 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WJoseph Berchtold was an early senior Nazi Party member and a co-founder of both the Sturmabteilung (SA) and Schutzstaffel (SS).
 W
WJohannes Block was a German general in the Wehrmacht during World War II who held commands at division and corps level. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves. Block was killed on 26 January 1945 near Kielce, Poland during the Soviet Vistula-Oder Offensive.
 W
WHermann Alois Boehm was a German eugenicist, doctor, professor of "racial hygiene" and during the Nazi era. Boehm became a member of the NSDAP on 24 March 1925, with member number 126.
 W
WSS-Oberführer Ernst Boepple was a Nazi official and SS officer, serving as deputy to Josef Bühler in occupied Poland during World War II and the Holocaust, who was executed for war crimes.
 W
WWilhelm Brückner was Adolf Hitler's chief adjutant until October 1940. Thereafter, Brückner joined the Heer (army), becoming an Oberst (colonel) by war's end. He died in August 1954 in Herbsdorf, Upper Bavaria.
 W
WWalter Buch was a German jurist as well as an SA and SS official during the Nazi era. He was Martin Bormann's father-in-law. As head of the Supreme Party Court, he was an important Party official. However due to his insistence on prosecuting major Party figures on moral issues, he alienated Adolf Hitler and his power and influence gradually diminished into insignificance. After the end of the Second World War in Europe, Buch was classified as a major regime functionary or "Hauptschuldiger" in the denazification proceedings in 1948. On 12 September of 1949, he committed suicide.
 W
WFranz Xaver Dorsch was a German civil engineer who became the chief engineer of the Organisation Todt (OT), a civil and military engineering group in Nazi Germany that was responsible for a huge range of engineering projects at home and in the territories occupied by the Germans during the Second World War. He played a leading role in many of the Third Reich's biggest engineering projects, including the construction of the Siegfried Line (Westwall), the Atlantic Wall and numerous other fortifications in Germany and occupied Europe. Following the war, he founded the Dorsch Consult consulting engineering company in Wiesbaden.
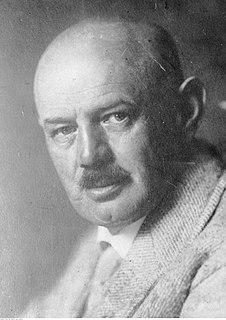 W
WDietrich Eckart was a German anti-Semitic völkisch poet, playwright, journalist, publicist, and political activist who was one of the founders of the German Workers' Party, the predecessor to the Nazi Party. Eckart was a key influence on Adolf Hitler in the early years of the Party, the original publisher of the party newspaper, the Völkischer Beobachter, and the lyricist of the first party anthem, Sturmlied. He was a participant in the failed Beer Hall Putsch in 1923 and died on 26 December of that year, shortly after his release from Landsberg Prison, from a heart attack.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WGottfried Feder was a German civil engineer, a self-taught economist, and one of the early key members of the Nazi Party and its economic theoretician. It was one of his lectures, delivered in 1919, that drew Adolf Hitler into the party.
 W
WKarl Fiehler was a German Nazi Party (NSDAP) official and Mayor of Munich from 1933 until 1945. He was an early member of the Nazi Party having joined in 1920. In 1933, he became a Reichsleiter in the party and was a member of the Reichstag. In March of 1933, he was appointed Mayor of Munich and held that post until the end of World War II in Europe. During his time as mayor, Fiehler was zealously anti-Semitic and saw to it that the Jewish population of the city was persecuted. After the war in January 1949, Fiehler was sentenced to two years in a labour camp, but the sentence was suspended given the previous three-and-a-half years of detention he had already served.
 W
WHans Michael Frank was a German politician and lawyer who served as head of the General Government in Nazi-occupied Poland during the Second World War.
 W
WWilhelm Frick was a prominent German politician of the Nazi Party (NSDAP), who served as Reich Minister of the Interior in Adolf Hitler's cabinet from 1933 to 1943 and as the last governor of the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia.
 W
WHermann Wilhelm Göring was a German politician, military leader and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which ruled Germany from 1933 to 1945.
 W
WUlrich Graf was an early member of the Nazi Party and one of Adolf Hitler's inner circle. In 1923, he served in a bodyguard unit for Hitler and in 1936 was elected to the Reichstag. After the war ended, Graf was sentenced to five years of hard labor and died in 1950.
 W
WJakob Grimminger was a German Nazi Party and Schutzstaffel (SS) member. As the official standard-bearer of the Blutfahne, an iconic flag of the Nazi movement that had been bloodied during the Munich Putsch in 1923, Grimminger often appeared nearby Hitler in photographs and during ceremonies.
 W
WErnst Franz Sedgwick Hanfstaengl was a German-American businessman and close friend of Adolf Hitler. He eventually fell out of favour with Hitler and defected from Nazi Germany to the United States. He later worked for Franklin D. Roosevelt and was once engaged to the author Djuna Barnes.
 W
WFranz Hayler was a German self-employed salesman who rose during the Third Reich to become State Secretary in the Reich Ministry of Economics and deputy to the Reich Economics Minister. He was a member of the NSDAP and the SS.
 W
WErhard Heiden was an early member of the Nazi Party and the third commander of the Schutzstaffel (SS), the paramilitary wing of the Sturmabteilung. He was appointed head of the SS, an elite subsection of the SA in 1927. At that time the SS numbered less than a thousand men and Heiden found it difficult to cope under the much larger SA. Heiden was not a success in the post, and SS membership dropped significantly under his leadership. He was dismissed from his post in 1929, officially for "family reasons". He was arrested after the Nazis came to power in 1933 and executed that same year.
 W
WEdmund Heines was a German Nazi politician and Deputy to Ernst Röhm, the Stabschef of the Sturmabteilung (SA). Heines was one of the earliest members of the Nazi Party and a leading member of the SA in Munich, participating in the Beer Hall Putsch and becoming a notorious enforcer of the party. He held several high-ranking positions in the Nazi administration until he was executed during the Night of the Long Knives in June 1934.
 W
WRudolf Walter Richard Hess was a German politician and a leading member of the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany. Appointed Deputy Führer to Adolf Hitler in 1933, Hess held that position until 1941, when he flew solo to Scotland in an attempt to negotiate peace with the United Kingdom during World War II. He was taken prisoner and eventually convicted of crimes against peace. He was still serving his life sentence at the time of his suicide in 1987.
 W
WWalther Hewel was a German diplomat before and during World War II, an early and active member of the Nazi Party, and one of German dictator Adolf Hitler's personal friends.
 W
WGebhard Ludwig Himmler was a German Nazi functionary, mechanical engineer and older brother of Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler.
 W
WHeinrich Luitpold Himmler was Reichsführer of the Schutzstaffel, and a leading member of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of the Holocaust.
 W
WAdolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Germany from 1933 to 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and then assuming the title of Führer und Reichskanzler in 1934. During his dictatorship, he initiated World War II in Europe by invading Poland on 1 September 1939. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust, the genocide of about six million Jews and millions of other victims.
 W
WAdolf Hühnlein was a German soldier and Nazi Party (NSDAP) official. He was the Korpsführer of the National Socialist Motor Corps (NSKK) from 1931 until his death in 1942.
 W
WKarl Kaufmann was a German politician who served as a Nazi Party Gauleiter from 1925 to 1945 and as the Reichsstatthalter of Hamburg from 1933 to 1945.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WHans Krüger was a former member of the NSDAP party and other Nazi organizations who served as an SS judge in occupied Poland during the Second World War. After the war he became West German politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU). He served as Federal Minister for Displaced Persons, Refugees and War Victims of the Federal Republic of Germany from 17 October 1963 to 7 February 1964, in the First Cabinet of Chancellor Ludwig Erhard, as President of the Federation of Expellees from 1959 to 1964, and as a Member of Parliament from 1957 to 1965. He stepped down from cabinet amid controversy about his war-time background.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WErich Friedrich Wilhelm Ludendorff was a German general, politician and military theorist. He achieved fame during World War I for his central role in the German victories at Liège and Tannenberg in 1914. Following his appointment as First Quartermaster-general of the Imperial Army's Great General Staff in 1916, he became the chief policymaker in a de facto military dictatorship that dominated Germany for the rest of the war. After Germany's defeat, he contributed significantly to the Nazis' rise to power.
 W
WEmil Maurice /e.mil mo.ʁis/ was an early member of the National Socialist German Workers' Party and a founding member of the Schutzstaffel (SS). He was Hitler's first personal chauffeur, and was one of the few persons of mixed Jewish and ethnic German ancestry to serve in the SS, being declared an honorary Aryan by Adolf Hitler in 1935.
 W
WJosef Albert Meisinger, also known as the "Butcher of Warsaw", was a SS functionary in Nazi Germany. He held a position in the Gestapo and was a member of the Nazi Party. During the early phases of World War II Meisinger served as commander of Einsatzgruppe IV on Poland. From 1941 to 1945 he worked as liaison for the Gestapo at the German embassy in Tokyo. He was arrested in Japan in 1945, convicted of war crimes and was executed in Warsaw, Poland.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WTheodor Oberländer was an Ostforschung scientist and Nazi German politician who after the Second World War served as Federal Minister for Displaced Persons, Refugees and Victims of War in West Germany from 1953 to 1960, and as a Member of the Bundestag from 1953 to 1961 and from 1963 to 1965.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WHeinz Pernet was a German military officer and Erich Ludendorff's stepson. He was a top figure in the Beer Hall Putsch of November 1923. He was among the nine men tried and convicted along with Adolf Hitler and Erich Ludendorff in 1924. He later became an SA-Brigadeführer.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WErnst Julius Günther Röhm was a German military officer and an early member of the Nazi Party. As one of the members of its predecessor, the German Workers' Party, he was a close friend and early ally of Adolf Hitler and a co-founder of the Sturmabteilung, the Nazi Party's militia, and later was its commander. By 1934, the German Army feared the SA's influence and Hitler had come to see Röhm as a potential rival, so he was executed during the Night of the Long Knives.
 W
WAlfred Ernst Rosenberg was a Baltic German Nazi theorist and ideologue. Rosenberg was first introduced to Adolf Hitler by Dietrich Eckart and held several important posts in the Nazi government. He was the head of the NSDAP Office of Foreign Affairs during the entire rule of Nazi Germany (1933–1945), and led Amt Rosenberg, an official Nazi body for cultural policy and surveillance, between 1934 and 1945. During World War II, Rosenberg was the head of the Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories (1941–1945). After the war, he was convicted of crimes against peace; planning, initiating and waging wars of aggression; war crimes; and crimes against humanity at the Nuremberg trials in 1946. He was sentenced to death and executed on 16 October 1946.
 W
WLudwig Maximilian Erwin von Scheubner-Richter was a German political activist and an influential early member of the Nazi Party.
 W
WJulius Schreck was an early senior Nazi official and close confidant of Adolf Hitler.
 W
WFranz Xaver Schwarz was a German Schutzstaffel (SS) functionary and politician in Nazi Germany. He served as Reichsschatzmeister of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) during most of the party's existence.
 W
WThe Beer Hall Putsch, also known as the Munich Putsch, was a failed coup d'état by Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff and other Kampfbund leaders in Munich, Bavaria, on 8–9 November 1923, during the Weimar Republic. Approximately two thousand Nazis marched on the Feldherrnhalle, in the city centre, but were confronted by a police cordon, which resulted in the deaths of 16 Nazi Party members and four police officers.
 W
WGregor Strasser was an early prominent German Nazi official and politician who was murdered during the Night of the Long Knives in 1934. Born in 1892 in Bavaria, Strasser served in World War I in an artillery regiment, rising to the rank of first lieutenant. He joined the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in 1920 and quickly became an influential and important figure. In 1923, he took part in the abortive Beer Hall Putsch in Munich and was imprisoned, but released early for political reasons. Strasser joined a revived NSDAP in 1925 and once again established himself as a powerful and dominant member, hugely increasing the party's membership and reputation in northern Germany. Personal and political conflicts with Adolf Hitler led to his death in 1934 during the Night of the Long Knives.
 W
WJulius Streicher was a member of the Nazi Party, the Gauleiter of Franconia and a member of the Reichstag, the national legislature. He was the founder and publisher of the virulently antisemitic newspaper Der Stürmer, which became a central element of the Nazi propaganda machine. The publishing firm was financially very successful and made Streicher a multi-millionaire.
 W
WJosef Antonius Heinrich Terboven was a Nazi leader, best known as the Reichskommissar for Norway during the German occupation of Norway and the Quisling regime.
 W
WAdolf Wagner was a German soldier and high-ranking Nazi Party official born in Algrange, Alsace-Lorraine.
 W
WFriedrich Weber, Dr. was an instructor in veterinary medicine at the University of Munich. In World War I he served in the Royal Bavarian 1st Heavy Cavalry Regiment "Prince Karl of Bavaria". He was the leader of the Oberland League and ranked alongside Adolf Hitler, Erich Ludendorff, Ernst Röhm and Hermann Kriebel as one of the chief conspirators of the Beer Hall Putsch in November 1923. He was convicted along with Hitler in 1925 but continued to head the Oberland League until 1929.
 W
WWilhelm Weiss was, in the time of the Third Reich, an SA-Obergruppenführer as well as editor-in-chief of the NSDAP's official newspaper, the Völkischer Beobachter