 W
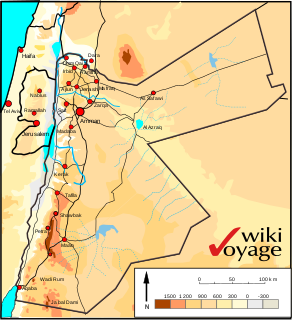
WJordan is situated geographically in Southwest Asia, south of Syria, west of Iraq, northwest of Saudi Arabia and east of Palestine and the West Bank; politically, the area has also been referred to in the West as the Middle or Near East. The territory of Jordan now covers about 91,880 square kilometres (35,480 sq mi).
 W
WAl-Maghtas, officially known as Baptism Site "Bethany Beyond the Jordan", is an archaeological World Heritage site in Jordan on the east bank of the Jordan River. It is considered to be the original location of the Baptism of Jesus by John the Baptist and has been venerated as such since at least the Byzantine period. The place has also been referred to as Bethany and Bethabara.
 W
WGergesa, also Gergasa or the Country of the Gergesenes, is a place on the eastern side of the Sea of Galilee located at some distance to the ancient Decapolis cities of Gadara and Gerasa. Today, it is identified with El-Koursi or Kursi. It is mentioned in some ancient manuscripts of the Gospel of Matthew as the place where the Miracle of the Swine took place, a miracle performed by Jesus who drove demons out of two possessed men and into a herd of pigs. All three Synoptic Gospels mention this miracle, but only Matthew writes about two possessed men instead of just one, and only some manuscripts of his Gospel name the location as Gergesa, while the other copies, as well as all versions of Luke and Mark, mention either Gadara or Gerasa.
 W
WThe Land of Israel is the traditional Jewish name for an area of indefinite geographical extension in the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine. The definitions of the limits of this territory vary between passages in the Hebrew Bible, with specific mentions in Genesis 15, Exodus 23, Numbers 34 and Ezekiel 47. Nine times elsewhere in the Bible, the settled land is referred as "from Dan to Beersheba", and three times it is referred as "from the entrance of Hamath unto the brook of Egypt".
 W
WThe King Talal Dam is a large dam in the hills of northern Jordan, across the Zarqa River. The dam was started in 1971, with the original construction being completed in 1978 at a height of 92.5 meters. The original dam cost $46 million and was partially funded by a $16.8 million loan from the Arab Fund for Economic and Social Development and a $5.6 million grant from the Abu Dhabi Fund. Energoprojekt of Yugoslavia was the consultant and Planum of Yugoslavia was the contractor.
 W
WThe Levant is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, it is equivalent to the historical region of Syria, which included present-day Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Palestine and most of Turkey southwest of the middle Euphrates. In its widest historical sense, the Levant included all of the Eastern Mediterranean with its islands; that is, it included all of the countries along the Eastern Mediterranean shores, extending from Greece to Cyrenaica in eastern Libya.
 W
WNaharayim, historically the Jisr Majami area, where the Yarmouk River flows into the Jordan River, was named by the Palestine Electric Company in a letter dated 27 February, 1929 to Palestine Railways giving "proper names" to the "different quarters of our Jordan Works" one of these being the "works as a whole including the labour camp" to be called "Naharaim" and another being the site of the "Power House and the adjoining staff quarters, offices" to be called Tel Or. Most of the plant was situated in the Emirate of Transjordan and stretched from the northern canal near the Ashdot Ya'akov in Northern Mandatory Palestine to the Jisr el-Majami in the south.
 W
WPalestine is a geographic region in Western Asia usually considered to include Israel, the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and in some definitions, parts of western Jordan.
 W
WThe historic region of Syria is an area located east of the Mediterranean sea. The oldest attestation of the name Syria is from the 8th century BC in a bilingual inscription in Hieroglyphic Luwian and Phoenician. In this inscription the Luwian word Sura/i was translated to Phoenician ʔšr "Assyria." For Herodotus in the 5th century BC, Syria extended as far north as the Halys and as far south as Arabia and Egypt.