 W
WThe Raid on Bardia was an amphibious landing at the coastal town of Bardia in North Africa by British Commandos over the night of 19/20 April 1941 during the Second World War. The raid was carried out by No. 7 Commando also known as A Battalion Layforce together with a small detachment from the Royal Tank Regiment supported by five navy ships and a submarine. The raid—which destroyed an Italian artillery battery and a supply dump—was deemed a success despite the loss of 71 men. The more lasting strategic effect of the raid was the diversion of a German armoured brigade from the front line to provide rear area security.
 W
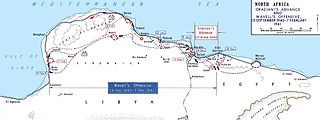
WThe Western Desert campaign took place in the deserts of Egypt and Libya and was the main theatre in the North African campaign of the Second World War. Military operations began in June 1940 with the Italian declaration of war and the Italian invasion of Egypt from Libya in September. Operation Compass, a five-day British raid in December 1940, led to the destruction of the Italian 10th Army. Benito Mussolini sought help from Adolf Hitler, who sent a small German force to Tripoli under Directive 22. The Afrika Korps was formally under Italian command, as Italy was the main Axis power in the Mediterranean and North Africa.
 W
WOperation Agreement was a ground and amphibious operation carried out by British, Rhodesian and New Zealand forces on Axis-held Tobruk from 13 to 14 September 1942, during the Second World War. A Special Interrogation Group party, fluent in German, took part in missions behind enemy lines. Diversionary actions extended to Benghazi, Jalo oasis and Barce. The Tobruk raid was an Allied disaster; the British lost several hundred men killed and captured, one cruiser, two destroyers, six motor torpedo boats and dozens of small amphibious craft.
 W
WThe Battle of Alam el Halfa took place between 30 August and 5 September 1942 south of El Alamein during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. Panzerarmee Afrika, attempted an envelopment of the British Eighth Army. In Unternehmen Brandung, the last big Axis offensive of the Western Desert Campaign, Rommel intended to defeat the Eighth Army before Allied reinforcements arrived.
 W
WThe Alamein Memorial is a Commonwealth War Graves Commission war memorial in the El Alamein War Cemetery, El Alamein, Egypt. The memorial commemorates 11,866 Commonwealth forces members who died during World War II. The memorial was designed by Hubert Worthington and unveiled by Viscount Montgomery of Alamein on 24 October 1954.
 W
WThe Baggush Box was a British Army field fortification built in the Western Desert near Maaten Baggush, 35 miles (56 km) east of Mersa Matruh during the Western Desert Campaign of World War II.
 W
WThe Battle of Bardia was fought between 3 and 5 January 1941, as part of Operation Compass, the first British military operation of the Western Desert campaign of the Second World War. It was the first battle of the war in which an Australian Army formation took part, the first to be commanded by an Australian general and the first to be planned by an Australian staff. The 6th Australian Division assaulted the strongly held Italian fortress of Bardia, Libya, assisted by air support and naval gunfire and under the cover of an artillery barrage. The 16th Australian Infantry Brigade attacked at dawn from the west, where the defences were known to be weak. Sappers blew gaps in the barbed wire with Bangalore torpedoes and filled in and broke down the sides of the anti-tank ditch with picks and shovels. This allowed the infantry and 23 Matilda II tanks of the 7th Royal Tank Regiment to enter the fortress and capture all their objectives, along with 8,000 prisoners.
 W
WThis is the order of battle for the Battle of Alam el Halfa, a World War II battle between the British Commonwealth and the European Axis Powers Germany and Italy in North Africa between 30 August and 5 September 1942.
 W
WThe Battle of Point 175 was a military engagement of the Western Desert Campaign that took place during Operation Crusader from 29 November – 1 December 1941, during the Second World War. Point 175 is a small rise just south of the Trigh Capuzzo, a desert track east of Sidi Rezegh and south of Zaafran, with a good view of the vicinity. In early November 1941, the feature was held by German infantry of Division z.b.V. Afrika. Troops of the 2nd New Zealand Division and Infantry tanks of the 1st Army Tank Brigade attacked and captured Point 175 on 23 November, during the Battle of Sidi Rezegh, at the start of Operation Crusader. The New Zealand troops then attacked westwards and made contact with the Tobruk garrison, which had broken out to meet them. From 29 November – 1 December, the New Zealanders defended the point and the area to the west against Axis attempts to sever the link with the Tobruk garrison and regain control of the local roads. The new 132nd Armoured Division Ariete re-captured Point 175 late on 29 November.
 W
WOperation Battleaxe was a British Army offensive during the Second World War to raise the Siege of Tobruk and re-capture eastern Cyrenaica from German and Italian forces. It was the first time during the war that a significant German force fought on the defensive. The British lost over half of their tanks on the first day and only one of three attacks succeeded.
 W
WThe rapid British advance during Operation Compass forced the Italian 10th Army to evacuate Cyrenaica, the eastern province of Libya. In late January, the British learned that the Italians were retreating along the Litoranea Balbo from Benghazi. The 7th Armoured Division was dispatched to intercept the remnants of the 10th Army by moving through the desert, south of the Jebel Akhdar via Msus and Antelat as the 6th Australian Division pursued the Italians along the coast road, north of the jebel. The terrain was hard going for the British tanks and Combeforce, a flying column of wheeled vehicles, was sent ahead across the chord of the jebel.
 W
WThe First Battle of Bir el Gubi took place on 19 November 1941 near Bir el Gubi, Libya. It was one of the opening engagements of Operation Crusader and the first tank battle in North Africa where Italian armoured forces achieved a success, after their previous poor performance during Operation Compass.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Bir el Gubi was fought near Bir el Gubi, Libya, between 3 and 7 December 1941, between Italian and Commonwealth forces. It followed the First Battle of Bir el Gubi a failed Allied attempt to capture Bir el Gubi two weeks' previous. Bir el Gubi was a tactical position whose fall would have allowed the Allies to outflank the German-Italian forces in Cyrenaica. The battle was part of Operation Crusader.
 W
WThe Battle of Bir Hakeim took place at Bir Hakeim, an oasis in the Libyan desert south and west of Tobruk, during the Battle of Gazala. The 1st Free French Brigade under Général de brigade Marie-Pierre Kœnig defended the position from 26 May – 11 June against much larger Axis forces of Panzerarmee Afrika commanded by Generaloberst Erwin Rommel. The Panzerarmee captured Tobruk ten days later.
 W
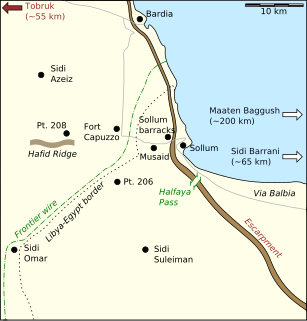
WOperation Brevity was a limited offensive conducted in mid-May 1941, during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. Conceived by the commander-in-chief of the British Middle East Command, General Archibald Wavell, Brevity was intended to be a rapid blow against weak Axis front-line forces in the Sollum–Capuzzo–Bardia area of the border between Egypt and Libya. Although the operation got off to a promising start, throwing the Axis high command into confusion, most of its early gains were lost to local counter-attacks, and with German reinforcements being rushed to the front the operation was called off after one day.
 W
WOperation Caravan was a subsidiary of Operation Agreement under which four simultaneous raids were carried out against important Axis Lines of Communication positions in September 1942.
 W
WOperation Compass was the first large British military operation of the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) during the Second World War. British, Indian, Commonwealth and Allied forces attacked Italian forces of the 10th Army in western Egypt and Cyrenaica, the eastern province of Libya, from December 1940 to February 1941.
 W
WOperation Crusader was a military operation of the Western Desert Campaign during World War II by the British Eighth Army against the Axis forces in North Africa commanded by Generalleutnant Erwin Rommel. The operation was intended to bypass Axis defences on the Egyptian–Libyan frontier, to defeat the Axis armoured forces and to relieve the 1941 Siege of Tobruk.
 W
WThe Defence of Outpost Snipe in Egypt, took place in the Second Battle of El Alamein, part of the Western Desert campaign during the Second World War. On the night of 26/27 October 1942, the 2nd Battalion of the Rifle Brigade, with thirteen 6-pounder anti-tank guns and the 239th Battery, 76th Anti-Tank Regiment, Royal Artillery, with six more 6-pounders, was ordered to occupy a desert feature known as Snipe, a small depression in the landscape 1.5 mi (2.4 km) south-west of Kidney Ridge that was suitable for an outpost. Once consolidated, it could be used as a jumping-off point for an advance by the 24th Armoured Brigade.
 W
WThe Desert Air Force (DAF), also known chronologically as Air Headquarters Western Desert, Air Headquarters Libya, the Western Desert Air Force, and the First Tactical Air Force (1TAF), was an Allied tactical air force created from No. 204 Group RAF under RAF Middle East Command in North Africa in 1941 to provide close air support to the British Eighth Army against Axis forces. Throughout the Second World War, the DAF was made up of squadrons from the Royal Air Force (RAF), the South African Air Force (SAAF), the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) and other Allied air forces.
 W
WThe Devil's gardens was the name given by Field Marshal Erwin Rommel, commander of the German Afrika Korps during the Second World War, to the defensive entanglements of land mines and barbed wire built to protect Axis defensive positions at El Alamein before the Second Battle of El Alamein in late 1942. The defences stretch from the Mediterranean coast to the Qattara Depression.
 W
WMajor-General James Thom Durrant was a highly successful South African pilot during World War II who eventually became the Director-General of the South African Air Force. In addition to commanding SAAF squadrons and wings, he also commanded RAF bomber groups. At the age of 32, he was the youngest Major-General in the Allied forces. He resigned from the SAAF as a result of the de-anglicisation policy instituted by the National Party after they took power after the 1948 general election.
 W
WThe Battle of El Agheila was a brief engagement of the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. It took place in December 1942 between Allied forces of the Eighth Army and the Axis forces of the German-Italian Panzer Army, during the long Axis withdrawal from El Alamein to Tunis. It ended with the German-Italian Panzer Army resuming its retreat towards Tunisia, where the Tunisia Campaign had begun with Operation Torch (8–16 November 1942).
 W
WThe First Battle of El Alamein was a battle of the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War, fought in Egypt between Axis forces of the Panzer Army Africa and Allied forces of the Eighth Army.
 W
WThe Second Battle of El Alamein was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa had prevented the Axis from advancing further into Egypt.
 W
WOperation Flipper was a British commando raid during the Second World War, mainly by men from No. 11 (Scottish) Commando. The operation included an attack on the headquarters of Erwin Rommel, the commander of Panzergruppe Afrika in North Africa. It was timed for the night of 17/18 November 1941, just before the start of Operation Crusader. The operation failed as Rommel had left the target house weeks earlier and all but two of the commandos who landed were killed or captured. One member of the Special Boat Section team, who had secured the beach for the commando party, also escaped.
 W
WFort Capuzzo Italian: (Ridotta Capuzzo) was a fort in the colony of Italian Libya, near the Libyan-Egyptian border, next to the Italian Frontier Wire. The Litoranea Balbo (Via Balbia) ran south from Bardia to Fort Capuzzo, 13 km (8 mi) inland, west of Sollum, then east across the Egyptian frontier to the port, over the coastal escarpment. The fort was built during Italian colonial repression of Senussi resistance in the Second Italo-Senussi War (1923–1931), as part of a barrier on the Libya-Egypt and Libya-Sudan borders.
 W
WLieutenant-General Charles Alan 'Pop' Fraser was a South African military commander. He joined the South African Army as a part-time Active Citizen Force soldier in 1934 and became a full-time Permanent Force member in 1946. He served in World War II.
 W
WThe Battle of Gazala was fought during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War, west of the port of Tobruk in Libya, from 26 May to 21 June 1942. Axis troops of the Panzerarmee Afrika consisting of German and Italian units fought the British Eighth Army composed mainly of British Commonwealth, Indian and Free French troops.
 W
WThe Siege of Giarabub in Libya, was an engagement between Commonwealth and Italian forces, during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. In the aftermath of Operazione E, the invasion of Egypt by the Italian 10th Army (9–16 September 1940), Operation Compass (9–16 December) by the Western Desert Force (WDF), the Battle of Sidi Barrani and the pursuit of the 10th Army into Cyrenaica (16 December 1940 – 9 February 1941) the fortified Italian position at the Al Jaghbub Oasis was besieged by parts of the 6th Australian Division.
 W
WThe Capture of Kufra was part of the Allied Western Desert Campaign during the Second World War. Kufra is a basin and oasis group in the Kufra District of south-eastern Cyrenaica in the Libyan Desert. In 1940, it was part of the colony of Italian Libya Libia Italiana, which was part of Africa Settentrionale Italiana (ASI), which was established in 1934.
 W
WErnest Thomas "Bob" Lilley M.M., B.E.M. was a British Army soldier. A founding member of the British Special Air Service Regiment, he formerly served with the Coldstream Guards. Lilley was one of the first four men selected by Colonel David Stirling to comprise L Detachment 1st S.A.S. in Middle East Headquarters at Cairo in 1940. He took part in many operations behind enemy lines in Libya against Italian and German forces during World War II.
 W
WThe action at Mechili was an engagement between units of the British 7th Armoured Division of the Western Desert Force and Italian forces of the 10th Army during Operation Compass.
 W
WThe Medjez-El-Bab Memorial is a Commonwealth War Graves Commission war memorial in the Medjez-el-Bab War Cemetery near Majaz al Bab, Tunisia. The memorial commemorates 2,525 Commonwealth forces members who died in Tunisia and Algeria during World War II and have no known grave.
 W
WThe Battle of Mersa Matruh was fought from 26 to 29 June 1942, following the defeat of the Eighth Army at the Battle of Gazala and was part of the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. The combatant on the Axis side was the Panzer Army Afrika (Panzerarmee Afrika, consisting of German and Italian units. The Allied forces of the Eighth Army comprised X Corps and XIII Corps. The battle developed as the Afrika Korps pursued the Eighth Army as it retreated into Egypt. Rommel intended to engage and destroy the Allied infantry formations in detail, before the British had a chance to regroup. The Axis cut off the line of retreat of X Corps and XIII Corps but was too weak to stop the British from breaking out. The fortress port of Mersa Matruh and 6,000 prisoners were captured, along with a great deal of supplies and equipment but the Eighth Army survived.
 W
WMiddle East Command, later Middle East Land Forces, was a British Army Command established prior to the Second World War in Egypt. Its primary role was to command British land forces and co-ordinate with the relevant naval and air commands to defend British interests in the Middle East and eastern Mediterranean region.
 W
WThe Italian XX Motorised Corps was an armoured formation of the Italian army. The Corps took part in the Western Desert Campaign in World War II from summer 1941 to 1943. It was also referred to as Mobile Armoured Corps.
 W
WThe Attack on Nibeiwa took place on 9 December 1940 near Nibeiwa, Egypt, when the Italian fortified camp held by the Maletti Group, the armoured force of the 10th Army, was overrun by British and Indian troops. The attack was the opening engagement of Operation Compass a British raid which, if successful, would be followed up to try to expel the Italians from Egypt. Italy had declared war on France and Britain on 10 June and in the Italian invasion of Egypt from 9–16 September 1940, the Italian 10th Army had reached Sidi Barrani and dug in to await the completion of the Via della Vittoria, an extension of the Via Balbia, being built from the frontier; the Maletti Group garrisoned a camp at Nibeiwa,12 mi (19 km) south of the port of Sidi Barrani.
 W
WThe North African campaign of the Second World War took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943. It included campaigns fought in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts and in Morocco and Algeria, as well as Tunisia.
 W
WMajor General Daniel Hermanus Pienaar was a South African World War II military commander.
 W
WMajor General William Henry Evered Poole, was a senior South African Army commander during the Second World War and later a diplomat.
 W
WThe Raid on Sidi Haneish Airfield was a military operation carried out the night of 26 July 1942. A British Special Air Service unit commanded by Major David Stirling attacked a German-held airfield in Egypt during the Western Desert Campaign of Second World War. Several Luftwaffe aircraft used to ferry supplies to the Axis forces were destroyed or damaged with machine-gun fire and explosives. Axis front line units were diverted to reinforce the garrisons in the rear vulnerable to attack.
 W
WThe Senussi Cave Railway was a 400-yard long 2 ft (610 mm) narrow gauge railway, which was built in 1941 during the Siege of Tobruk at the Senussi Cave near Tobruk, Libya.
 W
WThe Battle of Sidi Barrani (10–11 December 1940) was the opening battle of Operation Compass, the first big British attack of the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. Sidi Barrani, on the Mediterranean coast in Egypt, had been occupied by the Italian 10th Army, during the Italian invasion of Egypt (9–16 September 1940) and was attacked by British, Commonwealth and imperial troops, who re-captured the port.
 W
WOperation Skorpion from 26 to 27 May 1941, was a military operation during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. The operation was conducted by Axis forces under the command of Colonel Maximilian von Herff and British forces under Lieutenant-General William "Strafer" Gott. A counter-attack was made on British positions at Halfaya Pass in north-western Egypt, which had been captured during Operation Brevity (15–16 May). Unternehmen Skorpion was the second offensive operation commanded by Rommel in Africa.
 W
WOperation Sonnenblume was the name given to the dispatch of German troops to North Africa in February 1941, during the Second World War. The Italian 10th Army had been destroyed by the British, Commonwealth, Empire and Allied Western Desert Force attacks during Operation Compass (9 December 1940 – 9 February 1941). The first units of the new Deutsches Afrikakorps departed Naples for Africa and arrived on 11 February 1941. On 14 February, advanced units of the 5th Light Afrika Division, Aufklärungsbataillon 3 and Panzerjägerabteilung 39 arrived in Tripoli, Libya and were sent immediately to the front line east of Sirte.
 W
WThe siege of Tobruk lasted for 241 days in 1941, after Axis forces advanced through Cyrenaica from El Agheila in Operation Sonnenblume against Allied forces in Libya, during the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) of the Second World War. In late 1940, the Allies had defeated the Italian 10th Army during Operation Compass (9 December 1940 – 9 February 1941) and trapped the remnants at Beda Fomm. During early 1941, much of the Western Desert Force (WDF) was sent to the Greek and Syrian campaigns. As German troops and Italian reinforcements reached Libya, only a skeleton Allied force remained, short of equipment and supplies.
 W
WThe Axis capture of Tobruk, also known as the Fall of Tobruk and the Second Battle of Tobruk was part of the Western Desert Campaign in Libya during the Second World War. The battle was fought by Panzerarmee Afrika (Armata Corazzata Africa in Italian German–Italian military force in north Africa, which included the Afrika Korps and the British Eighth Army. The Eighth Army comprised contingents from Britain, India, South Africa and other Allied troops.
 W
WThe British capture of Tobruk was a battle fought between 21 and 22 January 1941, as part of Operation Compass, the first offensive of the Western Desert Force (WDF) in the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. After defeating the Italians in the Battle of Bardia, the 6th Australian Division and the 7th Armoured Division pressed on and made contact with the Italian garrison in Tobruk on 6 January.
 W
WThe Via della Vittoria was a military road between Bardia in Italian Libya and Sidi Barrani in western Egypt.