 W
WThe borders of the Roman Empire, which fluctuated throughout the empire's history, were realised as a combination of military roads and linked forts, natural frontiers and man-made fortifications which separated the lands of the empire from the countries beyond.
 W
WCastra ad Fluvium Frigidum, also simply Castra, referred to as mutatio Castra in Itinerarium Burdigalense, was a Late-Roman fortress (castrum) which constituted the centre of Claustra Alpium Iuliarum, an Ancient Roman defensive system of walls and towers stretching from the Gail Valley to the Učka mountain range. On its grounds, the Late Medieval market settlement of Ajdovščina developed.
 W
WRoman military borders and fortifications were part of a grand strategy of territorial defense in the Roman Empire, although this is a matter of debate. By the early 2nd century, the Roman Empire had reached the peak of its territorial expansion and rather than constantly expanding their borders as earlier in the Empire and Republic, the Romans solidified their position by fortifying their strategic position with a series of fortifications and established lines of defense. Historian Adrian Goldsworthy argues that the Romans had reached the natural limits which their military traditions afforded them conquest over and that beyond the borders of the early-to-mid Empire lay peoples whose military traditions made them militarily unconquerable, despite many Roman battle victories. In particular, Goldsworthy argues that the cavalry-based warfare of the Parthians, Sarmatians and Persians presented a major challenge to the expansion of Rome's infantry-based armies.
 W
WThe Antonine Wall, known to the Romans as Vallum Antonini, was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Forth and the Firth of Clyde. Built some twenty years after Hadrian's Wall to the south, and intended to supersede it, while it was garrisoned it was the northernmost frontier barrier of the Roman Empire. It spanned approximately 63 kilometres and was about 3 metres high and 5 metres wide. Lidar scans have been carried out to establish the length of the wall and the Roman distance units used. Security was bolstered by a deep ditch on the northern side. It is thought that there was a wooden palisade on top of the turf. The barrier was the second of two "great walls" created by the Romans in Great Britain in the second century AD. Its ruins are less evident than those of the better-known and longer Hadrian's Wall to the south, primarily because the turf and wood wall has largely weathered away, unlike its stone-built southern predecessor.
 W
WArgentovaria, also known as Ödenburg, is the collective term for a late Roman military installation and a civilian settlement in the area of Biesheim in Elsass.
 W
WAthanaric's Wall, also called Lower Trajan's Wall or Southern Trajan's Wall, was a fortification line probably erected by Athanaric, between the banks of river Gerasius and the Danube to the land of Taifali. Most probably, Athanaric's Wall has reused the old Roman limes called Limes Transalutanus.
 W
WBrazda lui Novac is a Roman limes in present-day Romania, known also as Constantine's Wall. It is believed by some historians like Alexandru Madgearu to border Ripa Gothica.
 W
WThe Castra Alteium is a former late-Roman border fort on the Danube-Iller-Rhine Limes (DIRL). It is located in the territory of the city of Alzey in Rhenish Hesse, Germany. The fort was presumably built in the course of the last reconstruction measures on the Rhine frontier between 367 and 370 AD under the western Emperor Valentinian I. Previously, there was a Roman civilian settlement (Vicus), Altiaia, which was devastated by Alamanni in 352/353. The fort was also destroyed twice, and probably abandoned at the end of the fifth century.
 W
WCelemantia was a Roman castellum and settlement on the territory of the present-day municipality Iža, some 4 km to the east of Komárno in Slovakia. It is the biggest known Roman castellum in present-day Slovakia. It was a part of the Roman limes, the frontier-zone of the Empire.
 W
WDacia Aureliana was a province in the eastern half of the Roman Empire established by Roman Emperor Aurelian in the territory of former Moesia Superior after his evacuation of Dacia Traiana beyond the Danube in 271. Between 271/275 and 285, it occupied most of what is today northwestern Bulgaria and eastern Serbia. Its capital was in Serdica.
 W
WThe Danube–Iller–Rhine Limes or DIRL was a large-scale defensive system of the Roman Empire that was built after the project for the Upper Germanic-Rhaetian Limes in the late 3rd century AD. In a narrower sense the term refers only to the fortifications between Lake Constance and the River Danube (Danubius); in a broader sense it also includes the other Late Roman fortifications along the river Rhine (Rhenus) on the High Rhine(between Lake Constance and Basle) and on the Upper Rhine as well as the Upper Danube.
 W
WThe Devil's Dykes, also known as the Csörsz árka or the Limes Sarmatiae, are several lines of Roman fortifications built mostly during the reign of Constantine I (312–337), stretching between today's Hungary, Romania and Serbia.
 W
WFossatum Africae is a linear defensive structure (limes) claimed to extend over 750 km (470 mi) or more in northern Africa constructed during the Roman Empire to defend and control the southern borders of the Empire in Africa. It is considered to have many similarities of construction to Hadrian's Wall, one of the northern borders of the Empire in Britain.
 W
WThe Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries CE that linked Exeter in the southwest and Lincoln to the northeast, via Ilchester, Bath, Cirencester and Leicester.
 W
WThe German and Sarmatian campaigns of Constantine were fought by the Roman Emperor Constantine I against the neighbouring Germanic peoples, including the Franks, Alemanni and Goths, as well as the Sarmatian Iazyges, along the whole Roman northern defensive system to protect the empire's borders, between 306 and 336.
 W
WGerulata was a Roman military camp located near today's Rusovce, a borough of Bratislava, Slovakia. It was part of the Roman province of Pannonia and was built in the 2nd century as a part of the frontier defence system. It was abandoned in the 4th century, when Roman legions withdrew from Pannonia.
 W
WHadrian's Wall, also known as the Roman Wall, Picts' Wall, or Vallum Hadriani in Latin, is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the emperor Hadrian. Running "from Wallsend on the River Tyne in the east to Bowness-on-Solway in the west", the Wall covered the whole width of the island, as Jarrett A. Lobell says. In addition to the wall's defensive military role, its gates may have been customs posts.
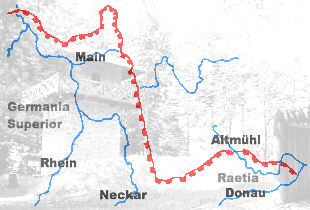 W
WThe Imperial Limes Commission or RLK, was set up to work out the route of the Upper Germanic-Rhaetian Limes, the Roman frontier north of the Alps, and the location of its associated forts at the time of the Roman Empire. It was the first institution to engage in a cross-border, historical project after German Unification in 1871.
 W
WKastell Wörth was a Roman limes numerus fort located on the north-western edge of today's Wörth am Main in the German state of Bavaria. The fort was probably part of the defenses of the Main Limes, and also, as part of the Upper Germanic-Rhaetian Limes, but also of the older Odenwald Limes section of the Neckar-Odenwald Limes, but this has not been definitively proven archaeologically.
 W
WThe līmes is a modern term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting system of Ancient Rome marking the borders of the Roman Empire, but it was not used by the Romans for that purpose. The term has been extended to refer to the frontier defences in other parts of the empire, such as in the east and in Africa.
 W
WThe borders of the Roman Empire, which fluctuated throughout the empire's history, were realised as a combination of military roads and linked forts, natural frontiers and man-made fortifications which separated the lands of the empire from the countries beyond.
 W
WThe Limes Alutanus was a fortified line consisting of a vallum, built in the North-South direction, on the eastern side of the Olt river and seven Roman castra, as is remembered by Tabula Peutingeriana. Limes Alutanus was the eastern border of the Roman province of Dacia.
 W
WThe Limes Mauretaniae was a portion of a 4,000-kilometre (2,500 mi) Roman fortified border (limes) in Africa approximately 100 kilometres (62 mi) south of the modern day Algiers.
 W
WThe Moesian Limes or Limes Moesiae is the modern term given to a collection of Roman fortifications between the Black Sea shore and Pannonia, present-day Hungary, consisting primarily of forts along the Danube to protect the Roman provinces of Upper and Lower Moesia south of the river.
 W
WLimes Transalutanus is the modern name given to a fortified frontier system of the Roman Empire, built on the western edge of Teleorman's forests in the Roman province of Dacia, modern-day Romania. The frontier was composed of a road following the border, a military stronghold, a three-metre vallum 10–12 metres wide, reinforced with wood palisades on stone walls, and also a ditch. The Transalutanus limes was 235 km long, parallel to Olt river at a distance varying from 5 to 30 km east of the river. The construction was started in 107 under the command of Marcius Turbo, and developed under Iulius Severus (120–126); the final stage of the construction was performed under Septimius Severus.
 W
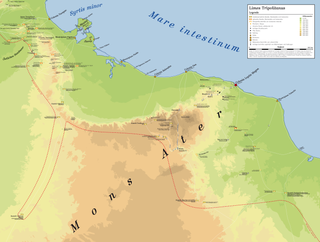
WThe Limes Tripolitanus was a frontier zone of defence of the Roman Empire, built in the south of what is now Tunisia and the northwest of Libya. It was primarily intended as a protection for the tripolitanian cities of Leptis Magna, Sabratha and Oea in Roman Libya.
 W
WThe Limesfall is the name given to the abandonment of the Upper Germanic-Rhaetian Limes in the mid-3rd century AD by the Romans and the withdrawal of imperial troops from the provinces on the far side of the rivers Rhine and Danube to the line of those rivers. It is sometimes called the fall of the limes.
 W
WThis is a list of Roman castra in Romania. They were built by the Roman army following the conquests of Moesia, Scythia Minor and Dacia, parts of which are now found in the territory of modern Romania. The Latin word castra, with its singular castrum, was used by the ancient Romans to mean buildings or plots of land reserved to or constructed for use as a military defensive position. Many of these castra were part of various limes.
 W
WThe Lower Germanic Limes is the former frontier between the Roman province of Germania inferior and Germania Magna. The Lower Germanic Limes separated that part of the Rhineland left of the Rhine as well as the Netherlands, which was part of the Roman Empire, from the less tightly controlled regions east of the Rhine.
 W
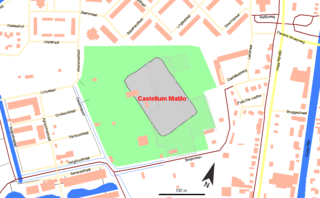
WMatilo or Matilone was once a Roman fort (castellum) in modern-day Leiden. Positioned on the southern banks of the Oude Rijn, it served to protect the Roman borders in the province of Germania inferior. On the Peutinger map, it lies between the encampments of Albaniana and Praetorium Agrippinae (Valkenburg). The seventh-century Ravenna Cosmography gives its name as Matellionem.
 W
WMeroë was an ancient city on the east bank of the Nile about 6 km north-east of the Kabushiya station near Shendi, Sudan, approximately 200 km north-east of Khartoum. Near the site is a group of villages called Bagrawiyah. This city was the capital of the Kingdom of Kush for several centuries from around 590 BC, until its collapse in the fourth century CE. The Kushitic Kingdom of Meroë gave its name to the "Island of Meroë", which was the modern region of Butana, a region bounded by the Nile, the Atbarah and the Blue Nile.
 W
WThe Neckar-Odenwald Limes is a collective term for two, very different early sections of the Upper Germanic-Rhaetian Limes, a Roman defensive frontier line that may have been utilised during slightly different periods in history. The Neckar-Odenwald Limes consists of the northern Odenwald Limes (Odenwaldlimes), a cross-country limes with camps, watchtowers and palisades, which linked the River Main with the Neckar, and the adjoining southern Neckar Limes (Neckarlimes), which in earlier research was seen as a typical 'riverine limes', whereby the river replaced the function of the palisade as an approach obstacle. More recent research has thrown a different light on this way of viewing things that means may have to be relativized in future. The resulting research is ongoing.
 W
WFor around 450 years, from around 55 BC to around 410 AD, the southern part of the Netherlands was integrated into the Roman Empire. During this time the Romans in the Netherlands had an enormous influence on the lives and culture of the people who lived in the Netherlands at the time and (indirectly) on the generations that followed.
 W
WThe Pannonian Limes is that part of the old Roman fortified frontier known as the Danubian Limes that runs for approximately 420 km (260 mi) from the Roman camp of Klosterneuburg in the Vienna Basin in Austria to the castrum in Singidunum (Belgrade) in present-day Serbia. The garrisons of these camps protected the Pannonian provinces against attacks from the north from the time of Augustus (31 BC-14 AD) to the beginning of the 5th century. In places this section of the Roman limes also crossed the river into the territory of the barbarians (Barbaricum).
 W
WPike Hill Signal Tower was one of a number of signal stations that were built on high ground overlooking the line of the Roman Stanegate road in northern Britannia during the early 2nd century. It later became incorporated into Hadrian's Wall. Its remains, a 2-metre long fragment of the south-east wall, lie south of a modern road cutting and field wall, and are located in the parish of Waterhead in Cumbria, United Kingdom. The tower is located between Turret 51B and Turret 52A with the fort of Banna located to the east.
 W
WThe Raša in Croatian Istria is a major river of Croatia's Istria County. It is 23 kilometres (14 mi) long, and its basin covers an area of 279 km2 (108 sq mi). Its mouth is in the long ria of Raški zaljev/Porto d'Arsia, which is a drowned river valley scoured out when world sea levels were lowered, then drowned by the rising waters of the post glacial era. The Raša rises in springs near Pićan and flows south through a steep-sided valley before opening into the head of the Adriatic Sea. The river, although short in length, has an ancient history as a border.
 W
WRoman Dacia was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat. During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians.
 W
WSidi Said, Morocco is a hamlet in Morocco located at 28° 27' 36" North, 10° 34' 12" was during the Roman Empire one of five Castra (fort) that guarded the city of Volubilis from incursion over the nearby Limes Africanus. Sidi Said was the base for the Cohors IV Gallorum equitata, an auxiliary cavalry unit from Gaul. Rome's control over the area ended, however, following the chaos of the Crisis of the Third Century, when the empire nearly disintegrated as a series of generals seized and lost power through civil wars, palace coups and assassinations.
 W
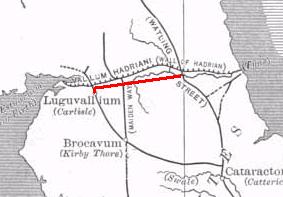
WThe Stanegate was an important Roman road built in what is now northern England. It linked two forts that guarded important river crossings: Corstopitum (Corbridge) on the River Tyne in the east, and situated on Dere Street, and Luguvalium (Carlisle) on the River Eden in the west. The Stanegate ran through the natural gap formed by the valleys of the River Tyne in Northumberland and the River Irthing in Cumbria. It predated Hadrian's Wall by several decades; the Wall would later follow a similar route, slightly to the north.
 W
WThe Strata Diocletiana was a fortified road that ran along the eastern desert border, the limes Arabicus, of the Roman Empire. As its name suggests and as it appears on milestones, it was constructed under Emperor Diocletian as part of a wide-ranging fortification drive in the later Roman Empire. The strata was lined with a series of similarly-built rectangular forts situated at one day's march from each other. It began at the southern bank of the river Euphrates and stretched south and west, passing east of Palmyra and Damascus down to northeast Arabia.
 W
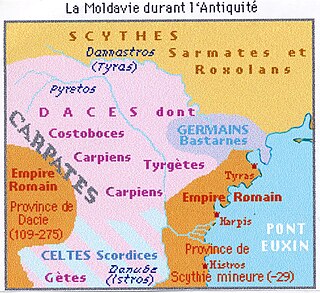
WTrajan's Wall is the name used for several linear earthen fortifications (valla) found across Eastern Europe, in Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine. Contrary to the name and popular belief, the ramparts were not built by Romans during Trajan's reign, but during other imperial periods. Furthermore, the association with the Roman Emperor may be a recent scholarly invention, only entering the imagination of the locals with the national awakening of the 19th century. Medieval Moldavian documents referred to the earthworks as Troian, likely in reference to a mythological hero in the Romanian and Slavic folklore. The other major earthen fortification in Romania, Brazda lui Novac, is also named after a mythological hero.
 W
WThe Trennfurt Roman Fort is a castrum in the village of Trennfurt at the river Main in Bavaria. It belongs to the Main Limes as a part of the Unesco world heritage site Upper Germanic-Rhaetian Limes and has the number ORL 37.
 W
WThe Upper Germanic-Rhaetian Limes, or ORL, is a 550-kilometre-long section of the former external frontier of the Roman Empire between the rivers Rhine and Danube. It runs from Rheinbrohl to Eining on the Danube. The Upper Germanic-Rhaetian Limes is an archaeological site and, since 2005, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Together with the Lower Germanic Limes it forms part of the Limes Germanicus.
 W
WThe Upper Trajan's Wall is the modern name given to a fortification located in the central area of modern Moldavia. Some scholars consider it to be of Roman origin, while others think it was built in the third/fourth century by the Germanic Greuthungi to defend their borders against the Huns. It may also have been called Greuthungian Wall in later Roman accounts, but this is uncertain owing to a single polysemic manuscript occurrence in the works of Ammianus Marcellinus.
 W
WThe Wetterau Limes is the name given in the field of historical research to that part of the Upper Germanic-Rhaetian Limes which enclosed the region that became known later as the Wetterau in the German state of Hesse.