 W
WUSS Abner Read (DD-526) was a Fletcher-class destroyer in the service of the United States Navy, named after Lieutenant Commander Abner Read, who fought in the American Civil War. The ship fought in World War II, seeing action in the Aleutian Islands Campaign and in 1943 she survived hitting a mine that blew off her stern. After repairs, she returned to service and operated in support of Allied forces in the New Guinea campaign and the Battle of Leyte. She was sunk in an air attack off Leyte on 1 November 1944.
 W
WAkebono was the eighteenth of twenty-four Fubuki-class destroyers, built for the Imperial Japanese Navy following World War I. When introduced into service, these ships were the most powerful destroyers in the world. They served as first-line destroyers through the 1930s, and remained formidable weapons systems well into the Pacific War.
 W
WAmerica Maru was the second of three high speed passenger liners built for the Oriential Steamship Company. Converted into an armed merchantman during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, she played a crucial role in the Battle of Tsushima. Although used as a hospital ship during the early part of World War II, she had been chartered by the IJN as a transport in 1943, and was sunk by the United States Navy in 1944 with great loss of civilian lives.
 W
WAsagumo was the fifth of ten Asashio-class destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy in the mid-1930s under the Circle Two Supplementary Naval Expansion Program.
 W
WThe Japanese destroyer Asanagi was one of nine Kamikaze-class destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during the 1920s. During the Pacific War, she participated in the occupation of the Gilbert Islands and the Battle of Wake Island in December 1941 and then the occupations of New Guinea and the Solomon Islands in early 1942.
 W
WAtago (愛宕) was the second vessel in the Takao-class heavy cruisers, active in World War II with the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). These were among the largest and most modern cruisers in the Japanese fleet, designed with the intention to form the backbone of a multipurpose long-range strike force. Her sister ships were Takao, Maya and Chōkai.
 W
WUSS Bittern (AM-36) was a Lapwing-class minesweeper in the United States Navy. She was named after the bittern, a bird of the heron family. The vessel was constructed by Alabama Dry Dock and Shipbuilding Co., in Mobile, Alabama, and launched on 15 February 1919 and commissioned on 28 May later that year. Initially operating in U.S. coastal waters, the vessel was reassigned to western Pacific operations in 1920, based in the Philippine Islands. Shortly after the U.S. entry into World War II, Bittern was scuttled to avoid capture after being severely damaged during a Japanese air raid on Cavite Navy Yard in December 1941.
 W
WChikuma (筑摩) was the second and last vessel in the Tone class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. The ship was named after the Chikuma River, in Nagano prefecture of Japan. Entering service in 1939, Chikuma saw battle during World War II in the Pacific. She was scuttled on 25 October 1944 after the Battle off Samar.
 W
WChitose (千歳) was a light aircraft carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. First laid down as a seaplane tender in 1934 at Kure Navy yard, the ship originally carried Kawanishi E7K Type 94 "Alf" and Nakajima E8N Type 95 "Dave" floatplanes. Although it has been speculated that Chitose also carried Type A midget submarines, only her sister ship, Chiyoda had that capability. Chitose saw several naval actions, taking part in the Battle of Midway though seeing no combat there. She was bombed by B-17 Flying Fortresses off Davao, Philippines, on 4 January 1942, sustaining negligible damage. She covered the Japanese landings in the East Indies and New Guinea from January–April 1942, and was damaged in the Eastern Solomons in August 1942.
 W
WChiyoda was a light aircraft carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. Originally constructed as the second vessel of the Chitose-class seaplane tenders in 1934, she continued to operate in that capacity during the Second Sino-Japanese War and the early stages of the Pacific War until her conversion into a light aircraft carrier after the Battle of Midway. She was sunk during the Battle of Leyte Gulf by a combination of naval bombers, cruiser shellfire and destroyer-launched torpedoes.
 W
WChūyō was a Taiyō-class escort carrier originally built as Nitta Maru , the first of her class of three passenger-cargo liners built in Japan during the late 1930s. She was requisitioned by the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in late 1941 and was converted into an escort carrier in 1942. She spent most of her service ferrying aircraft, cargo and passengers to Truk until she was torpedoed and sunk by an American submarine in late 1943 with heavy loss of life.
 W
WUSS Cooper (DD-695), was an Allen M. Sumner-class destroyer of the United States Navy.
 W
WFusō was the lead ship of the two Fusō-class dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy. Launched in 1914 and commissioned in 1915, she initially patrolled off the coast of China, playing no part in World War I. In 1923, she assisted survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake.
 W
WUSS Gambier Bay (CVE-73) was a Casablanca-class escort carrier of the United States Navy. She was sunk in the Battle off Samar during the Battle of Leyte Gulf after helping to turn back a much larger attacking Japanese surface force. She was the only American aircraft carrier sunk by enemy surface gunfire during World War II.
 W
WHiyō was the name ship of her class of two aircraft carriers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). Begun as the ocean liner Izumo Maru (出雲丸) in 1939, she was purchased by the Navy Ministry in 1941 for conversion to an aircraft carrier. Completed shortly after the Battle of Midway in June 1942, she participated in the Guadalcanal Campaign, but missed the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands in October because of an electrical generator fire.
 W
WUSS Hoel (DD-533) was a World War II-era Fletcher-class destroyer in the service of the United States Navy, named after Lieutenant Commander William R. Hoel.
 W
WUSS Hull (DD-350) was a Farragut-class destroyer in the United States Navy during World War II. She was named for Isaac Hull.
 W
WI-26 was a Japanese B1 type submarine which saw service in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. She was completed and commissioned at the Kure Dockyard on 6 November 1941, under the command of Commander Yokota Minoru.
 W
WI-48 was the last of three Type C cruiser submarines of the C2 sub-class built for the Imperial Japanese Navy. Commissioned in September 1944, she operated as a kaiten manned suicide attack torpedo carrier during World War II and was sunk in January 1945.
 W
WUSS Johnston (DD-557) was a Fletcher-class destroyer in the service of the United States Navy in World War II, the first Navy ship named after Lieutenant John V. Johnston. The ship is known for her action in the Battle off Samar. The small "tincan" destroyer, armed with torpedoes, and guns no larger than 5-inch (127 mm), led an attack by a handful of light ships which had inadvertently been left unprotected in the path of a Japanese fleet with battleships and cruisers. The actions of Johnston—sunk in the action—and the lightly armed and lightly armored Escort Carrier Task Unit 77.4.3, of which she was a member, helped stop Admiral Kurita's Center Force from attacking the U.S. landing forces and inflicted greater damage on the Japanese attackers than they suffered. Johnston's wreck is the deepest surveyed shipwreck when rediscovered and identified in March 2021.
 W
WSS Kachidoki Maru was a former US passenger ship, built in 1920 and captured by the Japanese in 1941. The ship was torpedoed on 12 September 1944, carrying 950 Allied prisoners of war of which 431 were killed.
 W
WKomahashi (駒橋), was an auxiliary vessel operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy, serving from the 1910s through World War II. Her classification changed numerous times during her operational life. Although officially designated as a submarine tender for most of her career, Komahashi very rarely functioned in this role, but was used instead as an oceanographic survey vessel throughout the Pacific, and as a kaibokan escort vessel for convoys of merchant ships during the Pacific War.
 W
WUSS Longshaw (DD-559), a Fletcher-class destroyer, was a ship of the United States Navy named for Dr. William Longshaw, Jr. (1839–1865), who served in the Navy and was killed during the Civil War.
 W
WUSS Mahan (DD-364) was the lead ship of the United States Navy's Mahan-class destroyers. The ship was named for Rear Admiral Alfred Thayer Mahan, a 19th-century naval historian and strategic theorist. Her design ushered in major advances over traditional destroyers. Among them were a third set of quadruple torpedo tubes, protective gun shelters, and emergency diesel generators. Along with a steam propulsion system that was simpler and more efficient to operate.
 W
WMaya (摩耶) was one of four Takao-class heavy cruisers, active in World War II with the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). These were the largest and most modern cruisers in the Japanese fleet, and were intended to form the backbone of a multipurpose long-range strike force. These ships were fast, powerful and heavily armed, with enough firepower to hold their own against any cruiser in any other navy in the world. Her sister ships were Takao, Atago and Chōkai.
 W
WMichishio was the third of ten Asashio-class destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy in the mid-1930s under the Circle Two Supplementary Naval Expansion Program.
 W
WUSS Monaghan (DD-354) was the last ship built of the Farragut-class destroyer design. She was named for Ensign John R. Monaghan. Monaghan was laid down on November 21, 1933 at the Boston Navy Yard, and launched on January 9, 1935. She was sponsored by Miss Mary F. Monaghan, niece of Ensign Monaghan, and commissioned on 19 April 1935, with Commander R. R. Thompson in command. During the next few years Monaghan operated primarily in the North Atlantic, training US Navy personnel who served in World War II. Monaghan was present during the Pearl Harbor raid on December 7, 1941. She participated in the Battle of the Coral Sea and the Battle of Midway in 1942. Monaghan was sunk in a typhoon east of the Philippines in 1944.
 W
WNatori was a Nagara-class light cruiser in the Imperial Japanese Navy. The ship was named after the Natori River in Miyagi prefecture, Japan. Natori was the third vessel completed in the Nagara class of light cruisers. Like other vessels of her class, she was intended for use as the flagship of a destroyer flotilla.
 W
WNumakaze was third and final vessel in the Nokaze sub-class, an improvement to the Minekaze-class 1st class destroyers, built for the Imperial Japanese Navy immediately following World War I. Advanced for their time, these ships served as first-line destroyers through the 1930s, but were considered obsolescent by the start of the Pacific War.
 W
WUSS Pillsbury (DD-227) was a Clemson-class destroyer of the United States Navy that served during World War II and the first of two ships named after John E. Pillsbury, a Rear Admiral in the United States Navy. She was sunk by Japanese cruisers, approximately 200 miles east of Christmas Island on or around 2 March 1942 with all hands, one of two major American surface warships lost in World War II with no survivors.
 W
WThe fourth USS Princeton (CVL-23) was a United States Navy Independence-class light aircraft carrier active in the Pacific Ocean during World War II. She was launched in 1942 and lost at the Battle of Leyte Gulf in 1944.
 W
WUSS Quail (AM-15) was an Lapwing-class minesweeper acquired by the U.S. Navy for the dangerous task of removing mines from minefields laid in the water to prevent ships from passing.
 W
WThe third USS Reid (DD-369) was a Mahan-class destroyer in the United States Navy before and during World War II. She was named for Samuel Chester Reid, a U.S. Navy officer in the War of 1812 who helped design the 1818 version of the flag of the United States.
 W
WUSS Samuel B. Roberts (DE-413) was a John C. Butler-class destroyer escort of the United States Navy that served during 1944.
 W
WSarushima (猿島) was a small Natsushima-class minelayer of the Imperial Japanese Navy, which was in service during World War II. She was named after Sarushima Island, a small island in Tokyo Bay, offshore Yokosuka, Kanagawa. She was designed as an auxiliary minelayer and escort vessel.
 W
WShimakaze (島風) (Island Wind) was an experimental destroyer of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II, and intended as the lead ship in a projected new "Type C" of destroyers. She was the only destroyer to be armed with 15 torpedo tubes, each capable of firing the deadly 610 mm (24 in) Type 93 "Long Lance" torpedo. The ship also served as a testbed for an enormously powerful, high-temperature, high-pressure steam turbine that was able to develop 79,240 shp (59,090 kW). This made her one of the fastest destroyers in the world: her design speed was 39 kn, but on trials she made 40.9 kn.
 W
WShiratsuyu was the lead ship of ten Shiratsuyu-class destroyers, and first of six to be built for the Imperial Japanese Navy under the Circle One Program.
 W
WShōkaku was the lead ship of her class of two aircraft carriers for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) shortly before the Pacific War. Along with her sister ship Zuikaku, she took part in several key naval battles during the war, including the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Battle of the Coral Sea and the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands before being torpedoed and sunk by a U.S. submarine at the Battle of the Philippine Sea.
 W
WUSS Snook (SS-279), a Gato-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the common snook, an Atlantic marine fish that is bluish-gray above and silvery below a black lateral line.
 W
WUSS Spence (DD-512), a Fletcher class destroyer, was laid down on 18 May 1942 by the Bath Iron Works, Bath, Maine; launched on 27 October 1942; sponsored by Mrs. Eben Learned; and commissioned on 8 January 1943, Lieutenant Commander H. J. Armstrong in command. The ship was named for Robert T. Spence, superintendent of the construction of USS Ontario (1813), and captain of USS Cyane (1815).
 W
WUSS St. Lo (AVG/ACV/CVE–63) was a Casablanca-class escort carrier of the United States Navy during World War II. On 25 October 1944, St. Lo became the first major warship to sink as the result of a kamikaze attack. The attack occurred during the Battle off Samar, part of the larger Battle of Leyte Gulf.
 W
WUSS Swallow (AM-65) was an Auk-class minesweeper built for the United States Navy during World War II. The ship was the second U.S. Navy ship named after the swallow. Swallow earned two battle stars for World War II service. She was sunk by a kamikaze aircraft off Okinawa on 22 April 1945. She was struck from the Naval Vessel Register on 2 June 1945.
 W
WUSS Tanager (AM-5) was an Lapwing-class minesweeper acquired by the U.S. Navy for the dangerous task of removing mines from minefields laid in the water to prevent ships from passing.
 W
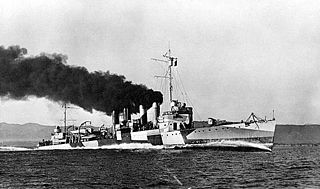
WTatsuta (龍田) was the second ship in the two ship Tenryū class of light cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). She was named after the Tatsuta River in Nara Prefecture, Japan.
 W
WUSS Ward (DD-139) was a 1,247-long-ton (1,267 t) Wickes-class destroyer in the United States Navy during World War I, later APD-16 in World War II. She caused the first American-caused casualties in World War II, when she engaged a Japanese submarine before the attack on Pearl Harbor, and successfully sank her, killing the two crew on board.
 W
WYamashiro was the second of two Fusō-class dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy. Launched in 1915 and commissioned in 1917, she initially patrolled off the coast of China, playing no part in World War I. In 1923, she assisted survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake.
 W
WYūbari (夕張) was an experimental light cruiser built between 1922 and 1923 for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). Although a test bed for various new designs and technologies, she was commissioned as a front-line warship and participated in numerous combat operations during World War II before she was sunk by the U.S. Navy. Designs pioneered on Yūbari had a major impact on future Japanese warship designs.
 W
WZuikaku was the second and last Shōkaku-class aircraft carrier built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) shortly before the beginning of the Pacific War. Her aircraft took part in the attack on Pearl Harbor that formally brought the United States into the war, and she fought in several of the most important naval battles of the war, before being sunk during the Battle of Leyte Gulf.