 W
WThe AAM-A-1 Firebird was an early American air-to-air missile, developed by the Ryan Aeronautical Company. The first air-to-air missile program developed for the United States Air Force, the Firebird was extensively tested in the late 1940s; although it proved successful in testing, it was soon obsolete due to the rapid advances in aircraft and missile technology at the time and did not enter production.
 W
WThe AAM-N-4 Oriole was an early American air-to-air missile, developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company for the United States Navy. Designed for launch from carrier-based aircraft, the missile programme was cancelled before flight testing began, and the missiles produced were utilized as test vehicles.
 W
WThe AAM-N-5 Meteor was an early American air-to-air missile, developed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Bell Aircraft for the United States Navy. Initially, both air-launched and ship-launched versions were considered. Versions designed for launch from carrier-based aircraft proceeded to the flight testing stage before the project was cancelled.
 W
WThe AAM-N-10 Eagle was a long-range air-to-air missile developed by the Bendix Corporation for use by the United States Navy. Intended for carriage by the Douglas F6D Missileer fleet defense fighter, the Eagle program was cancelled before testing could begin, but the lessons learned were used in the development of the AIM-54 Phoenix missile.
 W
WIn 1962, the U.S. Navy issued a requirement for a long-range high-precision air-to-surface missile. The missile, named the AGM-53A Condor, was to use a television guidance system with a data link to the launching aircraft similar to the system of the then projected AGM-62 Walleye.
 W
WThe AGM-76 Falcon was an air-to-surface anti-radiation missile developed by the United States Air Force during the Vietnam War. Intended as a conversion using off-the-shelf parts, it did not go into operational service.
 W
WThe AGM-83 Bulldog was a missile produced by the United States.
 W
WThe AGM-131 SRAM II was a nuclear air-to-surface missile intended as a replacement for the AGM-69 SRAM. The solid-fueled missile was to be dropped from a B-1B Lancer, carry the W89 warhead and have a range of 400km. However, the program was canceled by President George H.W. Bush for geopolitical reasons just as the first flight-test missile was delivered.
 W
WThe AGM-136A Tacit Rainbow was a United States military anti-radiation missile program run from 1982 to 1991.
 W
WThe AGR-14 ZAP was an air-to-surface unguided rocket developed by the United States Navy in the late 1960s. Intended for use in the suppression of enemy air defenses role, the rocket reached the flight-testing stage before being cancelled.
 W
WThe Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control system intended to arm the Mach 3 XF-108 Rapier interceptor aircraft and, after its cancellation, the YF-12A. It was never used operationally, but was a direct predecessor of the AIM-54 Phoenix.
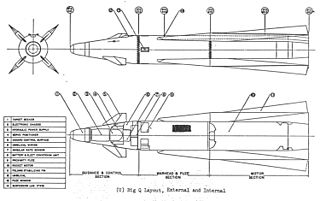 W
WThe AIM-68 is an American air-to-air missile design. It never entered production.
 W
WThe AIM-95 Agile was an air-to-air missile developed by the United States. It was developed by the US Navy to equip the F-14 Tomcat, replacing the AIM-9 Sidewinder. Around the same time, the US Air Force was designing the AIM-82 to equip their F-15 Eagle, and later dropped their efforts to join the Agile program. In the end, newer versions of Sidewinder would close the performance gap so much that the Agile program was cancelled.
 W
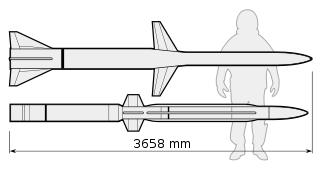
WThe AIM-97 Seekbat or XAIM-97A Seek Bat was a long-range air-to-air missile developed by the United States. It was intended to counter the perceived capabilities of the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25 and proposed to arm both the F-15 Eagle and F-4 Phantom, the missile ultimately never entered service.
 W
WThe AIM-152 AAAM was a long-range air-to-air missile developed by the United States. The program went through a protracted development stage but was never adopted by the United States Navy, due to the ending of the Cold War and the reduction in threat of its perceived primary target, Soviet supersonic bombers. Development was cancelled in 1992.
 W
WThe AQM-127 Supersonic Low-Altitude Target (SLAT) was a target drone developed during the 1980s by Martin Marietta for use by the United States Navy. Derived from Martin Marietta's work on the cancelled ASALM missile, SLAT proved to have severe difficulties in flight testing, and the project was cancelled during 1991.
 W
WThe Ares was a proposed intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) derived from the Titan II missile. It was a single-stage rocket with a high-performance engine to increase the rocket's specific impulse. Both Aerojet and Rocketdyne carried out engine design studies for the project, but Ares was ultimately cancelled in favour of solid-fuel ICBMs, which were safer to store and could be launched with much less notice. The Ares missile series was canceled due to the inconvenience of using liquid fuel. Some reasons included extensive protection from corrosion within the silos, as well as the liquid fuel propellant, ideally used in the proposed Ares missiles, being more expensive to maintain. Thus making the transition to use the Minuteman II missiles, that ran on solid fuel, easier because solid fuel was more reliable for sand was less expensive than previous projects. Hence the cancellation of the Ares missile series.
 W
WThe Advanced Strategic Air-Launched Missile (ASALM) was a medium-range strategic missile program, developed in the late 1970s for the United States Air Force. Intended for use in both the air-to-surface and anti-AWACS roles, the missile's development reached the stage of propulsion-system tests before being cancelled in 1980.
 W
WThe ASM-135 ASAT is an air-launched anti-satellite multistage missile that was developed by Ling-Temco-Vought's LTV Aerospace division. The ASM-135 was carried exclusively by United States Air Force (USAF) F-15 Eagle fighter aircraft.
 W
WThe ASM-N-6 Omar was a short-range air-to-surface missile developed for and evaluated by the United States Navy in the early 1950s. Intended to use existing unguided rockets as a basis and using a novel guidance system involving optical beam-riding, the program was unable to resolve difficulties with the guidance system and was cancelled without entering service.
 W
WThe AUM-N-6 Puffin, also known as Kingfisher F and AUM-6, was an anti-ship and anti-submarine missile developed for use by the United States Navy in the late 1940s. Pulsejet-powered and intended to allow an aircraft to launch a torpedo or bomb from stand-off range, it was flight-tested but failed to enter operational service.
 W
WThe Brazo missile was an American project, intended to produce an anti-radiation missile for air-to-air use. Developed by Hughes Aircraft and based on the AIM-7 Sparrow air-to-air missile, the Brazo underwent a series of successful test firings; however, the program was terminated at the end of its test program.
 W
WCommon Missile was an intercontinental ballistic missile project, developed to satisfy U.S. Navy and U.S. Air Force operational system requirements for both SLBM and silo-launched ICBM, defined in the 1978 commonality study.
 W
WThe FGR-17 Viper was an American one-man disposable antitank rocket, which was slated in the 1980s to be the replacement for the M72 LAW, but was canceled shortly after production began because of cost overruns and concerns about safety and capability.
 W
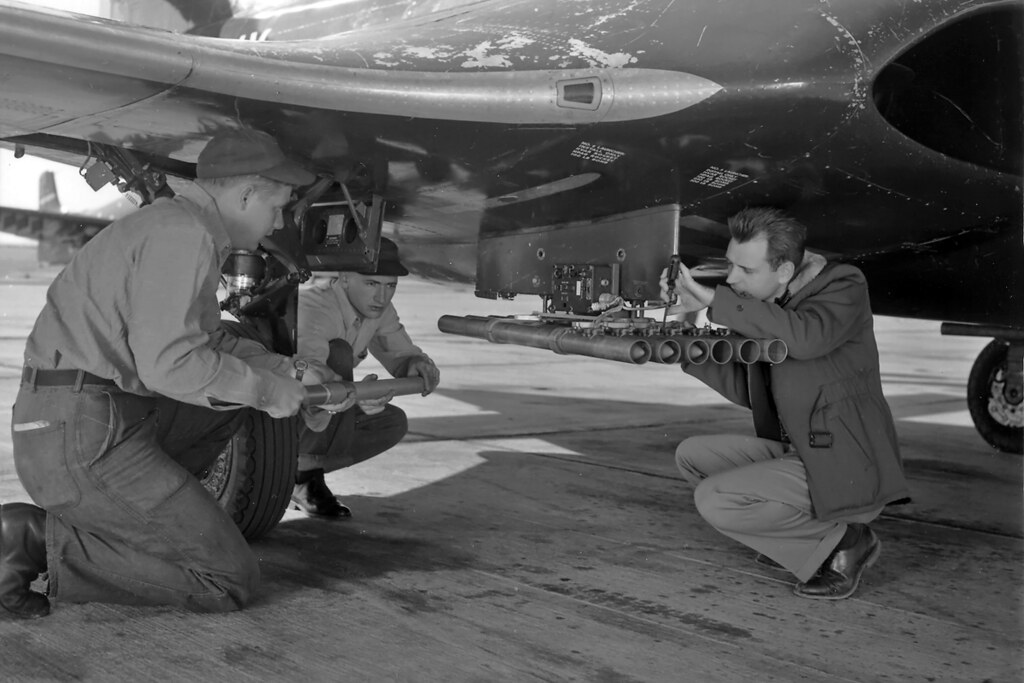
WThe Douglas GAM-87 Skybolt was an air-launched ballistic missile (ALBM) developed by the United States during the late 1950s. The basic concept was to allow US strategic bombers to launch their weapons from well outside the range of Soviet defenses, as much as 1,000 miles (1,600 km) from their targets. To do this in an air-launched form, a lightweight thermonuclear warhead was needed. Initially, the W47 from the Polaris missile was selected, but it was later replaced by the W59 from the Minuteman missile.
 W
WThe Gimlet was an unguided air-to-air and air-to-surface rocket developed by the United States Navy during the early 1950s. Although it proved successful in testing and was ordered into large-scale production, the arrival of the guided missile as a practical and reliable weapon resulted in the cancellation of the Gimlet rocket in 1957.
 W
WGlomb, from "glide bomb", was a project undertaken by the United States Navy during World War II to develop an unmanned aircraft for delivering bombs to high-value, well-protected targets without risk to aircrew. The project proceeded through the war, producing several prototype aircraft, but technical limitations meant no Glombs saw operational service and the program was cancelled at the end of the war.
 W
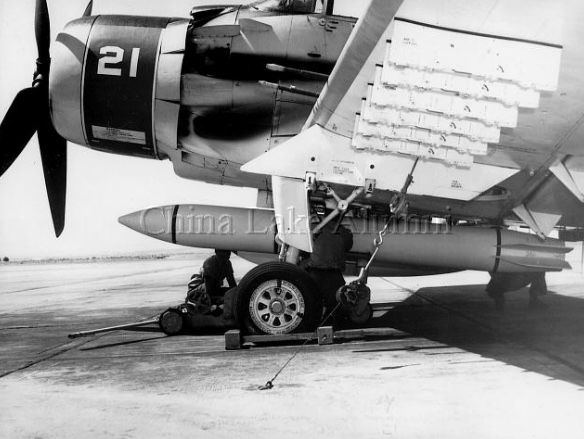
WHave Dash was a program conducted by the United States Air Force for the development of a stealthy air-to-air missile. Although the Have Dash II missile appears to have been flight tested, the results of the project remain classified and no production is believed to have been undertaken.
 W
WThe Hopi was an air-to-surface missile developed by the United States Navy's Naval Ordnance Test Station. Intended to provide a medium-range nuclear capability for carrier aircraft, the missile reached the flight test stage during 1958, but the project was cancelled following testing and no production was undertaken.
 W
WJaguar was a three-stage sounding rocket developed by the United States Air Force in the early 1960s. Designed for air launch to allow soundings from remote areas without infrastructure, it was only launched twice before the project was abandoned.
 W
WThe JB-4, also known as MX-607, was an early American air-to-surface missile developed by the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. Using television/radio-command guidance, the JB-4 reached the flight-testing stage before being cancelled at the end of the war.
 W
WThe KA2N Gorgon IIA – also designated KU2N, CTV-4, and CTV-N-4 – was an air-to-air missile developed by the United States Navy near the end of World War II. Proving a failure in its designed role, it was repurposed as an experimental testbed for missile technology.
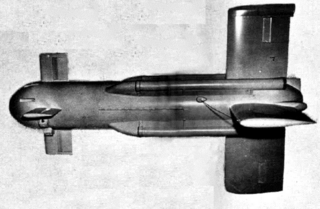 W
WThe Little Joe, also known by the United States Navy designation KAN, was an early American ship-based, short-range surface-to-air missile, the development of which was initiated in 1945 as a response to the Kamikaze tactics used by the Japanese. Although the missile was successfully tested, the end of World War II removed the requirement for the missile, and the project was abandoned in 1946.
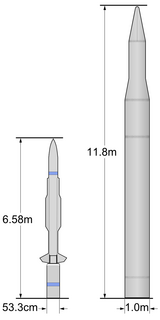 W
WThe Kinetic Energy Interceptor (KEI) was a planned U.S. missile defense program whose goal was to design, develop, and deploy kinetic energy-based, mobile, ground and sea-launched missiles that could intercept and destroy enemy ballistic missiles during their boost, ascent and midcourse phases of flight. The KEI consisted of the Interceptor Component, the Mobile Launcher Component, and the Command, Control, Battle Management, and Communications (C2BMC) component.
 W
WThe Low-Cost Aerial Target, or LOCAT, was designed as an inexpensive target rocket for use by the United States Army during the late 1960s. The missile was tested by the U.S. Army, but failed to win a production contract.
 W
WThe MGM-134A Midgetman, also known as the Small Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (SICBM), was an intercontinental ballistic missile developed by the United States Air Force. The system was mobile and could be set up rapidly, allowing it to move to a new firing location after learning of an enemy missile launch. To attack the weapon, the enemy would have to blanket the area around its last known location with multiple warheads, using up a large percentage of their force for limited gains and no guarantee that all of the missiles would be destroyed. In such a scenario, the U.S. would retain enough of their forces for a successful counterstrike, thereby maintaining a deterrence.
 W
WThe MGM-166 LOSAT was a United States anti-tank missile system designed by Lockheed Martin to defeat tanks and other individual targets. Instead of using a High Explosive Anti-Tank warhead like other anti-tank missiles, the LOSAT employed a solid steel kinetic energy penetrator to punch through armor. The LOSAT is fairly light; it was designed to be mounted onto a Humvee while allowing the vehicle to remain air-portable. LOSAT eventually emerged on an extended-length heavy-duty Humvee with a hard-top containing four KEMs used by special operations. Although LOSAT never "officially" entered service, it was used for the smaller Compact Kinetic Energy Missile.
 W
WThe General Dynamics Mauler was a self-propelled anti-aircraft missile system designed to a late 1950s US Army requirement for a system to combat low-flying high-performance tactical fighters and short-range ballistic missiles.
 W
WThe NOTS-EV-2 Caleb, also known as NOTS-500, Hi-Hoe and SIP was an expendable launch system, which was later used as a sounding rocket and prototype anti-satellite weapon. It was developed by the United States Navy's Naval Ordnance Test Station (NOTS) as a follow-up to the NOTS-EV-1 Pilot, which had been abandoned following ten launches officially classified as failed missions. Two were launched in July and October 1960, before the cancellation of the project. Following cancellation, two leftover Calebs were used in the Satellite Interceptor Program (SIP), while three more were used as sounding rockets, under the designation Hi-Hoe. These derivatives flew until July 1962, when the Hi-Hoe made its final flight.
 W
WProgram 437 was the second anti-satellite weapons program of the U.S. military. The US anti-satellite weapons program began development in the early 1960s and was officially discontinued on 1 April 1975. Program 437 was approved for development by U.S. Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara on November 20, 1962, after a series of tests involving high altitude nuclear explosions. The program's facilities were located on Johnston Island, an isolated island in the north central Pacific Ocean.
 W
WProject Wizard was a Cold War-era anti-ballistic missile system to defend against short and medium-range threats of the V-2 rocket type. It was contracted by the US Army Air Force in March 1946 with the University of Michigan's Aeronautical Research Center (MARC). A similar effort, Project Thumper, started at General Electric.
 W
WPye Wacket was the codename for an experimental lenticular-form air-to-air missile developed by the Convair Division of the General Dynamics Corporation in 1957. Intended as a defensive missile for the B-70 Valkyrie Mach 3 bomber, the program saw extensive wind-tunnel testing and seemed promising; however the cancellation of the B-70 removed the requirement for the missile, and the project was cancelled.
 W
WThe RGM-59 Taurus was an American project, conducted by the United States Navy, that was intended to develop a surface-to-surface missile for use as a fire support weapon during amphibious landings, replacing heavy-caliber naval guns. Developed during the early 1960s, the project was cancelled before any hardware development was undertaken.
 W
WTyphon was a missile system developed by the United States Navy in the late 1950s, intended to serve as an integrated air-defense system for Navy fleets. Consisting of the SAM-N-8 Typhon LR, later designated RIM-50A, and the SAM-N-9 Typhon MR, later RIM-55A, paired with the AN/SPG-59 radar system, the cost and expense of the Typhon system led to it being cancelled in favor of the Standard Missile program.
 W
WBoeing's Ground-to-Air Pilotless Aircraft (GAPA) was a short-range anti-aircraft missile (SAM) developed in the late 1940s by the US Army Air Force, and then the US Air Force after 1948. It was given the reference number SAM-A-1, the first Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) in the 1947 tri-service designation system. By 1950 over 100 test rockets had been launched using a variety of configurations and power plants, with one launch in 1949 setting the altitude record for a ramjet powered vehicle at 59,000 ft (18,000 m).
 W
WSAM-N-8 Zeus, also known as Zeus I, was a project by the Naval Ordnance Laboratory of the United States Navy to develop a guided anti-aircraft artillery shell for launch from 8-inch (200 mm) guns. Tested in the late 1940s, it was overtaken by advances in guided missile technology.
 W
WSentinel was a proposed US Army anti-ballistic missile (ABM) system designed to provide a light layer of protection over the entire United States, able to defend against small ICBM strikes like those expected from China, or accidental launches from the USSR or other states. The system would have seventeen bases, each centered on its Missile Site Radar (MSR) and a computerized command center buried below it. The system was supported by a string of five long-range Perimeter Acquisition Radars (PAR) spread across the US/Canada border area and another in Alaska. The primary weapon was the long-range Spartan missile, with short range Sprint missiles providing additional protection near US ICBM fields and PAR sites. The system would initially have a total of 480 Spartan and 192 Sprint missiles.
 W
WSentry, known for most of its lifetime as LoADS for Low Altitude Defense System, was a short-range anti-ballistic missile (ABM) design made by the US Army during the 1970s. It was proposed as a defensive weapon that would be used in concert with the MX missile, a US Air Force ICBM that was under development.
 W
WSky Scorcher was a nuclear-armed air-to-air missile proposed to the United States Air Force in the 1950s. Intended for use as a weapon for the disruption of enemy bomber formations, it failed to find favor among Air Force planners and did not undergo development.
 W
WThe Sprint was a two-stage, solid-fuel anti-ballistic missile (ABM), armed with a W66 enhanced-radiation thermonuclear warhead used by the United States Army. It was designed to intercept incoming reentry vehicles (RV) after they had descended below an altitude of about 60 kilometers, where the thickening air stripped away any decoys or radar reflectors and exposed the RV to observation by radar. As the RV would be traveling at about 5 miles (8.0 km) per second, Sprint had to have phenomenal performance to achieve an interception in the few seconds before the RV reached its target.
 W
WThe XSSM-A-5 Boojum, also known by the project number MX-775B, was a supersonic cruise missile developed by the Northrop Corporation for the United States Air Force in the late 1940s. Intended to deliver a nuclear warhead over intercontinental range, it was determined to be too ambitious a project given technical difficulties with the SM-62 Snark which it was to follow on from, and was canceled in 1951.
 W
WThe XSSM-A-23 Dart was an anti-tank guided missile developed for the United States Army in the 1950s. After protracted development, the missile, similar in design to the French SS.10, was cancelled in favor of purchasing the SS.11 missile.
 W
WThe Supersonic Low Altitude Missile or SLAM was a U.S. Air Force nuclear weapons project conceived around 1955, and cancelled in 1964. SLAMs were conceived of as unmanned nuclear-powered ramjets capable of delivering thermonuclear warheads deep into enemy territory. The development of ICBMs in the 1950s rendered the concept of SLAMs obsolete. Advances in defensive ground radar also made the stratagem of low-altitude evasion ineffective. Although it never proceeded beyond the initial design and testing phase before being declared obsolete, the design contained several radical innovations as a nuclear delivery system.
 W
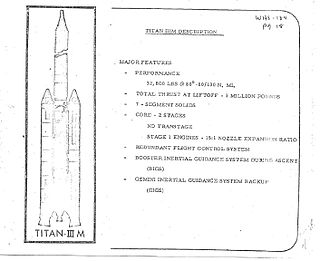
WThe Titan IIIM was a planned American expendable launch system, intended to launch the Manned Orbiting Laboratory and other payloads. Development was cancelled in 1969. The projected UA1207 solid booster rockets were eventually used on the Titan IV.
 W
WThe UUM-125 Sea Lance, known early in development as the Common ASW Standoff Weapon, was to be an American standoff anti-submarine missile, initially intended to carry a W89 thermonuclear warhead. It was conceived in 1980 as a successor to both the UUM-44 SUBROC and RUR-5 ASROC anti-submarine missiles. The Sea Lance was to be available in two versions, known as UUM-125A and RUM-125A. The former would be a submarine-launched version, the latter surface-launched. It was cancelled in 1990 as its importance was obviated by the collapse of the Soviet Union.
 W
WThe Convair XGAM-71 Buck Duck was a decoy missile that was developed by Convair in the late 1950s. It was intended to have the same radar signature as the Strategic Air Command's B-36 bomber, thereby allowing it to disrupt the enemy's air defenses and dilute their effort to shoot down an incoming bomber fleet.