 W
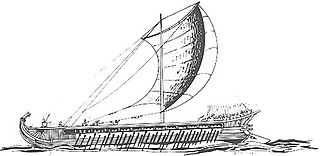
WThe naval Battle of Arginusae took place in 406 BC during the Peloponnesian War near the city of Canae in the Arginusae islands, east of the island of Lesbos. In the battle, an Athenian fleet commanded by eight strategoi defeated a Spartan fleet under Callicratidas. The battle was precipitated by a Spartan victory which led to the Athenian fleet under Conon being blockaded at Mytilene; to relieve Conon, the Athenians assembled a scratch force composed largely of newly constructed ships manned by inexperienced crews. This inexperienced fleet was thus tactically inferior to the Spartans, but its commanders were able to circumvent this problem by employing new and unorthodox tactics, which allowed the Athenians to secure a dramatic and unexpected victory. Slaves and metics who participated in the battle were granted Athenian citizenship.
 W
WThe Battle of Aegospotami was a naval confrontation that took place in 405 BC and was the last major battle of the Peloponnesian War. In the battle, a Spartan fleet under Lysander destroyed the Athenian navy. This effectively ended the war, since Athens could not import grain or communicate with its empire without control of the sea.
 W
WThe naval Battle of Cynossema took place in 411 BC during the Second Peloponnesian War. In the battle, an Athenian fleet commanded by Thrasybulus and Thrasyllus, although initially thrown on the defensive by a numerically superior Spartan fleet, won a narrow victory. This victory had an impact out of proportion to its tactical significance, coming when Athens' traditional democratic government had been replaced by an oligarchy and an Athenian defeat could have ended the war. The newly confident Athenian fleet proceeded to win two more victories in the Hellespont in quick succession, the second being the dramatic rout at Cyzicus, which ended the immediate Spartan threat to Athens' Black Sea lifeline.
 W
WThe naval Battle of Cyzicus took place in May or June 410 BC during the Peloponnesian War. In the battle, an Athenian fleet commanded by Alcibiades, Thrasybulus, and Theramenes routed and completely destroyed a Spartan fleet commanded by Mindarus. The victory allowed Athens to recover control over a number of cities in the Hellespont over the next year. In the wake of their defeat, the Spartans made a peace offer, which the Athenians rejected.
 W
WThe Battle of Naupactus was a naval battle in the Peloponnesian War. The battle, which took place a week after the Athenian victory at Rhium, set an Athenian fleet of twenty ships, commanded by Phormio, against a Peloponnesian fleet of seventy-seven ships, commanded by Cnemus.
 W
WThe Battle of Notium in 406 BC, was a Spartan naval victory in the Peloponnesian War. Prior to the battle, the Athenian commander, Alcibiades, left his helmsman, Antiochus, in command of the Athenian fleet, which was blockading the Spartan fleet in Ephesus. In violation of his orders, Antiochus attempted to draw the Spartans into battle by tempting them with a small decoy force. His strategy backfired, and the Spartans under Lysander scored a small but symbolically significant victory over the Athenian fleet. This victory resulted in the downfall of Alcibiades, and established Lysander as a commander who could defeat the Athenians at sea.
 W
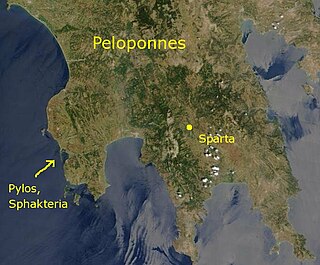
WThe naval Battle of Pylos took place in 425 BC during the Peloponnesian War at the peninsula of Pylos, on the present-day Bay of Navarino in Messenia, and was an Athenian victory over Sparta. An Athenian fleet had been driven ashore at Pylos by a storm, and, at the instigation of Demosthenes, the Athenian soldiers fortified the peninsula, and a small force was left there when the fleet departed again. The establishment of an Athenian garrison in Spartan territory frightened the Spartan leadership, and the Spartan army, which had been ravaging Attica under the command of Agis, ended their expedition and marched home, while the Spartan fleet at Corcyra sailed to Pylos.
 W
WThe Sicilian Expedition was an Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place from 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between Athens on one side and Sparta, Syracuse and Corinth on the other. The expedition ended in a devastating defeat for the Athenian forces, severely impacting Athens.