 W
WThis is a list of cities and colonies of Phoenicia in modern-day Lebanon, coastal Syria and northern Israel and the region of Palestine, as well as cities founded or developed by the Phoenicians in Eastern Mediterranean area, North Africa, Southern Europe, and the islands of the Mediterranean Sea.
 W
WAchziv is an ancient site on the Mediterranean coast of northern Israel, between the border with Lebanon and the city of Acre. It is located 13.5 kilometres (8.4 mi) north of Acre on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, within the municipal area of Nahariya. Today it is an Israeli national park.
 W
WAcre, known locally as Akko or Akka, is a city in the coastal plain region of the Northern District of Israel.
 W
WAmioun is the capital of the predominantly Greek Orthodox Koura District in the north of Lebanon.
 W
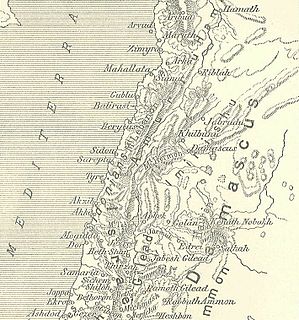
WAmrit, the classical Marathus, was a Phoenician port located near present-day Tartus in Syria. Founded in the third millennium BC, Marat was the northernmost important city of ancient Phoenicia and a rival of nearby Arwad. During the 2nd century BC, Amrit was defeated and its site largely abandoned, leaving its ruins well preserved and without extensive remodeling by later generations.
 W
WIn historiographical terms, ancient Carthage was a Phoenician civilization during classical antiquity, beginning from the founding of Carthage in modern Tunisia in the ninth century BC, to its destruction in 146 BC. At its height in the fourth century BC, the city-state grew to become the largest metropolis in the world, and the center of the Carthaginian Empire, a major power in the ancient world that dominated the western Mediterranean.
 W
WAnqoun, also called Ankoun, is a relatively large town in the Sidon District which is one of three districts of the South Governorate in Lebanon. The South Governorate, known also as, Mohafazah of South Lebanon is one of the eight mohafazats (governorates) of Lebanon, containing three major historic and economic cities: Sidon, Tyre, and Jezzine.
 W
WApollonia, known in the Early Islamic period as Arsuf and in the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem as Arsur, was an ancient city on the Mediterranean coast of what is today Israel. In Israeli archaeology it is known as Tel Arshaf. Founded by the Phoenicians during the Persian period in the late sixth century BCE, it was inhabited continuously until the Crusader period, through the Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine periods, during the latter being renamed to Sozusa. It was situated on a sandy area ending towards the sea with a cliff, about 34 kilometres (21 mi) south of Caesarea.
 W
WArab al-Mulk is a coastal village in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Jableh District in the Latakia Governorate, located south of Latakia. Nearby localities include Jableh to the north, Ayn al-Sharqiyah to the northeast, Qurfays and Dweir Baabda to the east and Baniyas to the south. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics, Arab al-Mulk had a population of 3,580 in the 2004 census. The inhabitants are mixed, with Sunni Muslims of Bedouin origins generally residing in the northern part of the village, and Alawites living in the southern part which is known as Beldi al-Melek.
 W
WArqa is a Sunni village near Miniara in Akkar Governorate, Lebanon, 22 km northeast of Tripoli, near the coast.
 W
WArwad, the classical Aradus, is a town in Syria on an eponymous island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is the administrative center of the Arwad Subdistrict (nahiyah), of which it is the only locality. It is the only inhabited island in Syria. It is located 3 km (1.9 mi) from Tartus, Syria's second-largest port.
 W
WAshkelon or Ashqelon, also known as Ascalon, is a coastal city in the Southern District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, 50 kilometres (31 mi) south of Tel Aviv, and 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) north of the border with the Gaza Strip. The ancient seaport of Ashkelon dates back to the Neolithic Age. In the course of its history, it has been ruled by the Ancient Egyptians, the Canaanites, the Philistines, the Assyrians, the Babylonians, the Greeks, the Phoenicians, the Hasmoneans, the Romans, the Persians, the Arabs and the Crusaders, until it was destroyed by the Mamluks in 1270.
 W
WBaalbek is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about 67 km (42 mi) northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In Greek and Roman times Baalbek was also known as Heliopolis. In 1998 Baalbek had a population of 82,608, mostly Shia Muslims, followed by Sunni Muslims and Christians.
 W
WBatroun is a coastal city in northern Lebanon and one of the oldest cities in the world. It is the capital city of Batroun District.
 W
WBeirut is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. As of 2014, Greater Beirut has a population of 2.2 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint of Lebanon's Mediterranean coast. Beirut has been inhabited for more than 5,000 years, and was one of Phoenicia's most prominent city states, making it one of the oldest cities in the world. The first historical mention of Beirut is found in the Amarna letters from the New Kingdom of Egypt, which date to the 15th century BC.
 W
WThe Phoenician port of Beirut, also known as the Phoenician Harbour of Beirut and archaeological site BEY039 is located between Rue Allenby and Rue Foch in Beirut, Lebanon. Studies have shown that the Bronze Age waterfront lay around 300 metres (330 yd) behind the modern port due to coastal regularisation and siltation. It was excavated and reported on by Josette Elayi and Hala Sayegh in 2000 and determined to date to the Iron Age III and Persian periods. Two nineteenth century Ottoman docks were also unearthed during construction, just to the north of this area at archaeological sites BEY018 and BEY019.
 W
WBodai is a Lebanese town in Baalbek District, Baalbek-Hermel Governorate, situated west of the Litani River in the foothills of Mount Lebanon. Bodai is located 15 km northwest of the ancient city of Baalbek and 26 km from the Lebanese–Syrian border and is 90 kilometers (55.926 mi) away from the capital of Beirut. Bodai, which sits in the foothills of the Mount Lebanon range, has views across the Beqaa Valley toward the city of Baalbek, and the Anti-Lebanon range that divides Lebanon from Syria.
 W
WByblos is a city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 8800 and 7000 BC and continuously inhabited since 5000 BC, making it one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
 W
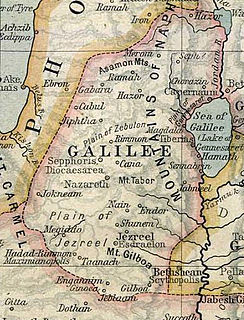
WCaesarea, Keysariya or Qesarya, often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesarea Maritima. Located midway between Tel Aviv and Haifa on the coastal plain near the city of Hadera, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hof HaCarmel Regional Council. With a population of 5,343, it is the only Israeli locality managed by a private organization, the Caesarea Development Corporation, and also one of the most populous localities not recognized as a local council.
 W
WCaesarea Maritima, formerly Strato's Tower, also known as Caesarea Palestinae, was an ancient city in the Sharon Plain on the coast of the Mediterranean, now in ruins and included in an Israeli national park.
 W
WTel Dor or Tell el-Burj, also Khirbet el-Burj in Arabic, is an archaeological site located on Israel's Mediterranean coast next to modern moshav Dor, about 30 kilometers (19 mi) south of Haifa, and 2.5 kilometers (1.6 mi) west of Hadera. Lying on a small headland at the north side of a protected inlet, it is identified with D-jr of Egyptian sources, Biblical Dor, and with Dor/Dora of Greek and Roman sources.
 W
WEl Kef, also known as Le Kef, is a city in northwestern Tunisia. It serves as the capital of the Kef Governorate.
 W
WEnfeh, or Enfe, Anfeh, Anfe, is a town in the Koura district of the North Governorate of Lebanon at Latitude 34°21'0"N and Longitude 35°44'0"E. Enfeh borders the towns of Chekka, Al-Qalamoun, Barghoun and Zakroun. It is located 65 kilometres (40 mi) north of Beirut and 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) south of Tripoli. Its total area is 4.93 square kilometres (1.90 sq mi), and its population is around 6,500.
 W
WEnišasi, was a city, or city-state located in the Beqaa Valley-(called Amqu, or Amka) of Lebanon, during the 1350-1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Of the 382–Amarna letters, Enišasi is only referenced in two letters. Enišasi was located near Hašabu,, and Hasi,, southwest of Baalbek.
 W
WGezer, or Tel Gezer, in Arabic: تل الجزر – Tell Jezar or Tell el-Jezari, the site of the abandoned Arab village of Abu Shusheh, is an archaeological site in the foothills of the Judaean Mountains at the border of the Shfela region roughly midway between Jerusalem and Tel Aviv. It is now an Israeli national park. In the Hebrew Bible, Gezer is associated with Joshua and Solomon.
 W
WHaifa is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of 285,316 in 2019. The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area in Israel. It is home to the Baháʼí Faith's Baháʼí World Centre, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a destination for Baháʼí pilgrimage.
 W
WJaffa, in Hebrew Yafo and in Arabic Yafa and also called Japho or Joppa, the southern and oldest part of Tel Aviv-Yafo, is an ancient port city in Israel. Jaffa is famous for its association with the biblical stories of Jonah, Solomon and Saint Peter as well as the mythological story of Andromeda and Perseus, and later for its oranges.
 W
WKfarhazir is a village in the Koura District of Lebanon. It is 350 meters above sea level, and has an area of 12.1 square kilometres (4.69 sq mi) - the largest town in Koura by size, with a population of about 2000. The population are Greek Orthodox and Maronite.
 W
WLatakia is the principal port city of Syria, as well as the capital of the Latakia Governorate. Historically, it has also been known as Laodicea in Syria or Laodicea ad Mare. In addition to serving as a port, the city is a manufacturing center for surrounding agricultural towns and villages. According to the 2004 official census, the population of the city is 383,786, Its population greatly increased as a result of the ongoing Syrian Civil War due to the influx of refugees from rebel held areas. It is the 4th-largest city in Syria after Aleppo, Damascus and Homs, and it borders Tartus to the south, Hama to the east, and Idlib to the north while Cape Apostolos Andreas, the most north-eastern tip of Cyprus is about 68 miles (109 km) away.
 W
WTel Michal is an archaeological site on Israel's central Mediterranean coast, near the modern city of Herzliya, about 6.5 kilometres (4.0 mi) north of the Yarkon River estuary and 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) south of Arsuf-Appolonia. Excavations have yielded remains from the Middle Bronze Age to the Early Arab period.
 W
WPtolemais was an ancient port city on the Canaanite coast in Palestine region. It was also called Ptolemais in Canaan (or Akko, Ake, or Akre in Canaanite Language. It was an Ancient bishopric, which became a double Catholic titular see.
 W
WPupput, also spelled "Putput", "Pudput", "Pulpud" and "Pulpite" in Latin, sometimes located in Souk el-Obiod ou Souk el-Abiod, is a Colonia in the Roman province of Africa which has been equated with an archaeological site in modern Tunisia. It is situated on the coast near the town of Hammamet, between the two wadis of Temad to the north and Moussa to the south. Much of the Pupput is buried under modern holiday developments which have been built over the major part of the site.
 W
WSafita is a city in the Tartous Governorate, northwestern Syria, located to the southeast of Tartous and to the northwest of Krak des Chevaliers. It is situated on the tops of three hills and the valleys between them, in the Syrian Coastal Mountain Range. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Safita had a population of 20,301 in the 2004 census.
 W
WSarepta was a Phoenician city on the Mediterranean coast between Sidon and Tyre, also known biblically as Zarephath. It became a bishopric, which faded, and remains a double Catholic titular see.
 W
WTel Shikmona, also spelt Sycamine, is an ancient tell (mound) situated near the sea coast on the modern city of Haifa, Israel, just south of the Israeli National Institute of Oceanography.
 W
WSidon, known locally as Sayda or Saida, is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located in the South Governorate, of which it is the capital, on the Mediterranean coast. Tyre to the south and Lebanese capital Beirut to the north are both about 40 kilometres away. Sidon has a population of about 80,000 within city limits, while its metropolitan area has more than a quarter-million inhabitants.
 W
WSumur was a Phoenician city in what is now Syria. Zemar was a major trade center. The city has also been referred to in English publications as Simyra, Ṣimirra, Ṣumra, Sumura, Ṣimura, Zemar, and Zimyra.
 W
WTartus is a city on the Mediterranean coast of Syria. It is the second largest port city in Syria, and the largest city in Tartus Governorate. The population is 115,769. In the summer it is a vacation spot for many Syrians. Many vacation compounds and resorts are located in the region. The port holds a small Russian naval facility.
 W
WTell Kazel is an oval-shaped tell that measures 350 m × 325 m at its base, narrowing to 200 m × 200 m at its top. It is located in the Safita district of the Tartus Governorate in Syria in the north of the Akkar plain on the north of the al-Abrash river approximately 18 km (11 mi) south of Tartus.
 W
WTell Sukas is a Late Bronze Age archaeological mound on the Eastern Mediterranean coast about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) south of Jableh, Syria.
 W
WThysdrus was a Carthaginian town and Roman colony near present-day El Djem, Tunisia. Under the Romans, it was the center of olive oil production in the provinces of Africa and Byzacena and was quite prosperous. The surviving amphitheater is a World Heritage Site.
 W
WTripoli is the largest city in northern Lebanon and the second-largest city in the country. Situated 85 kilometers north of the capital Beirut, it is the capital of the North Governorate and the Tripoli District. Tripoli overlooks the eastern Mediterranean Sea, and it is the northernmost seaport in Lebanon. It holds a string of four small islands offshore, and they are the only islands in Lebanon. The Palm Islands were declared a protected area because of their status of haven for endangered loggerhead turtles, rare monk seals and migratory birds. Tripoli borders the city of El Mina, the port of the Tripoli District, which it is geographically conjoined with to form the greater Tripoli conurbation.
 W
WTyre is a city in Lebanon, one of the oldest continually inhabited cities in the world, though in medieval times for some centuries by just a tiny population. It was one of the earliest Phoenician metropolises and the legendary birthplace of Europa, her brothers Cadmus and Phoenix, as well as Carthage's founder Dido (Elissa). The city has many ancient sites, including the Tyre Hippodrome, and was added as a whole to UNESCO's list of World Heritage Sites in 1984. The historian Ernest Renan noted that "One can call Tyre a city of ruins, built out of ruins".
 W
WUgarit was an ancient port city in northern Syria, in the outskirts of modern Latakia, discovered by accident in 1928 together with the Ugaritic texts. Its ruins are often called Ras Shamra after the headland where they lie.
 W
WUshu was an ancient mainland city that supplied the city of Tyre with water, supplies and burial grounds. Its name was based upon the mythical figure Usoos or Ousoüs, a descendant of Genos and Genea whose children allegedly discovered fire, as recorded by Sanchuniathon (Sankunyaton).