 W
WJehan Ariste Alain [ʒɑ̃ aʁist alɛ̃] was a French organist, composer, and soldier. Born into a family of musicians, he learned the organ from his father and a host of other teachers, becoming a composer at 18, and composing until the outbreak of the Second World War 10 years later. His compositional style was influenced by the musical language of the earlier Claude Debussy, and his contemporary Olivier Messiaen, as well as his interest in music, dance and philosophy of the far east. At the outbreak of WWII Alain became a dispatch rider in the Eighth Motorised Armour Division of the French Army; he took part in the Battle of Saumur, in which he was killed.
 W
WCarlos Roqué Alsina is a French composer and pianist of Argentinian origin.
 W
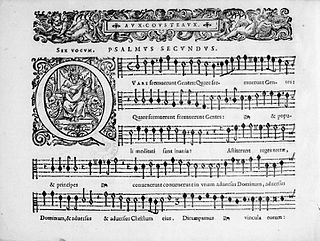
WArtus Aux-Cousteaux was a French singer and composer, active in Picardy and Paris.
 W
WLouis-Hector Berlioz was a French Romantic composer and conductor. His output includes orchestral works such as the Symphonie fantastique and Harold in Italy, choral pieces including the Requiem and L'Enfance du Christ, his three operas Benvenuto Cellini, Les Troyens and Béatrice et Bénédict, and works of hybrid genres such as the "dramatic symphony" Roméo et Juliette and the "dramatic legend" La Damnation de Faust.
 W
WLéon Boëllmann was a French composer, known for a small number of compositions for organ. His best-known composition is Suite gothique (1895), which is a staple of the organ repertoire, especially its concluding Toccata.
 W
WAlexandre Pierre François Boëly was a French composer, organist, and pianist. Born into a family of musicians, Boëly received his first music lessons from his father, Jean François, who was a countertenor at the Sainte-Chapelle in Paris and a composer and harp teacher at the court of Versailles. He also studied under the Tyrolian pianist Ignaz Ladurner, who introduced him to the work of Bach and Haydn, which Boëly would champion in his adult career. Besides mastering the piano and organ, Boëly was also a talented violist.
 W
WLouis-Albert Bourgault-Ducoudray was a French Breton composer, pianist, and professor of music history/theory at the Conservatoire de Paris as well as a Prix de Rome laureate. He was born at Nantes and died at Vernouillet, near Dreux. Debussy was one of his protégés.
 W
WJean de Bournonville was a French composer active in the first third of the 17th century, born in Noyon around 1585 and died in Paris on 27 May 1632. He should not be confused with his son Valentin de Bournonville, who published masses in the middle of the 17th century.
 W
WAndré Campra was a French composer and conductor.
 W
WMarc-Antoine Charpentier was a French Baroque composer during the reign of Louis XIV. One of his most famous works is the main theme from the prelude of his Te Deum, which is still used today as a fanfare during television broadcasts as part of Eurovision.
 W
WMichel Corrette was a French composer, organist and author of musical method books.
 W
WFrançois Couperin was a French Baroque composer, organist and harpsichordist. He was known as Couperin le Grand to distinguish him from other members of the musically talented Couperin family.
 W
WPierre Louis Deffès was a 19th-century French composer. He excelled as a composer of both operas and large-scale sacred music.
 W
WMichel Richard Delalande [de Lalande] was a French Baroque composer and organist who was in the service of King Louis XIV. He was one of the most important composers of grands motets. He also wrote orchestral suites known as Simphonies pour les Soupers du Roy and ballets.
 W
WJeanne Marie-Madeleine Demessieux, was a French organist, pianist, composer, and pedagogue.
 W
WHervé Désarbre is a French organist and organiste du ministère de la Défense [organist of the Ministry of Armed Forces]. He is titular of the Cavaillé-Coll organ of the Église Notre-Dame du Val-de-Grâce in Paris.
 W
WAdolphe Édouard Marie Deslandres was a French composer and organist.
 W
WHenri Desmarets was a French composer of the Baroque period primarily known for his stage works, although he also composed sacred music as well as secular cantatas, songs and instrumental works.
 W
WPierre Desvignes was a French composer.
 W
WFrançois-Clément Théodore Dubois was a French composer, organist, and music teacher.
 W
WAntoine Aimable Elie Elwart was a French composer and musicologist.
 W
WCharles-François Gounod, usually known as Charles Gounod, was a French composer. He wrote twelve operas, of which the most popular has always been Faust (1859); his Roméo et Juliette (1867) also remains in the international repertory. He composed a large amount of church music, many songs, and popular short pieces including his Ave Maria, and Funeral March of a Marionette.
Louis Théodore Gouvy was a French/German composer.
 W
WFélix-Alexandre Guilmant was a French organist and composer. He was the organist of La Trinité from 1871 until 1901. A noted pedagogue, performer, and improviser, Guilmant helped found the Schola Cantorum de Paris. He was appointed as Professor of Organ at the Paris Conservatoire in 1896.
 W
WBernard Jumentier was a French composer of classical and sacred music as well as maître de chapelle.
 W
WChristophe Looten is a French composer. Born in Bergues, he was made Chevalier des Arts et des Lettres in January 2000.
 W
WGuillaume de Machaut was a French poet and composer of late Medieval music who was the central figure of the ars nova style. Immensely influential, Machaut is regarded as the most important composer and poet of the 14th century and is the first significant composer whose name is known. Daniel Leech-Wilkinson called him "the last great poet who was also a composer", and well into the 15th century Machaut's poetry was greatly admired and imitated by other poets, including Geoffrey Chaucer.
 W
WCharles Casimir Manry was a French composer and choral conductor.
 W
WOlivier Eugène Prosper Charles Messiaen was a French composer, organist, and ornithologist, one of the major composers of the 20th century. His music is rhythmically complex; harmonically and melodically he employs a system he called modes of limited transposition, which he abstracted from the systems of material generated by his early compositions and improvisations. He wrote music for chamber ensembles and orchestra, vocal music, as well as for solo organ and piano, and also experimented with the use of novel electronic instruments developed in Europe during his lifetime.
 W
WÉmile Paladilhe was a French composer of the late romantic period.
 W
WGuillaume Poitevin was a French serpent player, maître de chapelle and composer.
 W
WFrancis Jean Marcel Poulenc was a French composer and pianist. His compositions include songs, solo piano works, chamber music, choral pieces, operas, ballets, and orchestral concert music. Among the best-known are the piano suite Trois mouvements perpétuels (1919), the ballet Les biches (1923), the Concert champêtre (1928) for harpsichord and orchestra, the Organ Concerto (1938), the opera Dialogues des Carmélites (1957), and the Gloria (1959) for soprano, choir and orchestra.
 W
WFélix Augustin Joseph Vasseur, known as Léon Vasseur, was a French composer, organist and conductor. While working as a cathedral organist, he turned to composing operettas and soon had a hit with La timbale d'argent (1872). He wrote another thirty operettas but never repeated that early success. He also composed church music including two settings of the mass.