 W
WThis is a list of sailing frigates of the United States Navy. Frigates were the backbone of the early Navy, although the list shows that many suffered unfortunate fates.
 W
WUSS Adams was a 28-gun (rated) sailing frigate of the United States Navy. She was laid down in 1797 at New York City by John Jackson and William Sheffield and launched on 8 June 1799. Captain Richard Valentine Morris took command of the ship.
 W
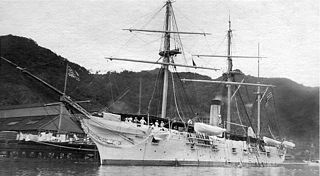
WUSS Adams was a screw gunboat and the lead ship of the Adams class.
 W
WThe first Alliance of the United States Navy was a 36-gun sailing frigate of the American Revolutionary War.
 W
WThe USS Ammonoosuc was a steam frigate laid down by the Boston Navy Yard during the American Civil War and was launched, apparently without ceremony, on 21 July 1864. She was intended to be used against the British should England decide to take the side of the Confederate States of America and attack the Northern part of the United States. However, as the war progressed, England's support of the Confederacy diminished, and the fast and powerful Ammonoosuc was never placed into service.
 W
WBonhomme Richard, formerly Duc de Duras, was a warship in the American Continental Navy. She was originally an East Indiaman, a merchant ship built in France for the French East India Company in 1765, for service between France and Asia. She was placed at the disposal of John Paul Jones on 4 February 1779, by King Louis XVI of France as a result of a loan to the United States by French shipping magnate Jacques-Donatien Le Ray.
 W
WThe second USS Boston was a 24-gun frigate, launched 3 June 1776 by Stephen and Ralph Cross, Newburyport, Massachusetts, and completed the following year. In American service she captured a number of British vessels. The British captured Boston at the fall of Charleston, South Carolina, renamed her HMS Charlestown, and took her into service. She was engaged in one major fight with two French frigates, which she survived and which saved the convoy she was protecting. The British sold Charlestown in 1783, immediately after the end of the war.
 W
WThe third USS Boston was a 32-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted frigate of the United States Navy. Boston was built by public subscription in Boston under the Act of 30 June 1798. Boston was active during the Quasi-War with France and the First Barbary War. On 12 October 1800, Boston engaged and captured the French corvette Berceau. Boston was laid up in 1802, and considered not worth repairing at the outbreak of the War of 1812. She was burned at the Washington Naval Yard on 24 August 1814 to prevent her capture by British forces.
 W
WUSS Brandywine was a wooden-hulled, three-masted frigate of the United States Navy bearing 44 guns which had the initial task of conveying the Marquis de Lafayette back to France. She was later recommissioned a number of times for service in various theaters, such as in the Mediterranean, in China and in the South Atlantic Ocean.
 W
WChesapeake was a 38-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy. She was one of the original six frigates whose construction was authorized by the Naval Act of 1794. Joshua Humphreys designed these frigates to be the young navy's capital ships. Chesapeake was originally designed as a 44-gun frigate, but construction delays, material shortages and budget problems caused builder Josiah Fox to alter his design to 38 guns. Launched at the Gosport Navy Yard on 2 December 1799, Chesapeake began her career during the Quasi-War with France and later saw service in the First Barbary War.
 W
WThe first USS Columbia of the United States Navy was a three-masted, wooden-hulled sailing frigate of the US Navy, rated for 50 guns. She was built at Washington Navy Yard. Her keel was laid in 1825, but as was typical of much Navy construction during this period, she was not launched until much later, on 9 March 1836.
 W
WUSS Confederacy was a 36-gun sailing frigate of the Continental Navy in the American Revolutionary War. The British Royal Navy captured her in March 1781, took her into service for about half-a-year as HMS Confederate, and broke her up in 1782.
 W
WUSS Congress was a nominally rated 38-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy. James Hackett built her in Portsmouth New Hampshire and she was launched on 15 August 1799. She was one of the original six frigates whose construction the Naval Act of 1794 had authorized. The name "Congress" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed.Joshua Humphreys designed these frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so Congress and her sisters were larger and more heavily armed and built than the standard frigates of the period.
 W
WUSS Constitution, also known as Old Ironsides, is a wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy. She is the world's oldest ship of any type still afloat. She was launched in 1797, one of six original frigates authorized for construction by the Naval Act of 1794 and the third constructed. The name "Constitution" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed. Joshua Humphreys designed the frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so Constitution and her sister ships were larger and more heavily armed and built than standard frigates of the period. She was built at Edmund Hartt's shipyard in the North End of Boston, Massachusetts. Her first duties were to provide protection for American merchant shipping during the Quasi-War with France and to defeat the Barbary pirates in the First Barbary War.
 W
WThe first USS Cumberland was a 50-gun sailing frigate of the United States Navy. She was the first ship sunk by the ironclad CSS Virginia.
 W
WCyane was a Royal Navy sailing Banterer-class sixth-rate ship of 22 guns, built in 1806 at Topsham, near Exeter, England. She was ordered in January 1805 as HMS Columbine and was renamed Cyane on 6 December of that year.
 W
WThe first USS Essex of the United States Navy was a 36-gun or 32-gun sailing frigate that participated in the Quasi-War with France, the First Barbary War, and in the War of 1812. The British captured her in 1814 and she then served as HMS Essex until sold at public auction on 6 June 1837.
 W
WUSS General Pike was a corvette in the United States Navy, which took part in Engagements on Lake Ontario during the Anglo-American War of 1812. She was launched in June 1813 and took part in several indecisive battles on the Great Lakes. She was laid up at the end of the war and was sold in 1825.
 W
WUSS Guerriere was the first frigate built in the United States since 1801. The name came from a fast 38-gun British frigate captured and destroyed in a half-hour battle by USS Constitution on 19 August 1812. This victory was one of the United States' first in the War of 1812.
 W
WThe second Hancock was one of the first 13 frigates of the Continental Navy. A resolution of the Continental Congress of British North America 13 December 1775 authorized her construction; she was named for John Hancock. In her career she served under the American, British and French flags.
 W
WThe first USS Hudson was a wooden hulled, three-masted sailing frigate in the United States Navy.
 W
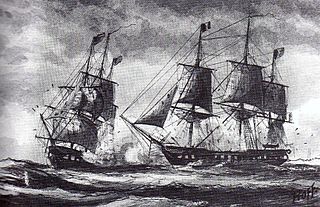
WL'Insurgente was a 40-gun Sémillante-class frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1793. During the Quasi War with the United States, the United States Navy frigate USS Constellation, with Captain Thomas Truxtun in command, captured her off the island of Nevis. After her capture she served in the United States Navy as USS Insurgent, patrolling the waters in the West Indies. In September 1800 she was caught up in a severe storm and was presumed lost at sea.
 W
WThe first John Adams was originally built in 1799 as a frigate for the United States Navy, converted to a corvette in 1809, and later converted back to a frigate in 1830. Named for President John Adams, she fought in the Quasi-War, the First and Second Barbary Wars, the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War. At the end of her career, she participated in the Union blockade of South Carolina's ports. She then participated in the raid on Combahee Ferry that Harriet Tubman, the former slave and Union operative, organized with Union colonel Montgomery. John Adams led three steam-powered gunboats up the Harbor River to Port Royal. The squadron relied on local black mariners to guide it past mines and fortifications. The squadron freed 750+ slaves and unsettled the Confederacy. Tubman was the first woman in U.S. history to plan and execute an armed expedition.
 W
WHMS Macedonian was a 38-gun fifth-rate Lively-class frigate in the Royal Navy, later captured by the USS United States during the War of 1812.
 W
WThe second USS Macedonian, was a three-masted, wooden-hulled sailing frigate of the US Navy, carrying 36 guns. Rebuilt from the keel of the first Macedonian at Gosport Navy Yard, Portsmouth, Virginia beginning in 1832, the new Macedonian was launched and placed in service in 1836, with Captain Thomas ap Catesby Jones in command.
 W
WUSS Merrimack, also improperly Merrimac, was a steam frigate, best known as the hull upon which the ironclad warship CSS Virginia was constructed during the American Civil War. The CSS Virginia then took part in the Battle of Hampton Roads in the first engagement between ironclad warships.
 W
WUSS Minnesota was a wooden steam frigate in the United States Navy. Launched in 1855 and commissioned eighteen months later, the ship served in east Asia for two years before being decommissioned. She was recommissioned at the outbreak of the American Civil War and returned to service as the flagship of the North Atlantic Blockading Squadron.
 W
WUSS Neshaminy was a large and powerful 3,850-ton screw frigate with a length of 335 feet that was under construction at the Philadelphia Navy Yard when she was surveyed by Navy officials who found her construction work to be poor. Construction was halted by the Navy, which eventually sold her for scrap.
 W
WThe second USS Niagara was a screw frigate in the United States Navy.
 W
WThe United States Congress authorized the original six frigates of the United States Navy with the Naval Act of 1794 on March 27, 1794, at a total cost of $688,888.82. These ships were built during the formative years of the United States Navy, on the recommendation of designer Joshua Humphreys for a fleet of frigates powerful enough to engage any frigates of the French or British navies yet fast enough to evade any ship of the line.
 W
WUSS Philadelphia, a 1240-ton, 36-gun sailing frigate, was the second vessel of the United States Navy to be named for the city of Philadelphia. Originally named City of Philadelphia, she was built in 1798–1799 for the United States government by the citizens of that city. Funding for her construction was the result of a funding drive which raised $100,000 in one week, in June 1798. She was designed by Josiah Fox and built by Samuel Humphreys, Nathaniel Hutton and John Delavue. Her carved work was done by William Rush of Philadelphia. She was laid down about November 14, 1798, launched on November 28, 1799, and commissioned on April 5, 1800, with Captain Stephen Decatur, Sr. in command. She was captured in Tripoli with William Bainbridge in command, and perhaps best remembered for a raid led by Stephen Decatur that burned her down.
 W
WUSS Potomac was a frigate in the United States Navy laid down by the Washington Navy Yard in August 1819 and launched in March 1822. Fitting out was not completed until 1831, when Captain John Downes assumed command as first commanding officer. Although called a "44" 1st class, she was built to mount 32 carronades on her spar deck, 30 long guns on her gun deck, two bow and three stern chasers on each of these decks, significantly under-rating her on the rating system of the Royal Navy.
 W
WThe first USS Powhatan was a sidewheel steam frigate in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She was named for Powhatan, a Native American chief of eastern Virginia. She was one of the last, and largest, of the United States Navy's paddle frigates.
 W
WUSS President was a wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy, nominally rated at 44 guns. She was launched in April 1800 from a shipyard in New York City. President was one of the original six frigates whose construction the Naval Act of 1794 had authorized, and she was the last to be completed. The name "President" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed.Joshua Humphreys designed these frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so President and her sisters were larger and more heavily armed and built than standard frigates of the period. Forman Cheeseman, and later Christian Bergh were in charge of her construction. Her first duties with the newly formed United States Navy were to provide protection for American merchant shipping during the Quasi War with France and to engage in a punitive expedition against the Barbary pirates in the First Barbary War.
 W
WUSS Raleigh was one of thirteen ships that the Continental Congress authorized for the Continental Navy in 1775. Following her capture in 1778, she served in the Royal Navy as HMS Raleigh. The ship is featured on the flag and seal of New Hampshire.
 W
WThe first USS Randolph was a 32-gun frigate in the Continental Navy named for Peyton Randolph.
 W
WThe first USS Raritan was a wooden-hulled, three-masted sailing frigate of the United States Navy built at the Philadelphia Navy Yard, laid down in 1820, but not launched until 13 June 1843, sponsored by Commodore Frederick Engle. She was one of the last sailing frigates of the United States Navy.
 W
WThe first USS Sabine was a sailing frigate built by the United States Navy in 1855. The ship was among the first ships to see action in the American Civil War. In 1862, a large portion of the USS Monitor crew were volunteers from the Sabine.
 W
WUSS Congress (1841)—the fourth United States Navy ship to carry that name—was a sailing frigate, like her predecessor, USS Congress (1799).
 W
WThe first USS San Jacinto was an early screw frigate in the United States Navy during the mid-19th century. She was named for the San Jacinto River, site of the Battle of San Jacinto during the Texas Revolution. She is perhaps best known for her role in the Trent Affair of 1861.
 W
WUSS Santee (1855) was a wooden-hulled, three-masted sailing frigate of the United States Navy. She was the first U.S. Navy ship to be so named and was one of its last sailing frigates in service. She was acquired by the Union Navy at the start of the American Civil War, outfitted with heavy guns and a crew of 480, and was assigned as a gunboat in the Union blockade of the Confederate States. She later became a training ship then a barracks ship for the U.S. Naval Academy.
 W
WThe second USS Savannah was a frigate in the United States Navy. She was named after the city of Savannah, Georgia.
 W
WSix Frigates: The Epic History of the Founding of the U.S. Navy is a book by Ian W. Toll, which was published by Norton in 2006. The book is a history of the original six frigates of the U.S. Navy.
 W
WUSS St. Lawrence was a frigate in the United States Navy that saw service during the mid-19th century, including the American Civil War. She was based on the same plans as USS Brandywine.
 W
WUSS Superior was built for the War of 1812, and was named after one of the Great Lakes. Superior was a U.S. Navy frigate built in 1814 at Sackets Harbor, New York, by Henry Eckford, and was laid down in February 1814 and launched on 2 May of the same year.
 W
WUSS Contoocook was a screw sloop-of-war built for the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She is named after a river and village in New Hampshire. She was launched 3 December 1864 at Portsmouth Navy Yard and commissioned 14 March 1868, commanded by Captain George Balch.
 W
WUSS United States was a wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy and the first of the six original frigates authorized for construction by the Naval Act of 1794. The name "United States" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed. Joshua Humphreys designed the frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so United States and her sisters were larger and more heavily armed and built than standard frigates of the period. She was built at Humphrey's shipyard in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and launched on 10 May 1797 and immediately began duties with the newly formed United States Navy protecting American merchant shipping during the Quasi-War with France.
 W
WUSS Wabash was a steam screw frigate of the United States Navy that served during the American Civil War. She was based on the same plans as Colorado. Post-war she continued to serve her country in European operations and eventually served as a barracks ship in Boston, Massachusetts, and was sold in 1912.