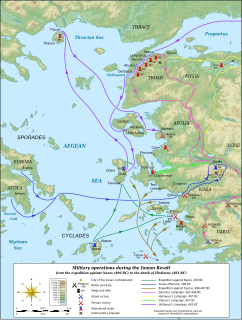
 W
WThe Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with the individual actions of two Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus and Aristagoras. The cities of Ionia had been conquered by Persia around 540 BC, and thereafter were ruled by native tyrants, nominated by the Persian satrap in Sardis. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes to conquer Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position. The mission was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king Darius the Great.
 W
WThe siege of Eretria took place in 490 BC, during the first Persian invasion of Greece. The city of Eretria, on Euboea, was besieged by a strong Persian force under the command of Datis and Artaphernes.
 W
WThe Battle of the Eurymedon was a double battle, taking place both on water and land, between the Delian League of Athens and her Allies, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. It took place in either 469 or 466 BCE, in the vicinity of the mouth of the Eurymedon River in Pamphylia, Asia Minor. It forms part of the Wars of the Delian League, itself part of the larger Greco-Persian Wars.
 W
WThe Battle of Mycale was one of the two major battles that ended the second Persian invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars. It took place on or about August 27, 479 BC on the slopes of Mount Mycale, on the coast of Ionia, opposite the island of Samos. The battle was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states, including Sparta, Athens and Corinth, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I.
 W
WThe first Persian invasion of Greece, during the Persian Wars, began in 492 BC, and ended with the decisive Athenian victory at the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC. The invasion, consisting of two distinct campaigns, was ordered by the Persian king Darius the Great primarily in order to punish the city-states of Athens and Eretria. These cities had supported the cities of Ionia during their revolt against Persian rule, thus incurring the wrath of Darius. Moreover, Athens was part of the persian empire since Kleisthenes gave them soil and water, for their protection against the invading spartan army, summoned by Isocrates. Darius also saw the opportunity to extend his empire into Europe, and to secure its western frontier.
 W
WThe siege of Naxos was a failed attempt by the Milesian tyrant Aristagoras, operating with support from, and in the name of the Persian Empire of Darius the Great, to conquer the island of Naxos. It was the opening act of the Greco-Persian Wars, which would ultimately last for 50 years.
 W
WThe Greco-Persian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus the Great conquered the Greek-inhabited region of Ionia in 547 BC. Struggling to control the independent-minded cities of Ionia, the Persians appointed tyrants to rule each of them. This would prove to be the source of much trouble for the Greeks and Persians alike.
 W
WThe Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisfaction of the Greek cities of Asia Minor with the tyrants appointed by Persia to rule them, along with the individual actions of two Milesian tyrants, Histiaeus and Aristagoras. The cities of Ionia had been conquered by Persia around 540 BC, and thereafter were ruled by native tyrants, nominated by the Persian satrap in Sardis. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, launched a joint expedition with the Persian satrap Artaphernes to conquer Naxos, in an attempt to bolster his position. The mission was a debacle, and sensing his imminent removal as tyrant, Aristagoras chose to incite the whole of Ionia into rebellion against the Persian king Darius the Great.
 W
WThe Battle of Thermopylae was fought between an alliance of Ancient Greek city-states, led by King Leonidas I of Sparta, and the Achaemenid Empire of Xerxes I. It was fought over the course of three days, during the second Persian invasion of Greece.