 W
WThe No.1 class auxiliary patrol boat was a class of patrol boat of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II. 280 vessels were planned under the Maru Sen Programme, however, only 27 vessels were completed before the end of the war.
 W
WThe No.1 class auxiliary submarine chaser was a class of submarine chasers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II. 200 vessels were built under the Maru Kyū Programme and the Maru Sen Programme.
 W
WThe No. 1-class submarine chaser was a class of submarine chasers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II. Three vessels were built in 1933-36 under the Maru 1 Programme and the Maru 2 Programme. They have two sub classes; this article handles them collectively.
 W
WThe No.1-class landing ship was a class of amphibious assault ships of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during and after World War II. The IJN also called them 1st class transporter .
 W
WThe No. 1-class patrol boat was a class of patrol boats of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II. 2 vessels were converted from Minekaze-class destroyers in 1940.
 W
WThe No.4 class submarine chaser was a class of submarine chasers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during and after World War II. Nine vessels were built between 1937 and 1939 under the Maru 3 Programme.
 W
WThe No.13 class submarine chaser were a class of submarine chasers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during and after World War II; there were three sub classes, however the IJN's official document calls all of them the No.13 class.
 W
WThe No. 31-class patrol boats were a class of patrol boats of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II. 9 vessels were converted from Momi-class destroyers and 1 vessel was converted from a Wakatake-class destroyer in 1940.
 W
WThe No.101-class landing ships were a class of amphibious assault ships of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) and Imperial Japanese Army (IJA), serving during and after World War II. The No.101 class ships were powered by diesel engines, while the similar No.103-class landing ships were powered by a steam turbine engine. The IJN called them 2nd class transporter . The No.103 class included the IJA's SB craft variant. This article handles them collectively.
 W
WThe No.251 class auxiliary submarine chaser was a class of submarine chasers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II. 3 vessels were built in 1936 – 1939 under the Maru 2 Programme. They have two sub classes, this article handles them collectively.
 W
WAkashi was a Japanese repair ship, serving during World War II. She was the only specifically designed repair ship operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. The navy based her design on the US Navy's USS Medusa.
 W
WThe Ashizuri-class combat support ship was a class of two support ships of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II.
 W
WChōgei , was the second and final vessel of the Jingei-class submarine tenders operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy, from the 1920s through World War II. Along with her sister ship Jingei, she was the first purpose-built submarine tender in the Imperial Japanese Navy.
 W
WEtorofu was the lead ship of her class of fourteen ships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.
 W
WSS Fatshan was a passenger ferry steamer which sank in stormy seas off Lantau Island during Typhoon Rose resulting in the loss of 88 lives.
 W
WFuji (富士) was the lead ship of the Fuji class of pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy by the British firm of Thames Iron Works in the late 1890s. The ship participated in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, including the Battle of Port Arthur on the second day of the war with her sister Yashima. Fuji fought in the Battles of the Yellow Sea and Tsushima and was lightly damaged in the latter action. The ship was reclassified as a coastal defence ship in 1910 and served as a training ship for the rest of her career. She was hulked in 1922 and finally broken up for scrap in 1948.
 W
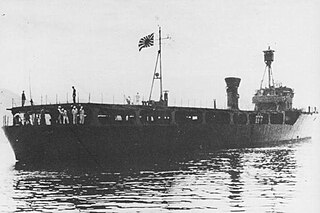
WHachijo was one of four Shimushu-class escort ships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.
 W
WThe Hakachi (波勝) was a bomb target ship of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) serving during the Second World War, the only ship of her class.
 W
WHashidate was the lead vessel in the Hashidate-class gunboats in the Imperial Japanese Navy, that operated in China during the 1940s.
 W
WThe Hashima-class cable layers were the only class of purpose-built cable layers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II. Four vessels were built in 1939–41 under the Maru 4 Programme.
 W
WThe Hayasui was a Japanese fleet oiler of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II.
 W
WHeian Maru (平安丸) was a Japanese ocean liner launched in 1930 and operated primarily on the NYK line's trans-Pacific service between Yokohama and Seattle. Shortly before the outbreak of the Pacific War, it was requisitioned by the Imperial Japanese Navy and converted to use as an auxiliary submarine tender. In 1944 it was sunk by American aircraft at Chuuk Lagoon during Operation Hailstorm. Its submerged hulk – the largest of Chuuk's "Ghost Fleet" – remains a popular scuba diving destination.
 W
WThe Hiburi-class escort ship was a sub-class of the Mikura-class escort ships of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during and after World War II.
 W
WThe Hikawa Maru-class ocean liner was a class of ocean liners of Japan, serving during the 1930s, and after World War II.
 W
WThe Hōkoku Maru-class ocean liner was a class of ocean liners of Japan, serving during 1940 and World War II.
 W
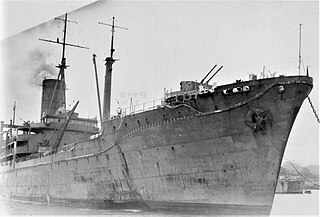
WThe Italian auxiliary cruiser Ramb II was a pre-war banana boat built at Monfalcone by the CRDA in 1937. She briefly served as an auxiliary cruiser with Regia Marina early in World War II before becoming an auxiliary transport with the Imperial Japanese Navy later in her career.
 W
WIrako (伊良湖) was a Japanese food supply ship that served during the Second World War. Constructed for the transport of food-stuffs, Irako was eventually commissioned for other roles, including troop transport, munitions transport, and Pacific survey missions. The crew of Irako is honored, along with many other seamen, in Tokyo, Japan.
 W
WIshigaki (石垣) was one of four Shimushu-class escort ships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.
 W
WJingei , was the lead vessel of the Jingei-class submarine tenders operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy, from the 1920s through World War II. She was the first purpose-built submarine tender in the Imperial Japanese Navy.
 W
WThe Jingei-class submarine tenders were a class of submarine tenders of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), and served from the 1920s through World War II. Two vessels of this class were built between 1922 and 1924 under the Eight-eight fleet plan.
 W
WKaimei Maru was a Japanese troop transport ship operated by the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II which was sunk off Honshu on 4 September 1942 by the American submarine USS Guardfish. The ship was a British WWI Type B military cargo ship built by the Hong Kong and Whampoa Dock Company.
 W
WThe Kamikawa Maru-class cargo ship was a type of cargo ship of Japan, serving during the 1930s and World War II. Four of the five ships of the class were converted to seaplane tenders during the war.
 W
WKatsuriki (勝力) was a minelayer of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) serving during World War I and World War II, the only ship of her class. She was the first purpose-built ocean-minelayer in the Japanese Navy.
 W
WThe Kawasaki-type oiler was a type of oiler of Japan, serving during the 1930s and World War II. They do not have an official class name. Therefore, this article uses common class names. And, this type has some variants. This article handles them collectively.
 W
WThe Kazahaya was a Japanese fleet oiler, serving during the Second World War.
 W
WThe Kinesaki-class food supply ship was a class of four reefer ships of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during and after World War II. Eleven vessels were planned under the Maru 4 Programme, Maru Rin Programme and Kai-Maru 5 Programme, however, only four vessels were completed.
 W
WKomahashi (駒橋), was an auxiliary vessel operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy, serving from the 1910s through World War II. Her classification changed numerous times during her operational life. Although officially designated as a submarine tender for most of her career, Komahashi very rarely functioned in this role, but was used instead as an oceanographic survey vessel throughout the Pacific, and as a kaibokan escort vessel for convoys of merchant ships during the Pacific War.
 W
WKunashiri (国後) was one of four Shimushu-class escort ships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.
 W
WMamiya (間宮) was a food supply ship of the Imperial Japanese Navy which was in service from the 1920s to the Second World War.
 W
WMatsuwa (松輪) was one of fourteen Etorofu-class escort ships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.
 W
WThe Muroto-class colliers were a class of collier of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving from roughly the end of World War I into World War II. Two vessels were built in 1918-19 under the Eight-four fleet plan.
 W
WNo. 1 was a No.1-class landing ship of the Imperial Japanese Navy during the Pacific War. Completed in early 1944, the ship was used as a convoy escort on one successful mission to resupply Imperial Japanese Army units on Saipan. On the return trip, No. 1 was badly damaged by American aircraft and towed to Palau. Redesignated as an anti-aircraft ship, she was sunk by American bombers in July 1944.
 W
WThe Nosaki (野埼) was a food supply ship of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) serving during World War II, the only ship of her class.
 W
WThe Notoro-class oilers were a class of seven oilers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during the 1920s and World War II. They were also called the Erimo-class oilers , after Notoro and Shiretoko were converted to other ship types.
 W
WThe Ondo-class oilers were a class of three oilers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during the 1920s and World War II.
 W
WŌryoku Maru was a Japanese passenger cargo ship which was commissioned by the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II as a troop transport and prisoner of war (POW) transport ship. Japanese POW transport ships are often referred to as hell ships, due to their notoriously unpleasant conditions and the many deaths that occurred on board. In December 1944, the ship was bombed by American aircraft, killing 200 Allied POWs. Hundreds more died in the months that followed.
 W
WThe Ōtomari (大泊) was an icebreaker of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) serving during the 1920s through World War II, the only ship of her class. She was the only icebreaker warship in the IJN.
 W
WThe Ōtori-class torpedo boat were a class of eight fast torpedo boats of the Imperial Japanese Navy built before and operated during World War II.
 W
WThe pagoda mast was a type of superstructure that was common on Japanese capital ships that were reconstructed during the 1930s in a bid to improve their fighting performance. These modifications were deemed to be necessary by the Imperial Japanese Navy as a result of the "Battleships Holiday" that was imposed by the Washington Naval Treaty, which strictly limited the construction of new battleships.
 W
WShimushu (占守) was the lead ship of her class of four escort ships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.
 W
WShinshū Maru was a ship of the Japanese Imperial Army during World War II. She was the world's first landing craft carrier ship to be designed as such, and a pioneer of modern-day amphibious assault ships. During some of her operations, she was known to have used at least four cover names, R1, GL, MT, and Ryujo Maru.
 W
WThe SS-class landing ship was a class of amphibious assault ships of the Imperial Japanese Army which served during World War II. The SS meaning are Sensha-Small.
 W
WThe Sunosaki-class combat support ship was a class of two support ships of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II.
 W
WTeiyō Maru was an auxiliary fleet oiler of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) during World War II. She was converted from civilian service to a naval auxiliary as the Pearl Harbor attack force sailed; and participated in the major offensive operations of the first six months of Pacific combat. She then served in the northern Pacific until July 1944, and was sunk in the battle for convoy Hi-71 when reassigned to the defense of the Philippines.
 W
WThe Terukuni Maru-class ocean liner was a class of ocean liners of Japan, serving during the 1930s, and into World War II.
 W
WTomozuru (友鶴) was one of four Chidori-class torpedo boats of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). It capsized in a storm on 12 March 1934, shortly after its completion. This incident forced the IJN to review the stability of all recently completed, under construction and planned ships. It was salvaged and put back into service after extensive modifications. During World War II, the Tomozuru fought in the Battle of the Philippines and in the Dutch East Indies campaign as an escort, and it continued to play that role for the rest of the war.
 W
WThe Tsukushi-class survey ship was a class of auxiliary ships of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II. The class consists of two subclasses, which this article handles collectively.
 W
WUji (宇治) was the second and final vessel in the Hashidate-class gunboats in the Imperial Japanese Navy, that operated in China during the 1940s.
 W
WYat Sen, named after the founding father Dr. Sun Yat-sen of the Republic of China and completed in 1931, was a light cruiser— having more in common with the small cruisers of pre–World War I era—in the ROC Navy before World War II. An enlarged design was laid down but never completed due to the Japanese occupation of Kiangnan shipyard.