 W
WBarr & Stroud Limited was a pioneering Glasgow optical engineering firm. They played a leading role in the development of modern optics, including rangefinders, for the Royal Navy and for other branches of British Armed Forces during the 20th century. There was a non-military arm of the company which made medical equipment, like photocoagulators and electronic filters, some of which were used by the BBC. The company and its intellectual property passed through Pilkington group to Thales Optronics. The Barr and Stroud name was sold on to an importer of optical equipment who use the trademarked name for a line of binoculars and similar instruments.
 W
WA coincidence rangefinder or coincidence telemeter is a type of rangefinder that uses mechanical and optical principles to allow an operator to determine the distance to a visible object. There are subtypes split-image telemeter, inverted image, or double-image telemeter with different principles how two images in a single ocular are compared. Coincidence rangefinders were important elements of fire control systems for long-range naval guns and land-based coastal artillery circa 1890–1960. They were also used in rangefinder cameras.
 W
WA fire-control system is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director, and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system in targeting, tracking and hitting its target. It performs the same task as a human gunner firing a weapon, but attempts to do so faster and more accurately.
 W
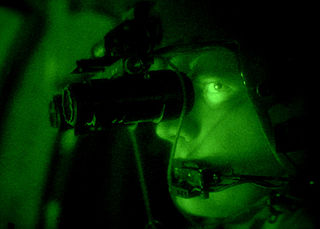
WA night-vision device (NVD), also known as night optical/observation device (NOD) and night-vision goggles (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows images to be produced in levels of light approaching total darkness. The image may be a conversion to visible light of both visible light and near-infrared, while by convention detection of thermal infrared is denoted thermal imaging. The image produced is typically monochrome green, because it was considered to be the easiest color to look at for prolonged periods in the dark. NVDs are most often used by the military and law enforcement agencies, but are available to civilian users. The term usually refers to a complete unit, including an image intensifier tube, a protective and generally water-resistant housing, and some type of mounting system. Many NVDs include a protective sacrificial lens, or optical components such as telescopic lenses or mirrors. An NVD may have an IR illuminator, making it an active as opposed to passive night-vision device. They are often used in conjunction with IR laser sights which project a beam onto the target that is only visible through an NVD.
 W
WPilkington is a Japanese-owned glass-manufacturing company which is based in Lathom, Lancashire, United Kingdom. In the UK it includes several legal entities and is a subsidiary of Japanese company NSG Group.
 W
WRoss is the name of a succession of London-based lens designers and their company.
 W
WCarl Zeiss AG, branded as ZEISS, is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe and Otto Schott he laid the foundation for today's multi-national company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue, Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide.