 W
WAmira is a software platform for 3D and 4D data visualization, processing, and analysis. It is being actively developed by Thermo Fisher Scientific in collaboration with the Zuse Institute Berlin (ZIB), and commercially distributed by Thermo Fisher Scientific.
 W
WAnalysis of Functional NeuroImages (AFNI) is an open-source environment for processing and displaying functional MRI data—a technique for mapping human brain activity.
 W
WCARET is a software application for the structural and functional analysis of the cerebral and cerebellar cortex. CARET is developed in the Van Essen Laboratory in the Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology at the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri.
 W
WCONN is a Matlab-based cross-platform imaging software for the computation, display, and analysis of functional connectivity in fMRI in the resting state and during task.
 W
WFiji is an open source image processing package based on ImageJ.
 W
WThe FMRIB Software Library, abbreviated FSL, is a software library containing image analysis and statistical tools for functional, structural and diffusion MRI brain imaging data.
 W
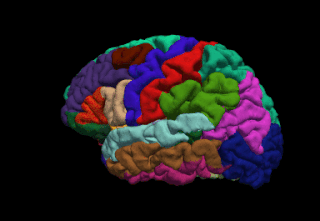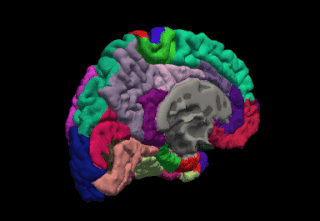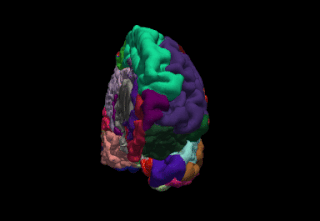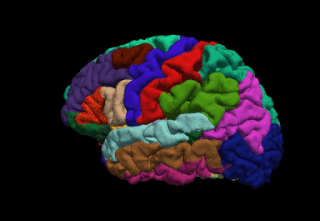
WFreeSurfer is a brain imaging software package originally developed by Bruce Fischl, Anders Dale, Martin Sereno, and Doug Greve. Development and maintenance of FreeSurfer is now the primary responsibility of the Laboratory for Computational Neuroimaging at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging. FreeSurfer contains a set of programs with a common focus of analyzing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of brain tissue. It is an important tool in functional brain mapping and contains tools to conduct both volume based and surface based analysis. FreeSurfer includes tools for the reconstruction of topologically correct and geometrically accurate models of both the gray/white and pial surfaces, for measuring cortical thickness, surface area and folding, and for computing inter-subject registration based on the pattern of cortical folds.
 W
WInVesalius is a free medical software used to generate virtual reconstructions of structures in the human body. Based on two-dimensional images, acquired using computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging equipment, the software generates virtual three-dimensional models correspondent to anatomical parts of the human body. After constructing three-dimensional DICOM images, the software allows the generation of STL (stereolithography) files. These files can be used for rapid prototyping.
 W
WThe LONI Pipeline is a free distributed system for designing, executing, monitoring and sharing scientific workflows on grid computing architectures. Pipeline allows users to connect and run any number of different software tools, and conveniently visualize and download the results.
 W
WMango is a non-commercial software for viewing, editing and analyzing volumetric medical images. Mango is written in Java, and distributed freely in precompiled versions for Linux, Mac OS and Microsoft Windows. It supports NIFTI, ANALYZE, NEMA and DICOM formats and is able to load and save 2D, 3D and 4D images.