz is forced on the run and, with Charles being hot on his heels, eventually retreats out of Samogitia altogether. A Swedish detachment is established at Wilno (Vilnius) in Lithuania, as a sort of forward operating base before the inevitable Swedish invasion of Poland (1701–1706); further engagements, foremost the Battle of Darsūniškis, confirms the Swedish invasion. Although only a small action in a major war, the battle quickly sparked false rumours to be spread around Europe; one spoke of the death of Charles, somewhere in Lithuania, while the other mentioned a major defeat for Grzegorz, involving many thousands of participants.
 W
WThe Siege of Veprik took place on January 3 to January 17, 1709 during the Swedish invasion of Russia in the Great Northern War. After the unusual cold winter, many troops had died from both armies and Charles XII of Sweden decided to siege the Russian city of Veprik to put pressure on Tsar Peter I of Russia. In the town there was a garrison of about 1,500 men. After the Russian commander, the Scot Colonel Fermor refused to surrender, Charles XII started a bombardment of the town and later, on 17 January also an assault. After about two hours of intense fighting the Swedes pulled back, unable to capture the town. However, the Russians surrendered on the night to the 18th January and the Swedes could march in by diplomatic. The result of the capture was little, another town had fallen for the Russians but in a strategic view, not much had changed. About 400 Swedes was killed and another 600 wounded. The whole Russian garrison was either killed, captured or wounded. After several days Charles XII burnt down the town.
 W
WThe siege of Viborg took place in the spring of 1710 during the Great Northern War (1700–1721), as a second attempt by the Russians to capture the fortress port of Viborg (Vyborg), near the modern border between Russia and Finland, after a failed attempt in 1706. After the outbreak of the war, Swedish forces had fortified themselves in the port of Viborg. In order to assure safety for the newly founded city of Saint Petersburg, Peter the Great ordered the Swedish fort to be secured. A first unsuccessful attempt was made in 1706. Later plans were put on hold because of other ongoing conflicts but, after the Russian success at the Battle of Poltava in June 1709, the men and resources were available to capture the town.
 W
WThe Battle of Warsaw was fought on 31 July 1705 near Warsaw, Poland, during the Great Northern War. The battle was part of a power struggle for the Polish–Lithuanian throne. It was fought between Augustus II the Strong and Stanisław Leszczyński and their allies. Augustus II entered the Northern war as elector of Saxony and king of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and had formed an alliance with Denmark–Norway and Russia. Stanisław Leszczyński had seized the Polish throne in 1704, with the support of the Swedish army of Charles XII of Sweden. The struggle for the throne forced the Polish nobility to pick sides; the Warsaw Confederation supported Leszczyński and Sweden, and the Sandomierz Confederation supported Augustus II and his allies. The conflict resulted in the Polish civil war of 1704–1706.