 W
WThe New Orleans Squadron or the New Orleans Station was a United States Navy squadron raised out of the growing threat the United Kingdom posed to Louisiana during the War of 1812. The first squadron consisted of over a dozen vessels and was mostly defeated during the war. Afterward, new ships were stationed at New Orleans which engaged in counter-piracy operations for over twenty years. The New Orleans Squadron was eventually merged with the Home Squadron.
 W
WDetroit was a 6-gun brig launched in 1798 as Adams in the United States. During the War of 1812 the British captured her, renamed her, and took her into the Provincial Marine. She served on Lake Erie during the War of 1812, giving the British control of the lake. The Americans briefly recaptured her, but she grounded and came under heavy fire. The Americans had to abandon her. The vessel was set afire and burnt.
 W
WUSS Adams was a 28-gun (rated) sailing frigate of the United States Navy. She was laid down in 1797 at New York City by John Jackson and William Sheffield and launched on 8 June 1799. Captain Richard Valentine Morris took command of the ship.
 W
WUSS Alligator was a sloop in the United States Navy during the War of 1812. The U.S. Navy purchased Alligator in 1813 at New Orleans, Louisiana. Commissioned as a tender at New Orleans, she served on that station under the command of Sailing Master Richard S. Sheppard until late in 1814 when the British captured her at the Battle of Lake Borgne.
 W
WThe first USS Argus, originally named USS Merrimack, was a brig in the United States Navy commissioned in 1803. She enforced the Embargo Act of 1807 and fought in the First Barbary War – taking part in the blockade of Tripoli and the capture of Derna – and the War of 1812. During the latter conflict, she had been audaciously raiding British merchant shipping in British home waters for a month, when the heavier British Cruizer-class brig-sloop HMS Pelican intercepted her. After a sharp fight during which Argus's captain, Master Commandant William Henry Allen, was mortally wounded, Argus surrendered when the crew of Pelican were about to board.
 W
WThe third USS Boston was a 32-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted frigate of the United States Navy. Boston was built by public subscription in Boston under the Act of 30 June 1798. Boston was active during the Quasi-War with France and the First Barbary War. On 12 October 1800, Boston engaged and captured the French corvette Berceau. Boston was laid up in 1802, and considered not worth repairing at the outbreak of the War of 1812. She was burned at the Washington Naval Yard on 24 August 1814 to prevent her capture by British forces.
 W
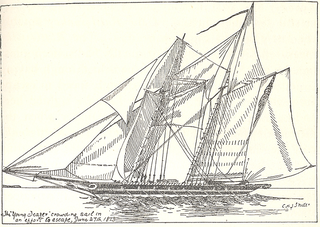
WYoung Teazer was a United States privateer schooner that captured 12 British vessels, five of which made it to American ports. A member of her crew blew her up at Mahone Bay, Nova Scotia during the War of 1812 after a series of British warships chased her and after HMS Hogue trapped her. The schooner became famous for this deadly explosion, which killed most of her crew, and for the folklore about the ghostly "Teazer Light."
 W
WChesapeake was a 38-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy. She was one of the original six frigates whose construction was authorized by the Naval Act of 1794. Joshua Humphreys designed these frigates to be the young navy's capital ships. Chesapeake was originally designed as a 44-gun frigate, but construction delays, material shortages and budget problems caused builder Josiah Fox to alter his design to 38 guns. Launched at the Gosport Navy Yard on 2 December 1799, Chesapeake began her career during the Quasi-War with France and later saw service in the First Barbary War.
 W
WComet, an American schooner, was built in 1810 at Baltimore, Maryland. She was owned by "a group of wealthy Baltimore investors." Under Captain Thomas Boyle, who was a part owner of the schooner, Comet sailed from July 1812 to March 1814 as a privateer, which was a type of ships licensed by the United States during the War of 1812 to harass the British merchant vessels and divest their cargoes.
 W
WUSS Congress was a nominally rated 38-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy. James Hackett built her in Portsmouth New Hampshire and she was launched on 15 August 1799. She was one of the original six frigates whose construction the Naval Act of 1794 had authorized. The name "Congress" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed.Joshua Humphreys designed these frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so Congress and her sisters were larger and more heavily armed and built than the standard frigates of the period.
 W
WUSS Constitution, also known as Old Ironsides, is a wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy. She is the world's oldest ship of any type still afloat. She was launched in 1797, one of six original frigates authorized for construction by the Naval Act of 1794 and the third constructed. The name "Constitution" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed. Joshua Humphreys designed the frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so Constitution and her sister ships were larger and more heavily armed and built than standard frigates of the period. She was built at Edmund Hartt's shipyard in the North End of Boston, Massachusetts. Her first duties were to provide protection for American merchant shipping during the Quasi-War with France and to defeat the Barbary pirates in the First Barbary War.
 W
WHMS Detroit was a 20-gun sloop of the Royal Navy, launched in July 1813 and serving on Lake Erie during the War of 1812. She was the most powerful British ship in the Lake Erie squadron until the Americans captured her during the Battle of Lake Erie on 10 September 1813. Detroit was commissioned into the United States Navy as its first USS Detroit. However, she was so damaged that the sloop took no further part in the war. Postwar, Detroit was sunk for preservation at Misery Bay off Presque Isle until 1833, when she was refloated and converted for commercial service. In 1841, Detroit was reduced to a hulk at Buffalo, New York where she was purchased with the intent of sending her over Niagara Falls. The plan went awry and Detroit ran aground on a shoal before the falls and broke up.
 W
WThe third US ship to be named Enterprise was a schooner, built by Henry Spencer at Baltimore, Maryland, in 1799. Her first commander thought that she was too lightly built and that her quarters, in particular, should be bulletproofed. Enterprise was overhauled and rebuilt several times, effectively changing from a twelve-gun schooner to a fourteen-gun topsail schooner and eventually to a brig. Enterprise saw action in the Caribbean, the Mediterranean, and the Caribbean again, capturing numerous prizes. She wrecked in July 1823.
 W
WHMS Epervier was an 18-gun Cruizer-class brig-sloop of the Royal Navy, built by Ross at Rochester, England, and launched on 2 December 1812. USS Peacock captured her in 1814 and took her into service. USS Epervier disappeared in 1815 while carrying dispatches reporting the signing of a treaty with the Dey of Algiers.
 W
WUSS Erie was a three-masted, wooden-hulled sloop-of-war of the United States Navy in the early 19th century.
 W
WThe first USS Essex of the United States Navy was a 36-gun or 32-gun sailing frigate that participated in the Quasi-War with France, the First Barbary War, and in the War of 1812. The British captured her in 1814 and she then served as HMS Essex until sold at public auction on 6 June 1837.
 W
WThe USS Firefly, was a brig with two masts, square-rigged, formerly named Volant and originally built as a schooner for use as a privateer. The vessel was purchased at New York by the U.S. Navy on 8 December 1814 and was fitted out as US war ship with 14 guns and used in service during the War of 1812 and Second Barbary War of 1815. Firefly was purchased because of the several US blockade efforts where smaller ships with better maneuverability were needed for the task.
 W
WGeneral Armstrong was an American brig built for privateering in the Atlantic Ocean theater of the War of 1812. She was named for Brigadier General John Armstrong, Sr., who fought in the American Revolutionary War.
 W
WUSS General Pike was a corvette in the United States Navy, which took part in Engagements on Lake Ontario during the Anglo-American War of 1812. She was launched in June 1813 and took part in several indecisive battles on the Great Lakes. She was laid up at the end of the war and was sold in 1825.
 W
WThe first USS Hamilton was a United States Navy schooner which served on Lake Ontario from 1812 to 1813 during the War of 1812.
 W
WThe third USS Hornet was a brig-rigged sloop-of-war in the United States Navy. During the War of 1812, she was the first U.S. Navy ship to capture a British privateer.
 W
WThe first John Adams was originally built in 1799 as a frigate for the United States Navy, converted to a corvette in 1809, and later converted back to a frigate in 1830. Named for President John Adams, she fought in the Quasi-War, the First and Second Barbary Wars, the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War. At the end of her career, she participated in the Union blockade of South Carolina's ports. She then participated in the raid on Combahee Ferry that Harriet Tubman, the former slave and Union operative, organized with Union colonel Montgomery. John Adams led three steam-powered gunboats up the Harbor River to Port Royal. The squadron relied on local black mariners to guide it past mines and fortifications. The squadron freed 750+ slaves and unsettled the Confederacy. Tubman was the first woman in U.S. history to plan and execute an armed expedition.
 W
WUSS Lawrence was one of two 493-ton Niagara-class brigs built at Erie, Pennsylvania, by Adam and Noah Brown under the supervision of Sailing Master Daniel Dobbins and Master Commandant Oliver Hazard Perry, for United States Navy service on the Great Lakes during the War of 1812.
 W
WHMS Linnet was a 16-gun brig, built in 1814 by the Royal Navy at Ile aux Noix, Canada, as Niagara. Renamed Linnet and commanded by Commander Daniel Pring, RN, she served on Lake Champlain during the War of 1812. The Americans captured her in 1814 at the Battle of Lake Champlain at Plattsburgh, New York, and took her into service though she never sailed again. She was sold in 1825.
 W
WUSS Lynx, a 6-gun Baltimore Clipper-rigged schooner, was built for the United States Navy by James Owner of Georgetown, Washington, D.C., in 1814, intended for service in one of the two raiding squadrons being built as part of President James Madison's administration’s plan to establish a more effective Navy, one capable not only of breaking the British naval blockade, but also of raising havoc with the British merchant marine.
 W
WHMS Macedonian was a 38-gun fifth-rate Lively-class frigate in the Royal Navy, later captured by the USS United States during the War of 1812.
 W
WNautilus was a schooner launched in 1799. The United States Navy purchased her in May 1803 and commissioned her USS Nautilus; she thus became the first ship to bear that name. She served in the First Barbary War. She was altered to a brigantine. The British captured Nautilus early in the War of 1812 and renamed her HMS Emulous. After her service with the Royal Navy, the Admiralty sold her in 1817.
 W
WThe first USS New Orleans was a ship-of-the-line intended for use by the United States Navy in the War of 1812. She was never finished.
 W
WUSS Niagara, commonly called the US Brig Niagara or the Flagship Niagara, is a wooden-hulled snow-brig that served as the relief flagship for Oliver Hazard Perry in the Battle of Lake Erie during the War of 1812. As the ship is certified for sail training by the United States Coast Guard, she is also designated SSV Niagara. Niagara is usually docked behind the Erie Maritime Museum in downtown Erie in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania as an outdoor exhibit for the museum. She also often travels the Great Lakes during the summer, serving as an ambassador of Pennsylvania when not docked. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973 and was designated the official state ship of Pennsylvania by the Pennsylvania General Assembly in 1988.
 W
WThe first USS Oneida was a brig of war in the United States Navy during the War of 1812.
 W
WUSS Peacock was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the War of 1812.
 W
WUSS President was a wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy, nominally rated at 44 guns. She was launched in April 1800 from a shipyard in New York City. President was one of the original six frigates whose construction the Naval Act of 1794 had authorized, and she was the last to be completed. The name "President" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed.Joshua Humphreys designed these frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so President and her sisters were larger and more heavily armed and built than standard frigates of the period. Forman Cheeseman, and later Christian Bergh were in charge of her construction. Her first duties with the newly formed United States Navy were to provide protection for American merchant shipping during the Quasi War with France and to engage in a punitive expedition against the Barbary pirates in the First Barbary War.
 W
WThe Prince de Neufchatel was a fast sailing United States schooner-rigged privateer, built in New York by Adam and Noah Brown in approximately 1812. She is a fine example of the peak of development of the armed schooner. Neufchatel operated in mainly European waters, damaging British shipping during the War of 1812. Noted for her speed, at one time she outran seventeen men-of-war. In 1813, operating in the English channel, she took nine British prizes in quick succession. She also delivered a crushing defeat to the boats of a British frigate that tried to capture her. The British finally captured her in December 1814; she was broken up in 1815.
 W
WReaper was a Massachusetts privateer schooner that Captain Ephraim Sturdivant commanded during the War of 1812. Captain Sturdivant was officially charged by President James Madison to use the ship to attack British shipping. There is no evidence that she captured any British vessels.
 W
WUSS Scorpion was a self-propelled floating artillery battery in commission with the United States Navy from 1812 to 1814.
 W
WUSS Scourge was an American warship converted from a confiscated Canadian merchant schooner. She and the American warship Hamilton foundered at 2:00am on Sunday, August 8, 1813 during a squall on Lake Ontario. during the War of 1812.
 W
WUSS Spark (1813) was a heavily armed brig in the services of the United States Navy, built for service in the War of 1812. However, she was completed too late for that war and was assigned, instead, to the Barbary Wars in the Mediterranean. After two voyages in support of that action, she was assigned to suppress pirates in the Caribbean, where she was successful in capturing a number of pirate ships and their crews.
 W
WUSS Superior was built for the War of 1812, and was named after one of the Great Lakes. Superior was a U.S. Navy frigate built in 1814 at Sackets Harbor, New York, by Henry Eckford, and was laid down in February 1814 and launched on 2 May of the same year.
 W
WUSRC Surveyor was a ship of the United States Revenue Marine captured by the United Kingdom during the War of 1812. Despite the vessel's loss, the "gallant and desperate" defense of her crew against a superior force of the Royal Navy and the Corps of Royal Marines is commemorated by the United States Coast Guard. Along with the Royal Navy frigate which bested her in battle, HMS Narcissus, Surveyor is among six legendary ships memorialized in the lyrics of the Coast Guard march "Semper Paratus".
 W
WUSS Syren was a brig of the United States Navy built at Philadelphia in 1803. She served during the First Barbary War and the War of 1812 until the Royal Navy captured her in 1814. The British never commissioned her but apparently used her for a year or so as a lazaretto, or a prison vessel. She then disappears from records.
 W
WThe USS Troup was the British Post Office Packet Service packet Princess Amelia, which Joshua Barney in the American privateer Rossie captured at the start of the War of 1812. After a short but intense fight, Princess Amelia struck on 16 September 1812.
 W
WUSS United States was a wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy and the first of the six original frigates authorized for construction by the Naval Act of 1794. The name "United States" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed. Joshua Humphreys designed the frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so United States and her sisters were larger and more heavily armed and built than standard frigates of the period. She was built at Humphrey's shipyard in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and launched on 10 May 1797 and immediately began duties with the newly formed United States Navy protecting American merchant shipping during the Quasi-War with France.
 W
WUSS Viper – commissioned as USS Ferret – was a brig serving the United States Navy during the early days of the republic. Viper was assigned to enforce the Embargo Act of 1807 along the U.S. East Coast. During the War of 1812, while cruising in the Caribbean, she was captured by the more heavily armed British warships. She then served the Royal Navy as HMS Mohawk until the Navy sold her in 1814. While in British service she served in several actions that earned her crew the Naval General Service Medal,
 W
WUSS Vixen was a schooner in the United States Navy during the First Barbary War. Vixen was one of four vessels authorized by Congress on 28 February 1803. She was built at Baltimore, Maryland, in the spring of 1803; and launched on 25 June, Lieutenant John Smith in command.
 W
WUSS Wasp of the United States Navy was a sailing sloop-of-war captured by the British in the early months of the War of 1812. She was constructed in 1806 at the Washington Navy Yard, was commissioned sometime in 1807, Master Commandant John Smith in command. In 1812 she captured HMS Frolic, but was immediately herself captured. The British took her into service first as HMS Loup Cervier and then as HMS Peacock. She was lost, presumed foundered with all hands, in mid-1814.
 W
WUSS Wasp was a sloop-of-war that served in the United States Navy in 1814 during the War of 1812. She was the fifth United States Navy ship to carry that name. She carried out two successful raiding voyages against British trade during the summer of 1814, in the course of which she fought and defeated three British warships. Wasp was lost, cause unknown, in the Atlantic in early autumn, 1814.